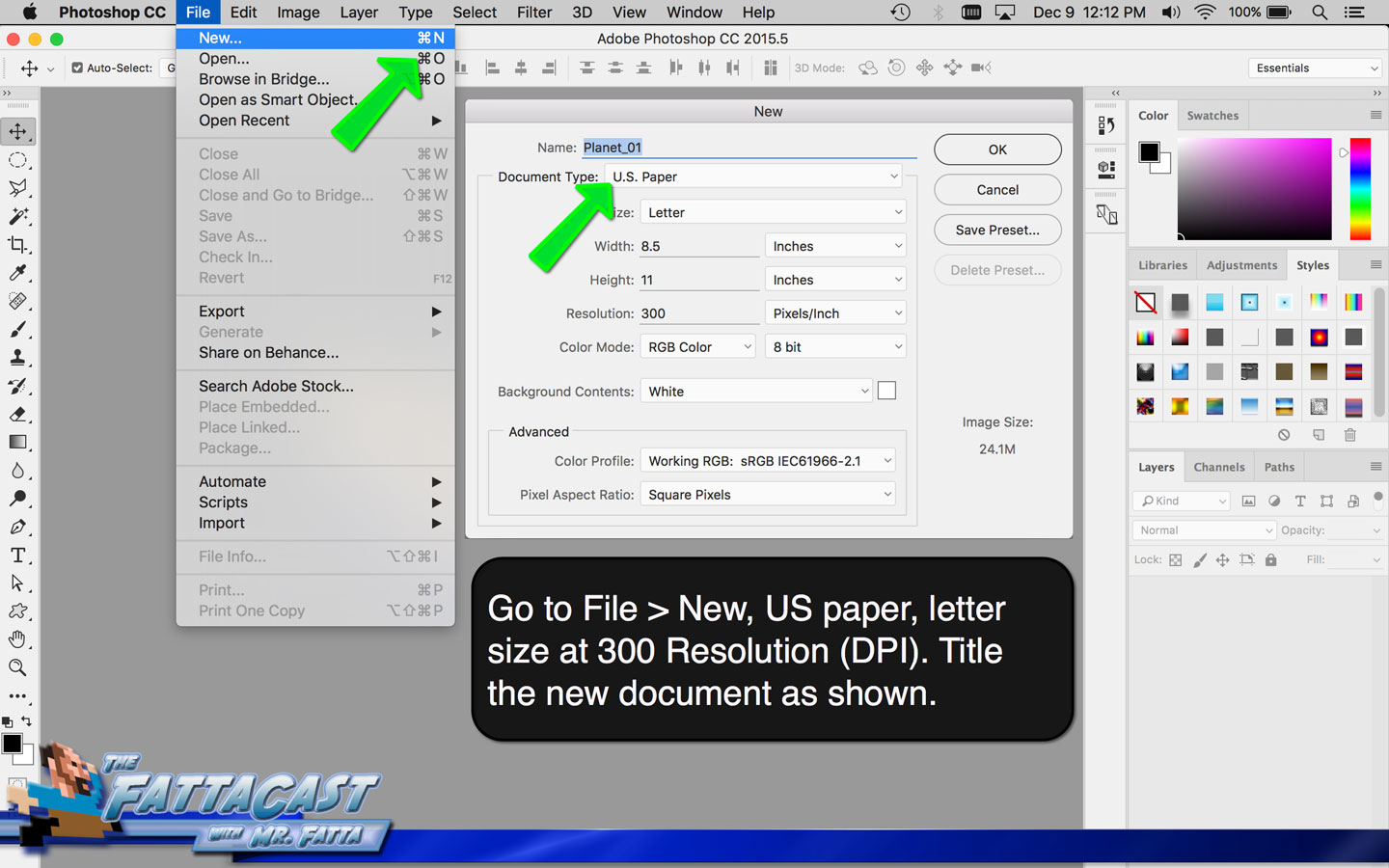
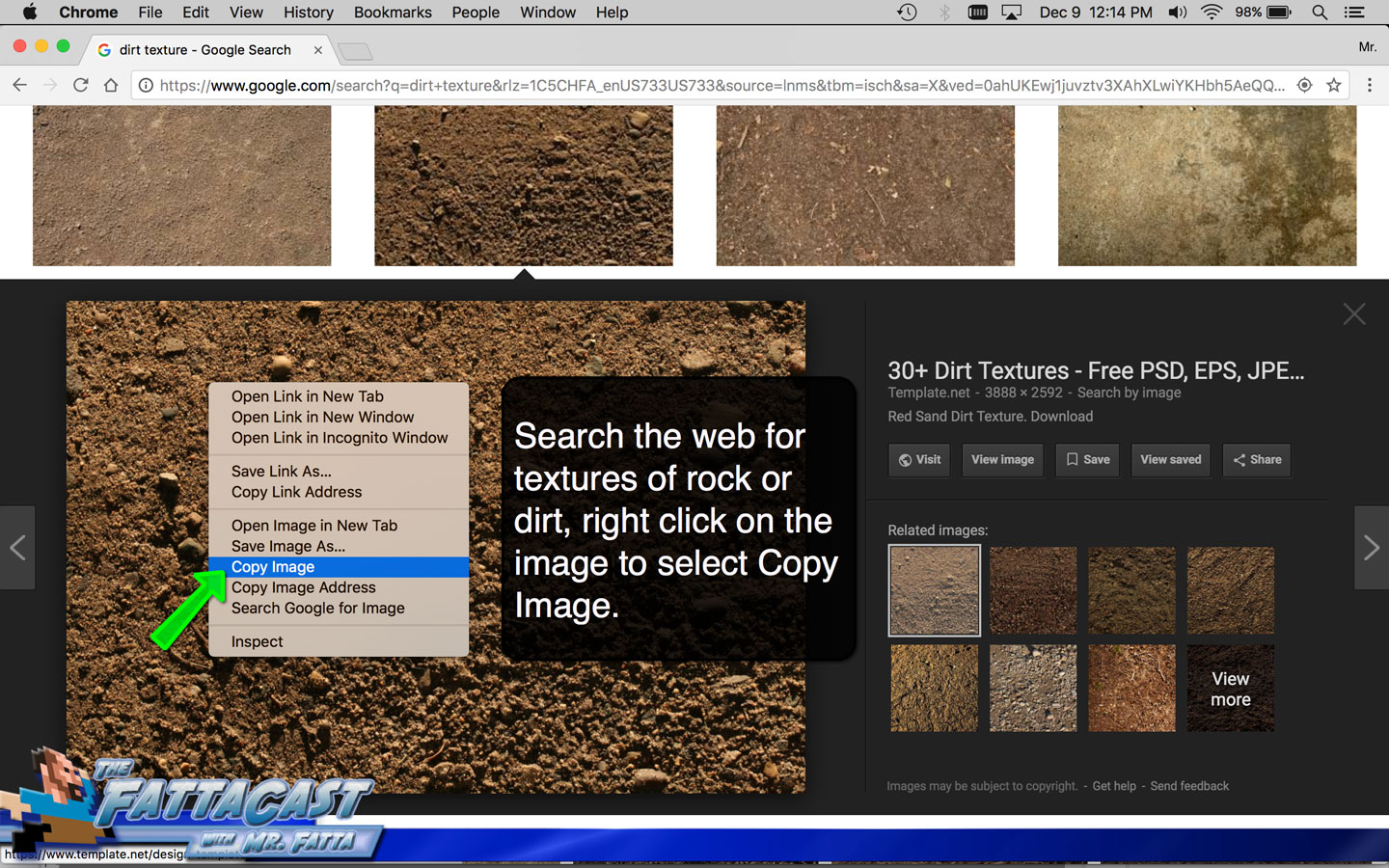
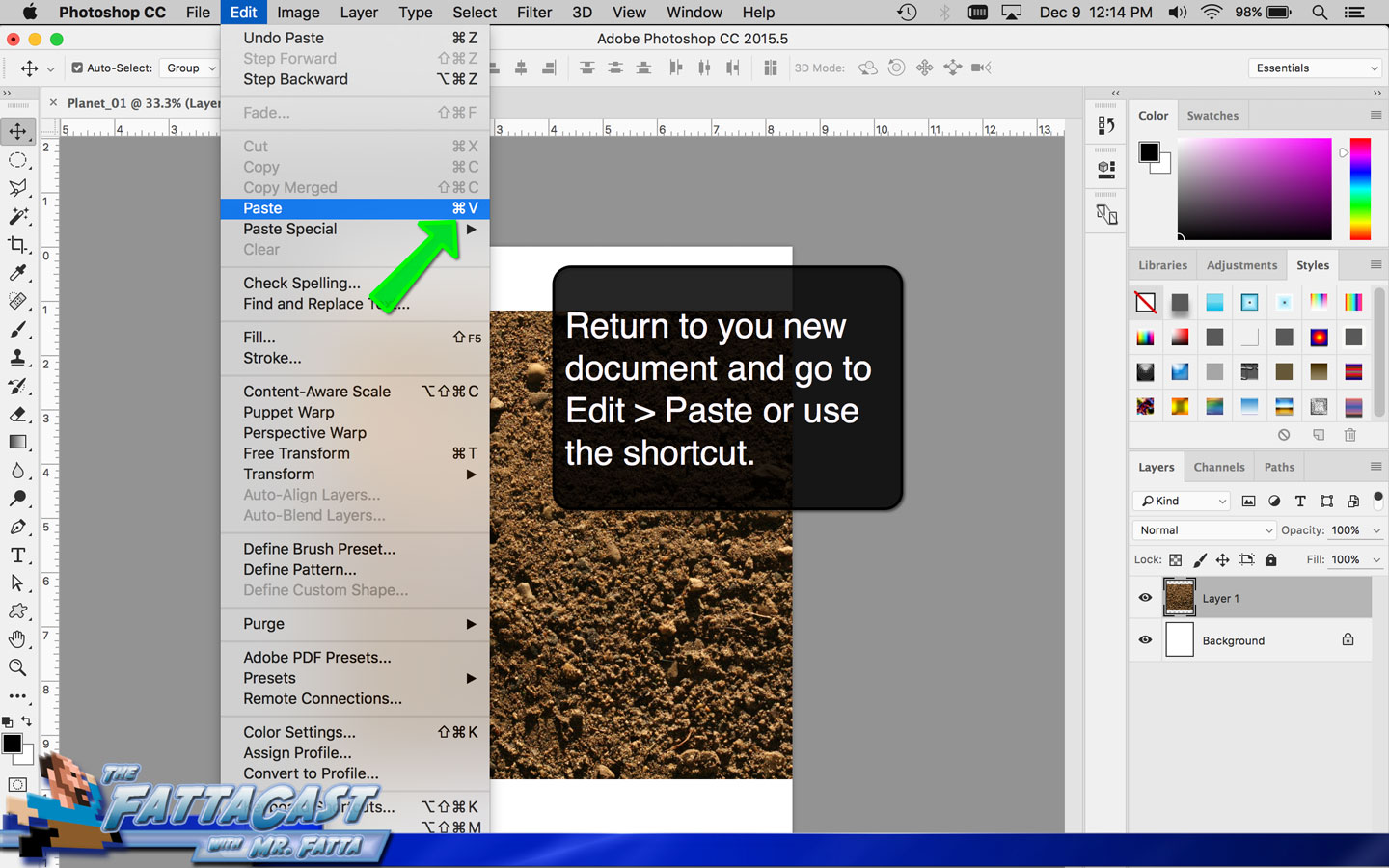
https://eos.co1.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_bpdQA6V1zeXv0vr
Named from the ancient Roman sun deity Sol, the solar system consisted of seven visible moving objects in the sky. Like many ancient cultures, the ancient Greeks observed how certain lights moved differently than fixed stars and referred to these moving bodies as wandering stars, asters planetai. The Sun, Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn form the seven classical planets of the ancients.
Although Uranus was visible to the eye like the classical planets it was confused with being a star and wasn’t recognized as a planet until it was observed it with a telescope in 1781. Neptune (1846) and Pluto (1930) were later discovered with a telescope along with several dwarf-planets in what is known as the Kuiper Belt discovered in 1992.
Ancient Greeks observed how
certain lights moved differently
than fixed stars.
Use the resources at National Geographic Solar System to get familiar with the solar system and analyze the different features of the various planets. Find images that best represent the planet showing any distinguishing features it is known for. As you study the planets become familiar with the planet’s statistical data.
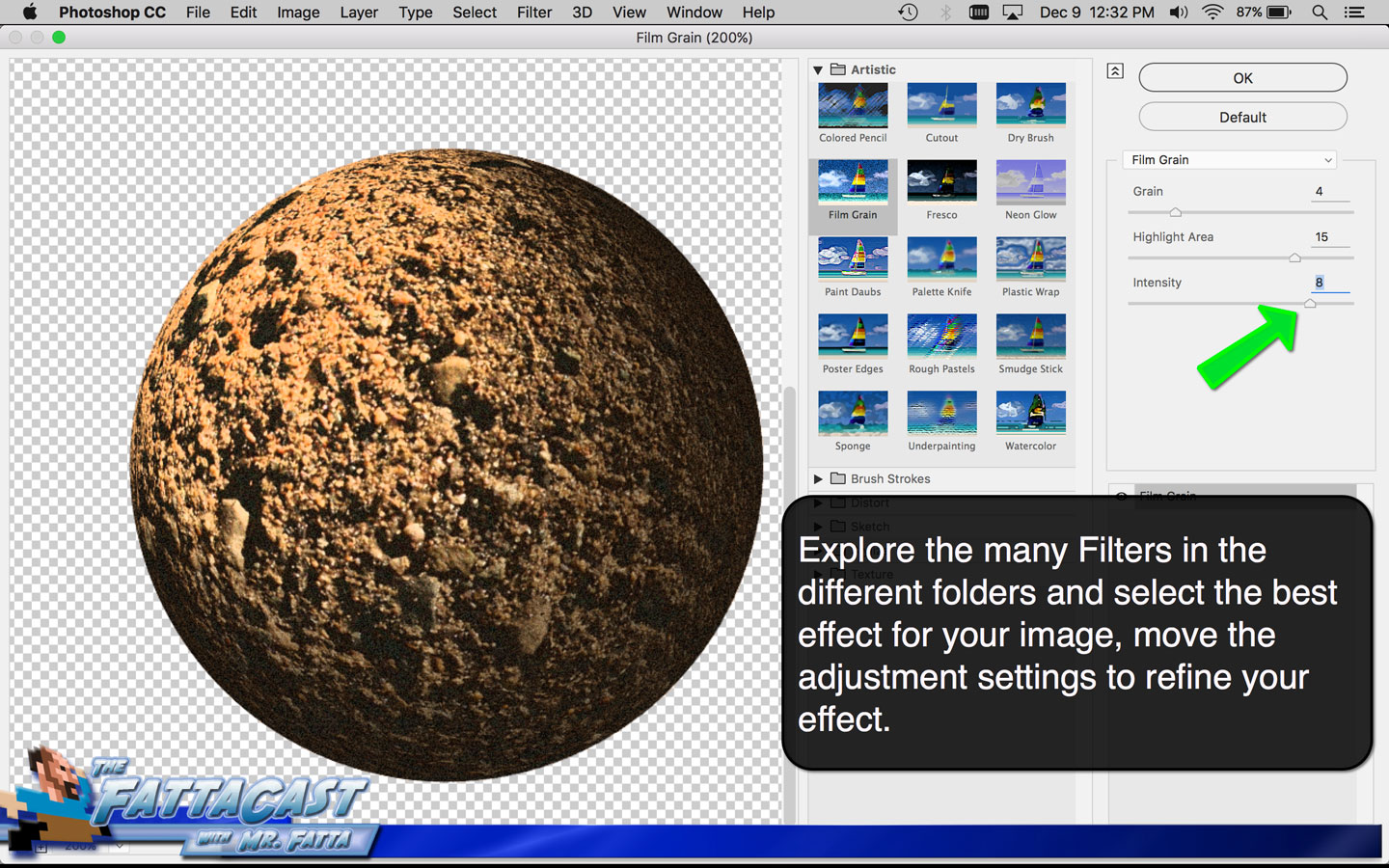
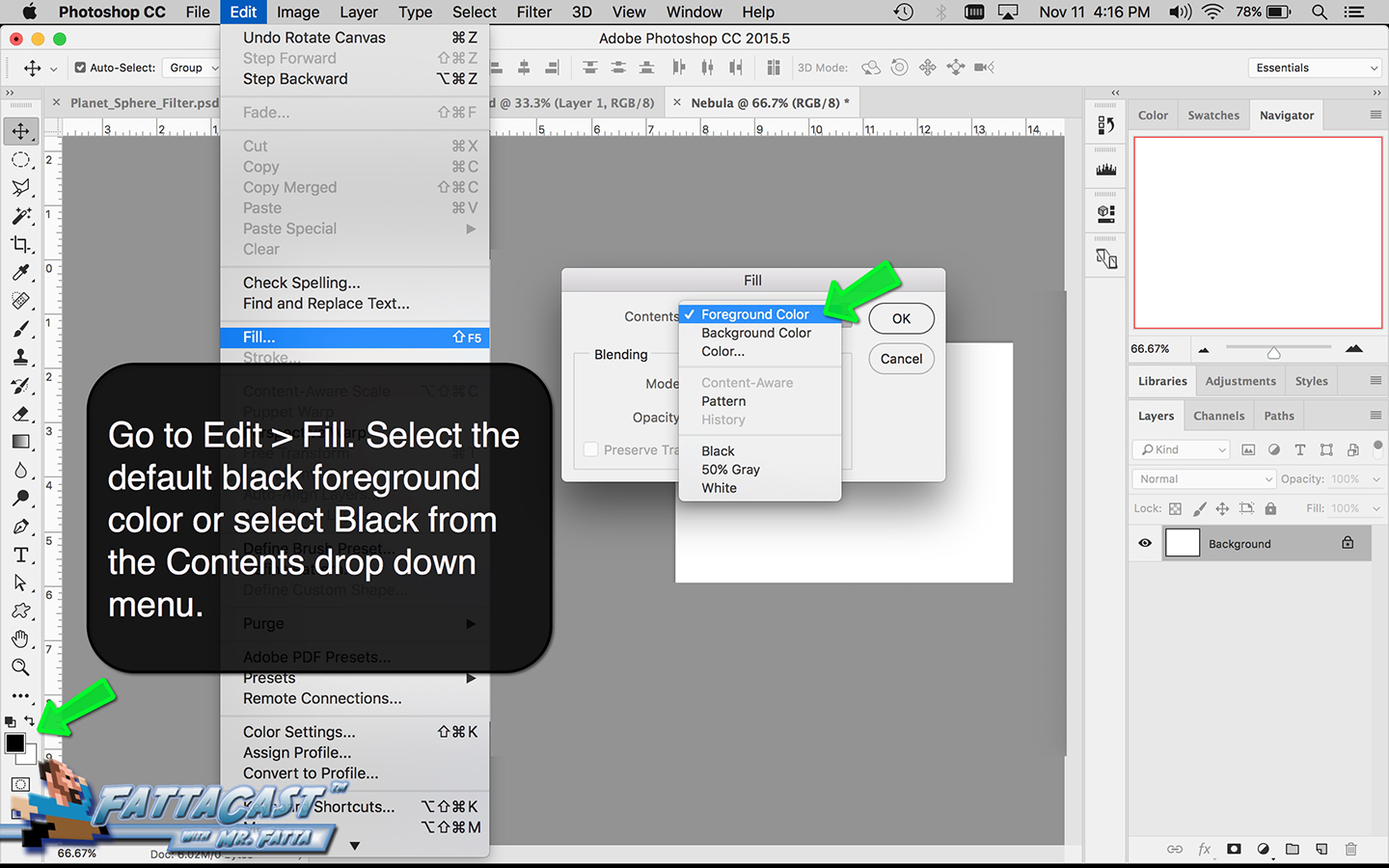
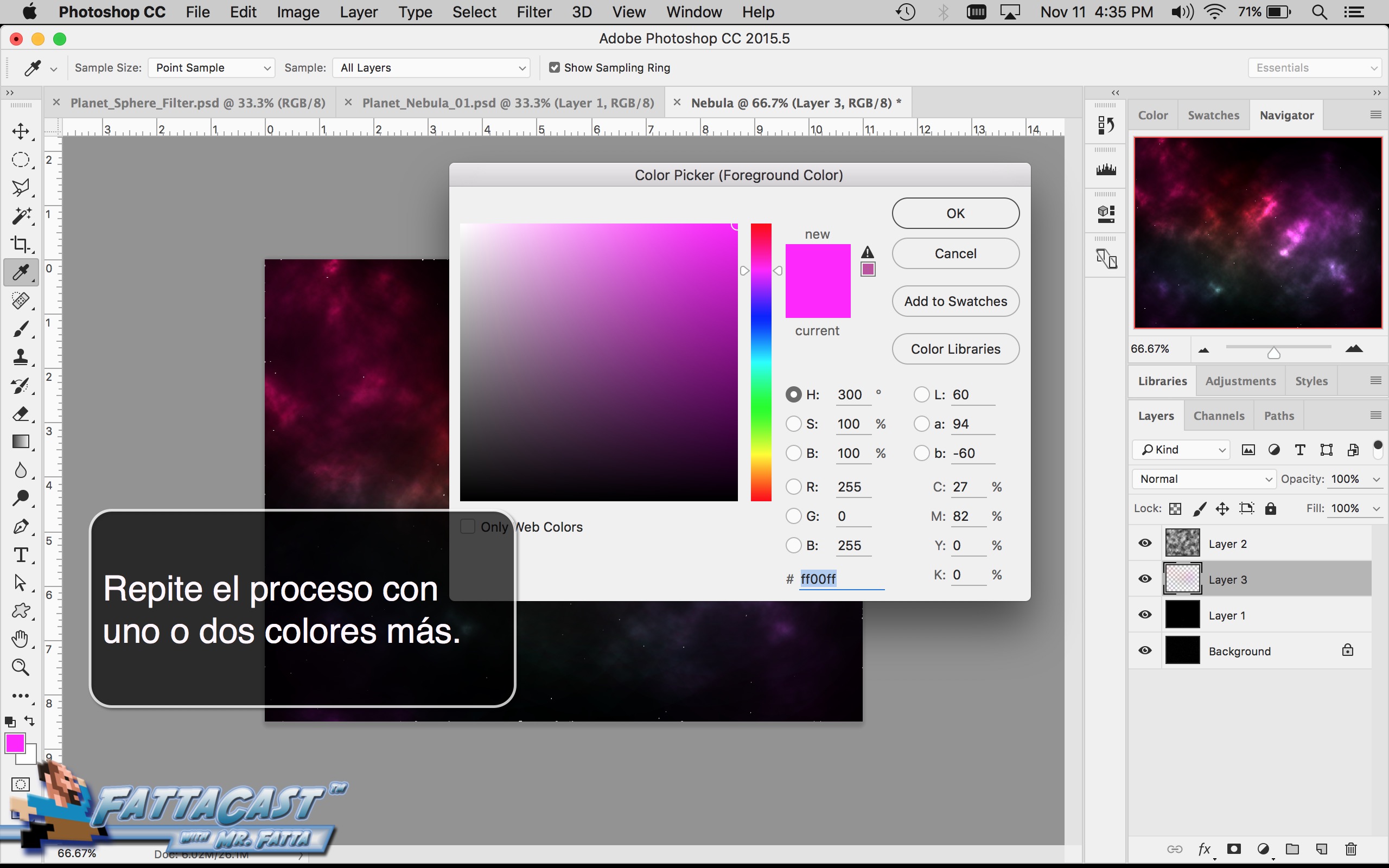
As you analyze the planets identify the colors evident and utilize the Swatch and Color Guide panels in Adobe to establish a color palate. Identify atmospheric effects and terrestrial textures, navigate to the Brush Library and make use of textured brushes Artistic_ChaulkCharcoalPencil, Artistic_Ink Paintbrush, and Artistic_Water Color. Analyze the appearance of form within the planet whether it is evident in the change in value, the striations, or a combination of both.
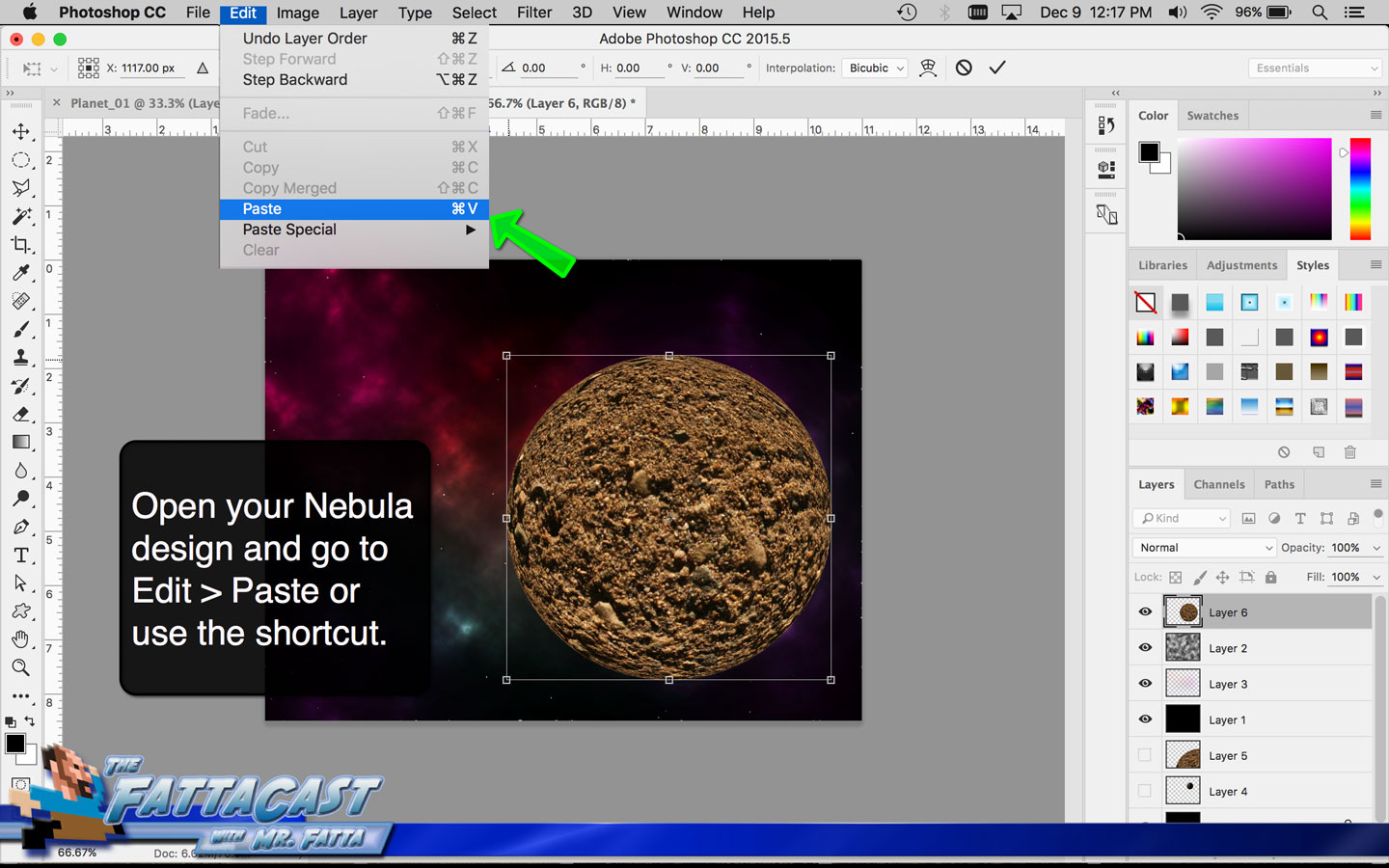
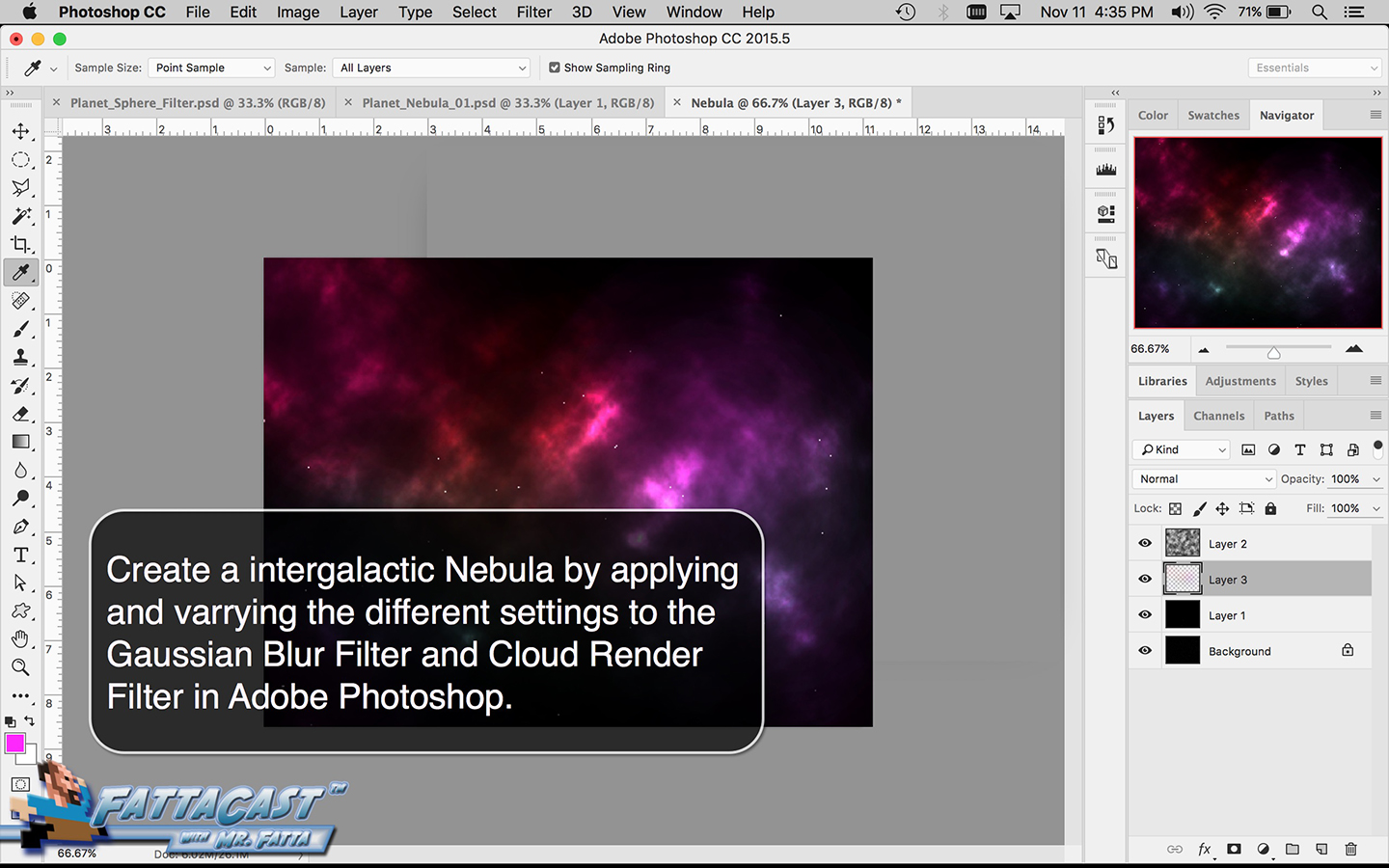
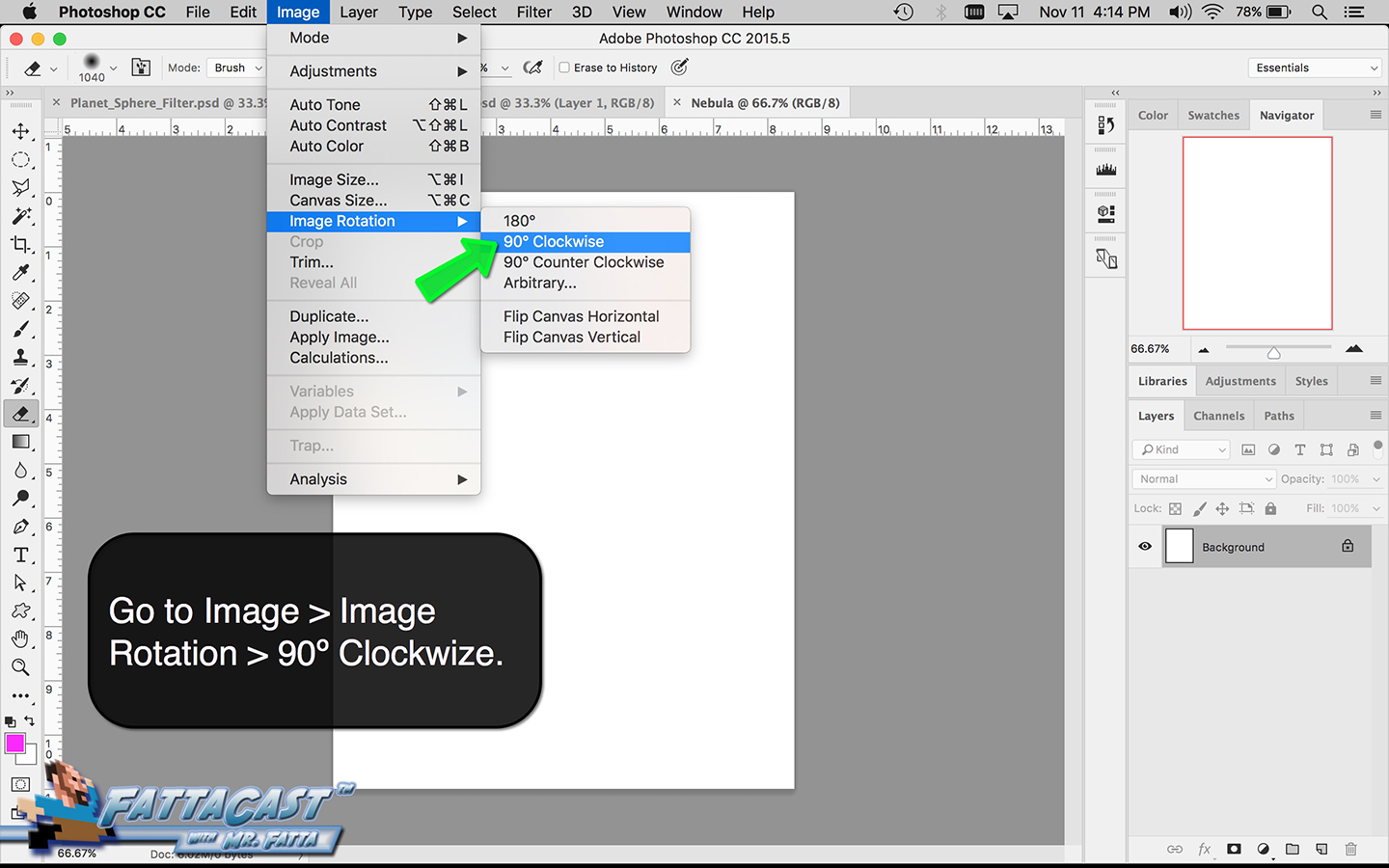
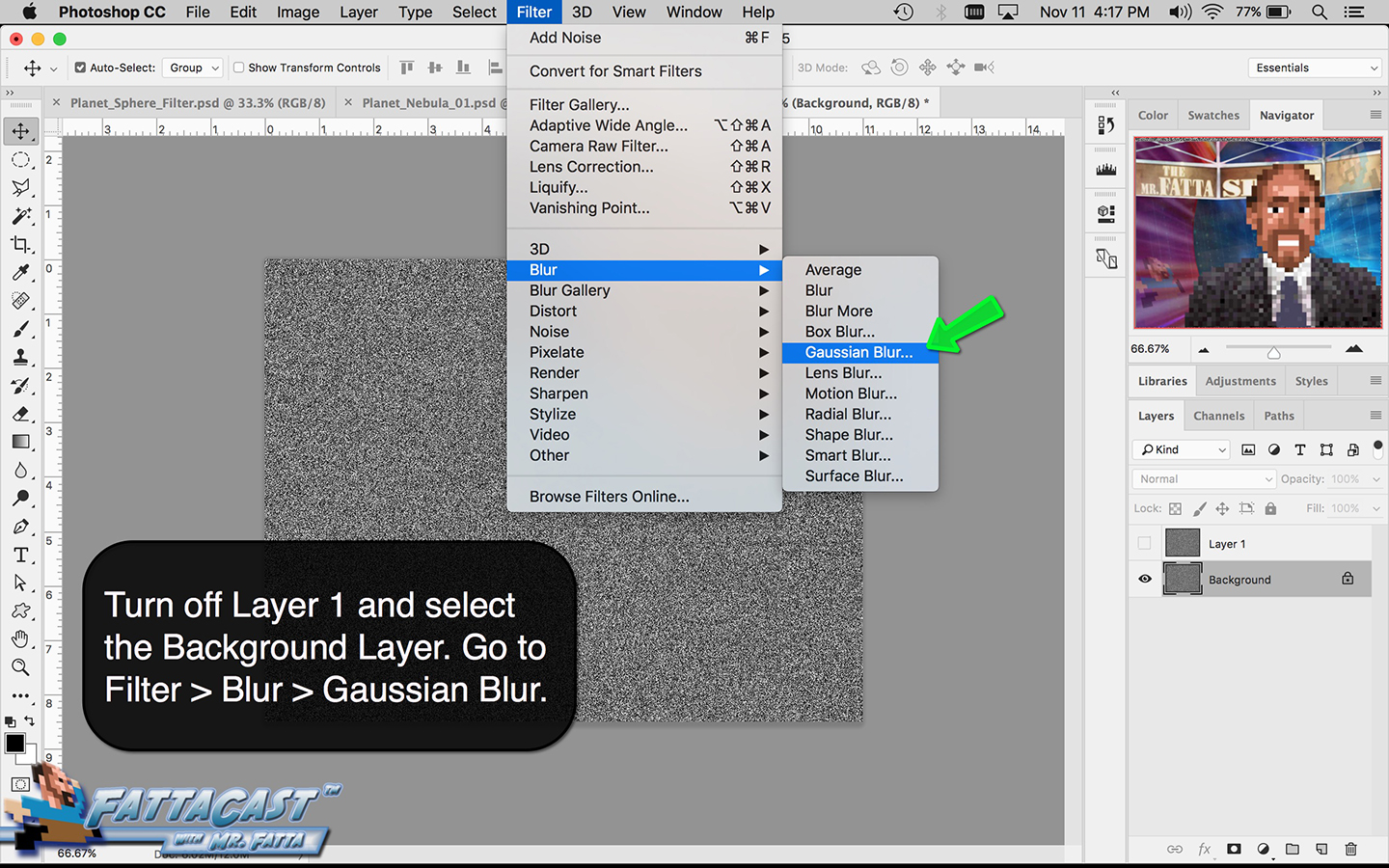
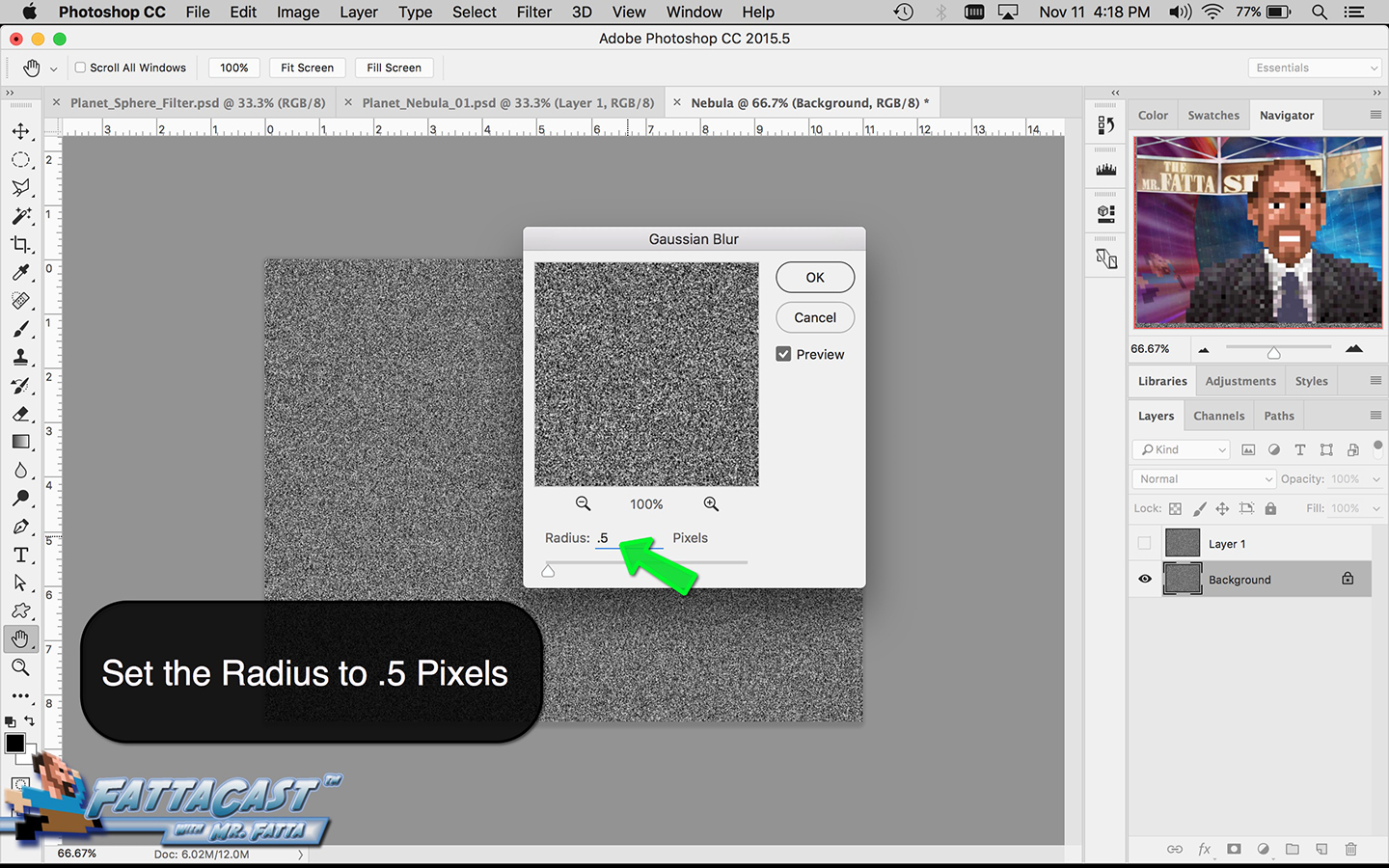
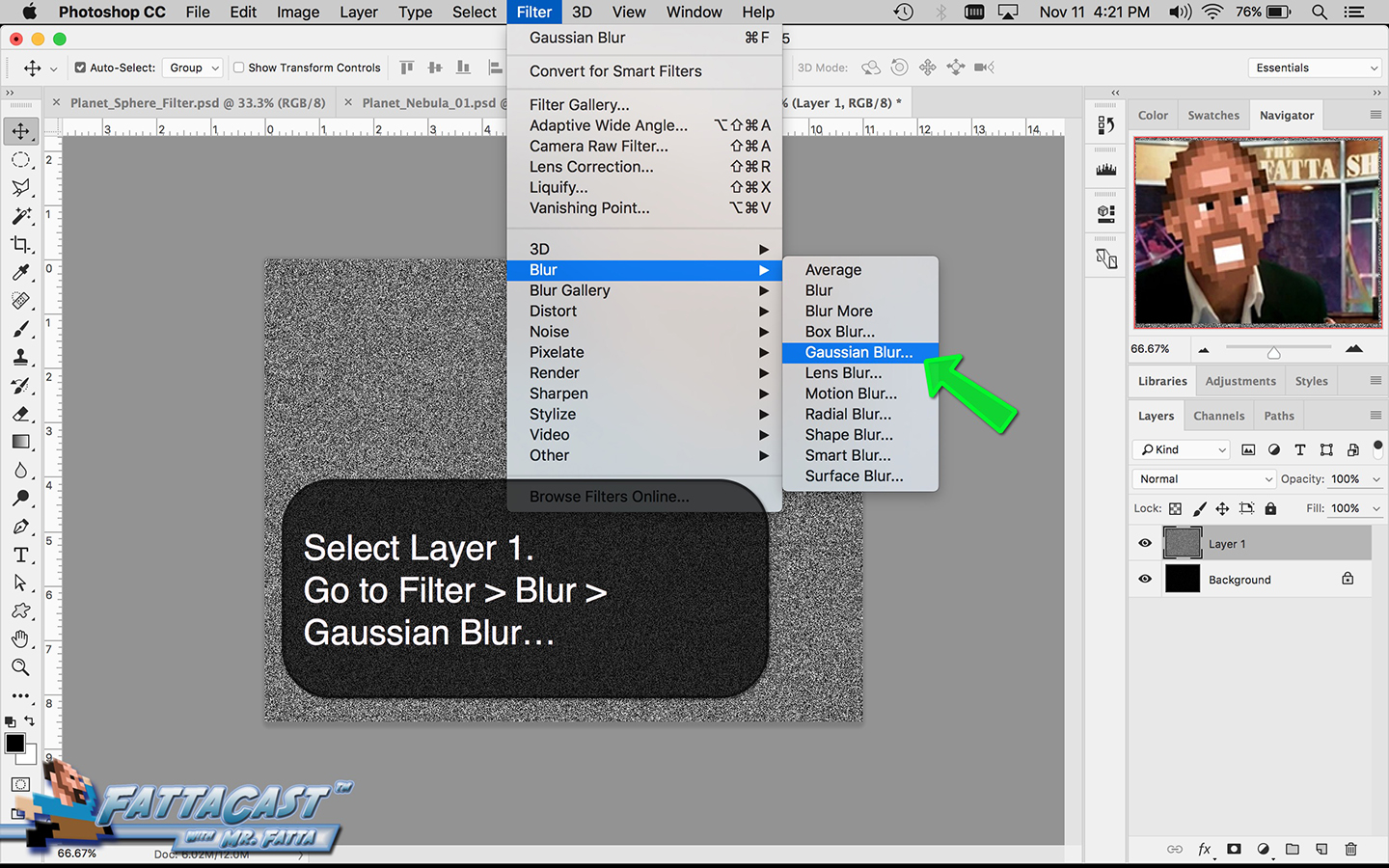
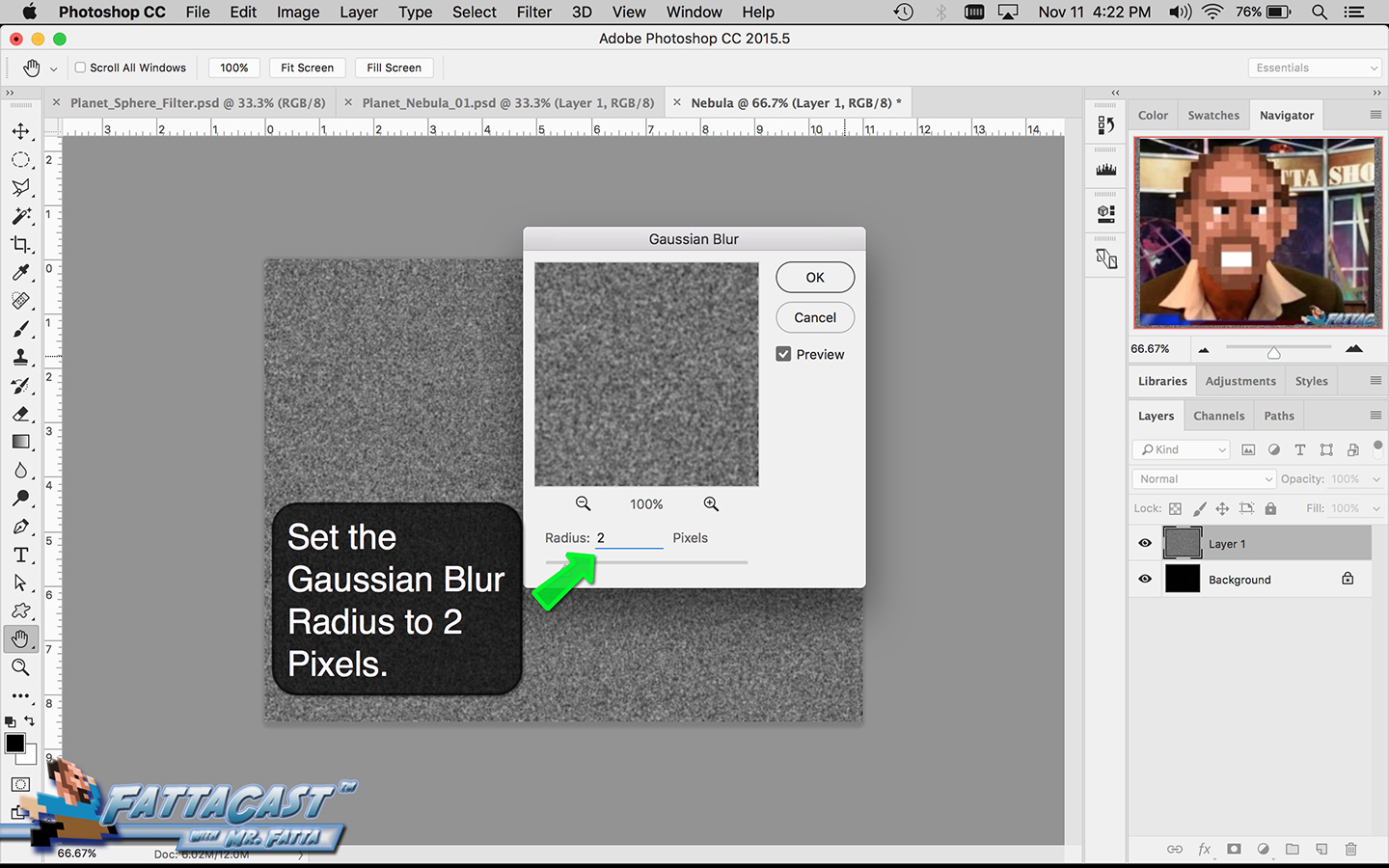
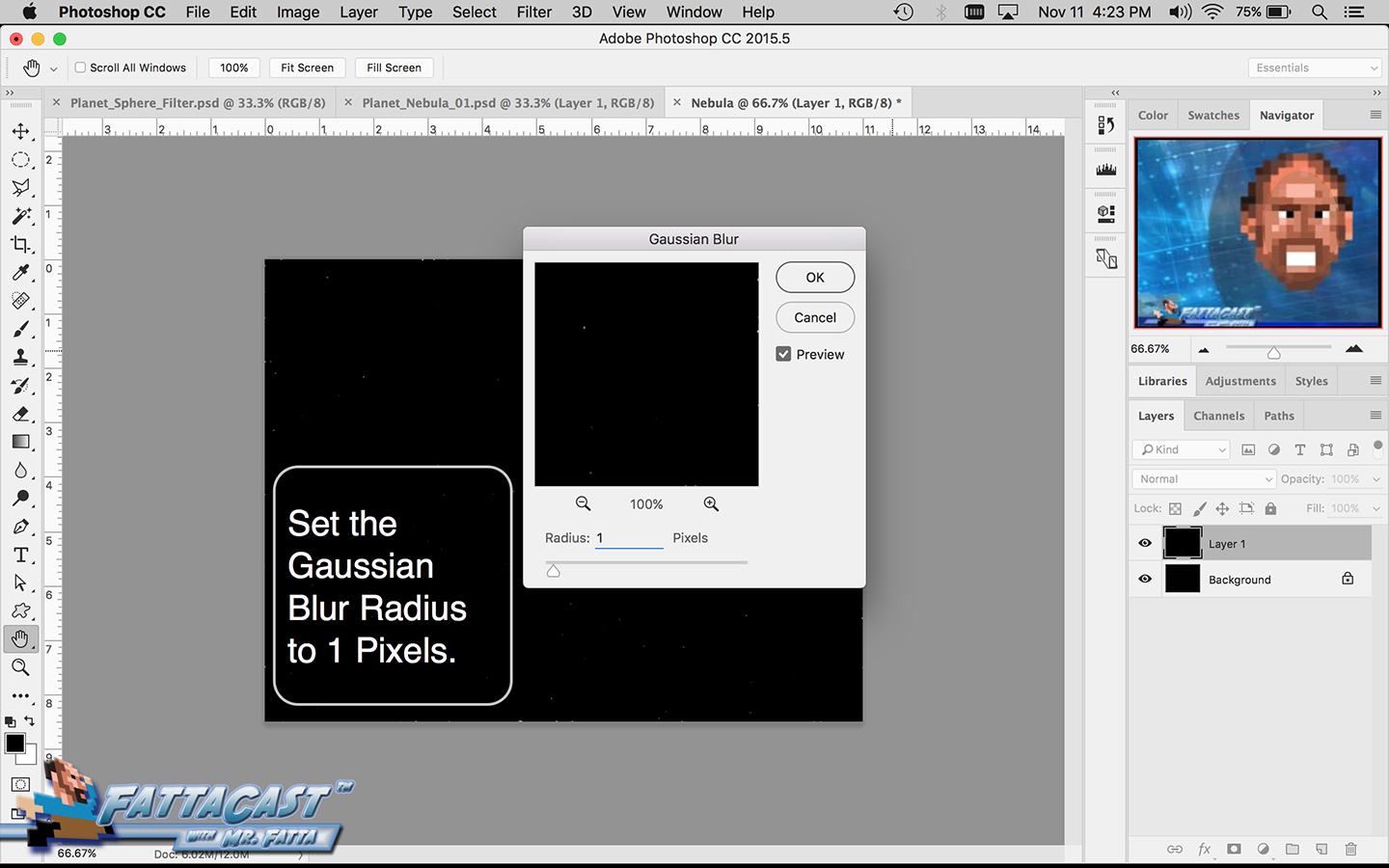
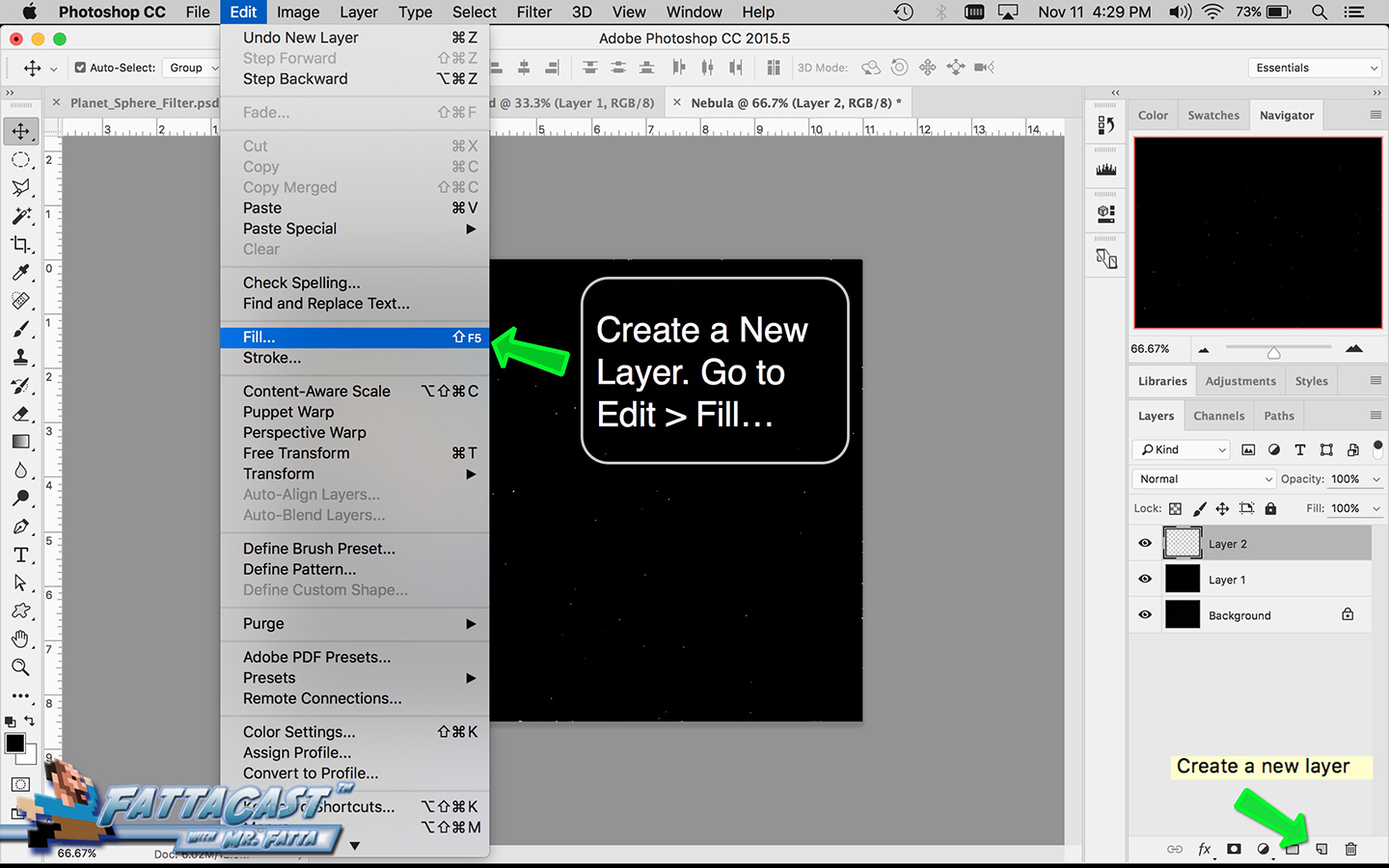
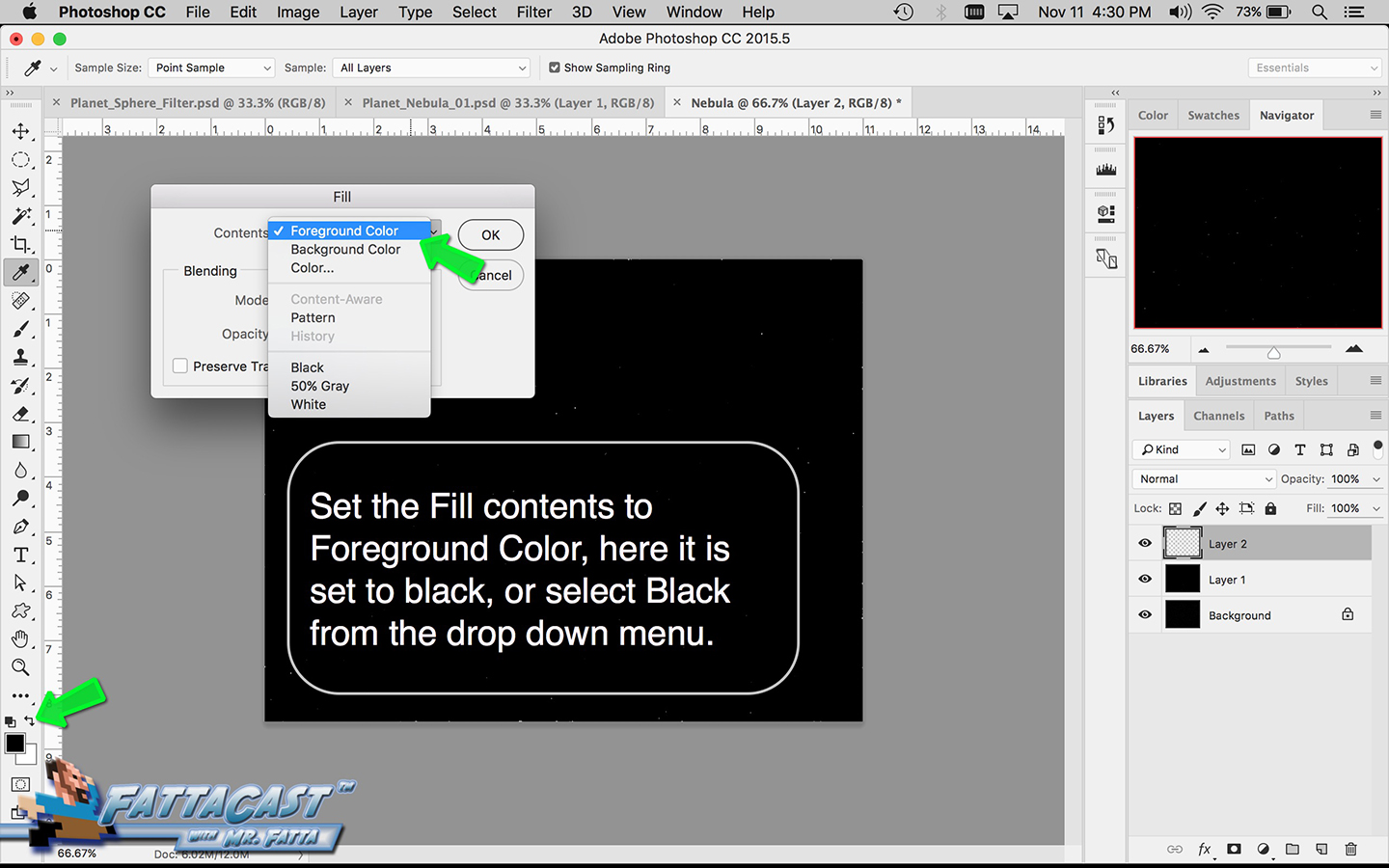
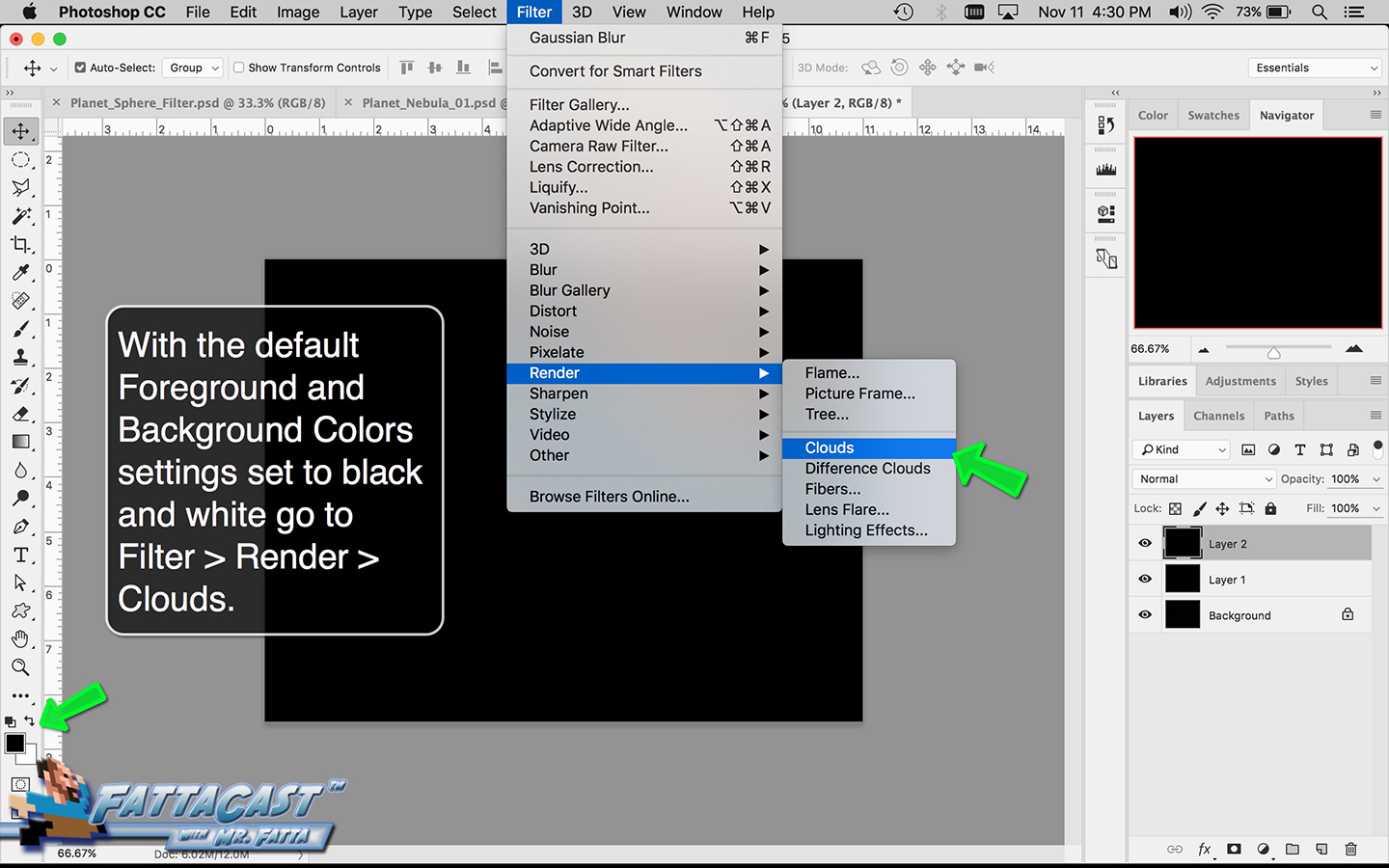
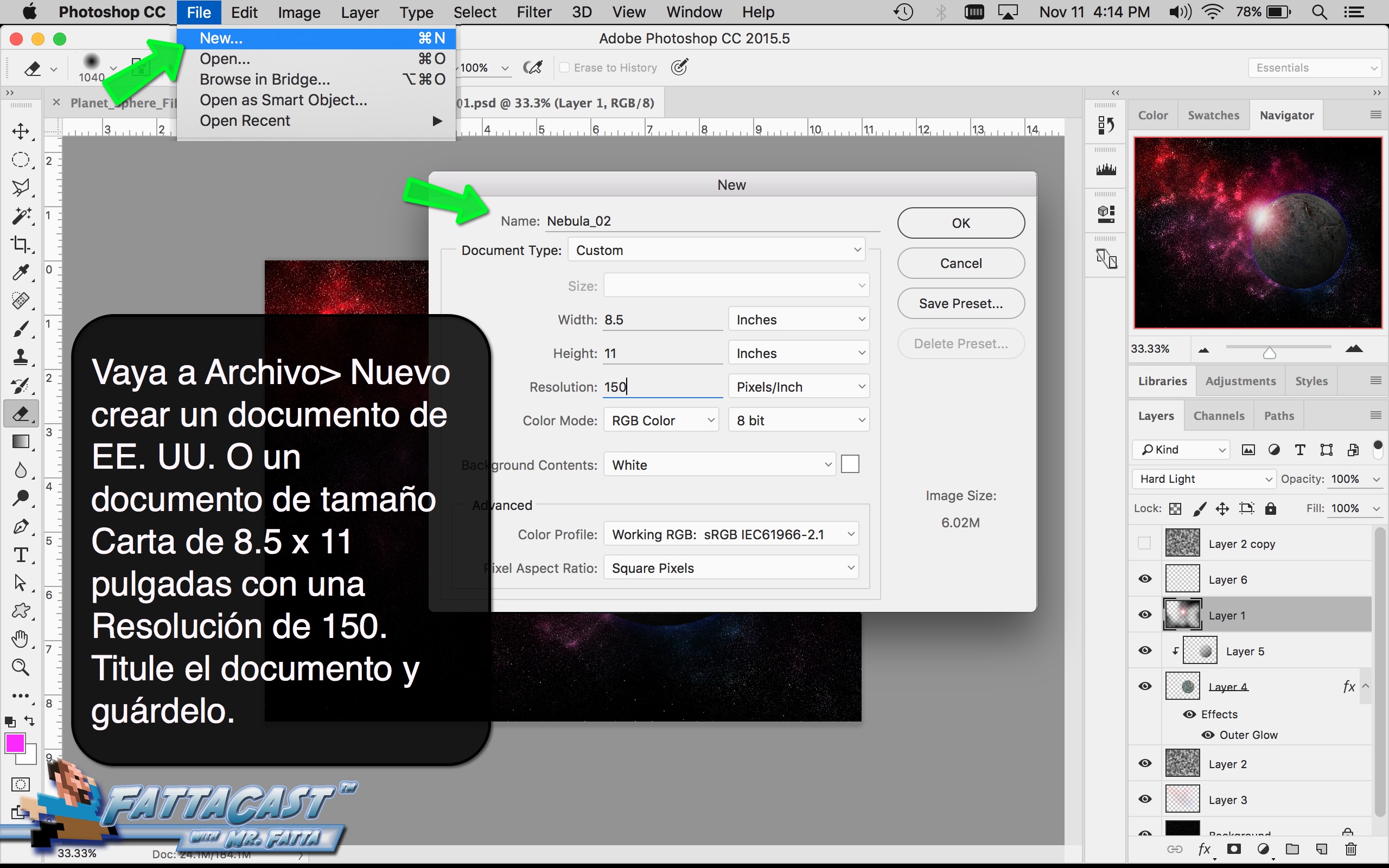
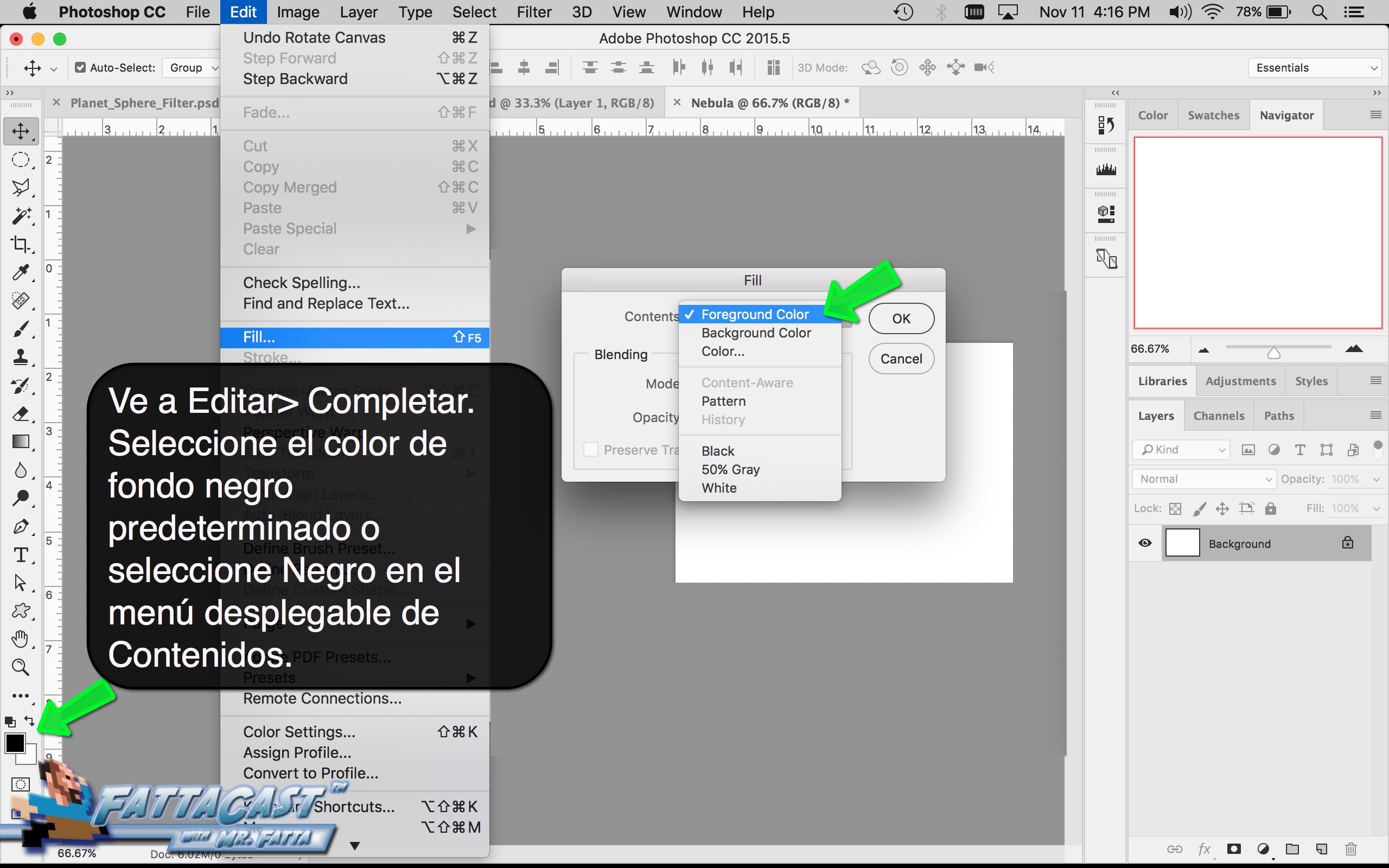
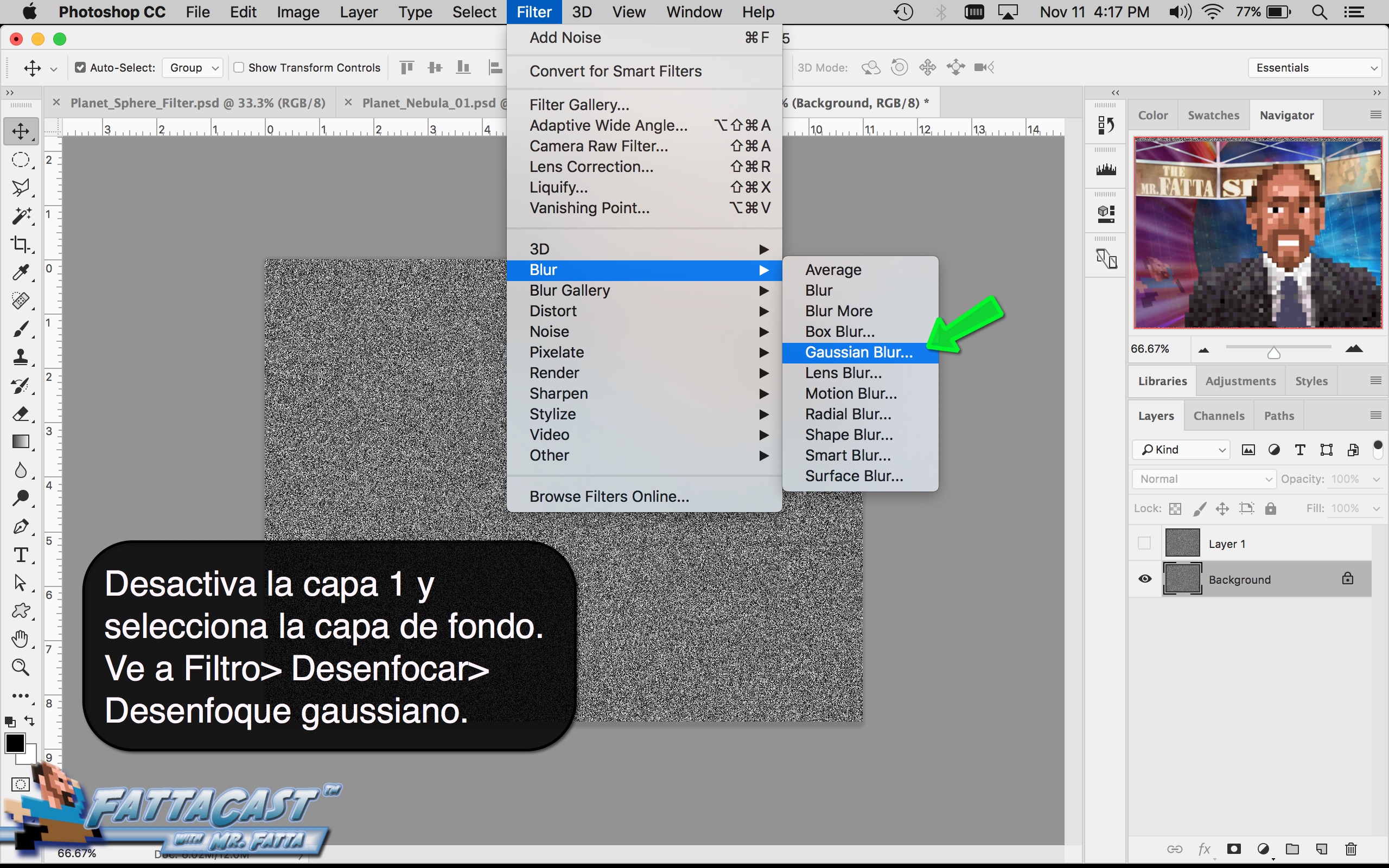
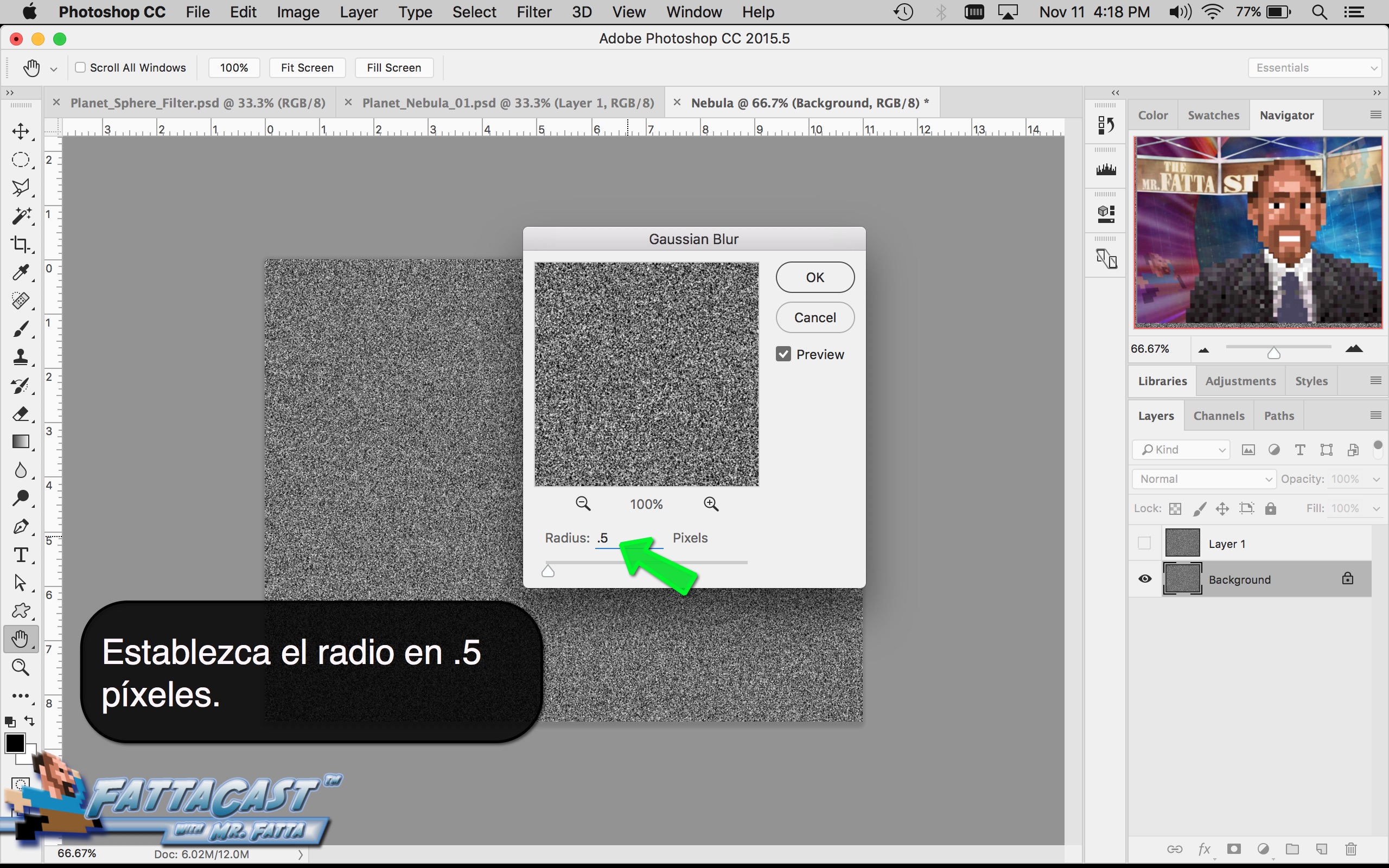
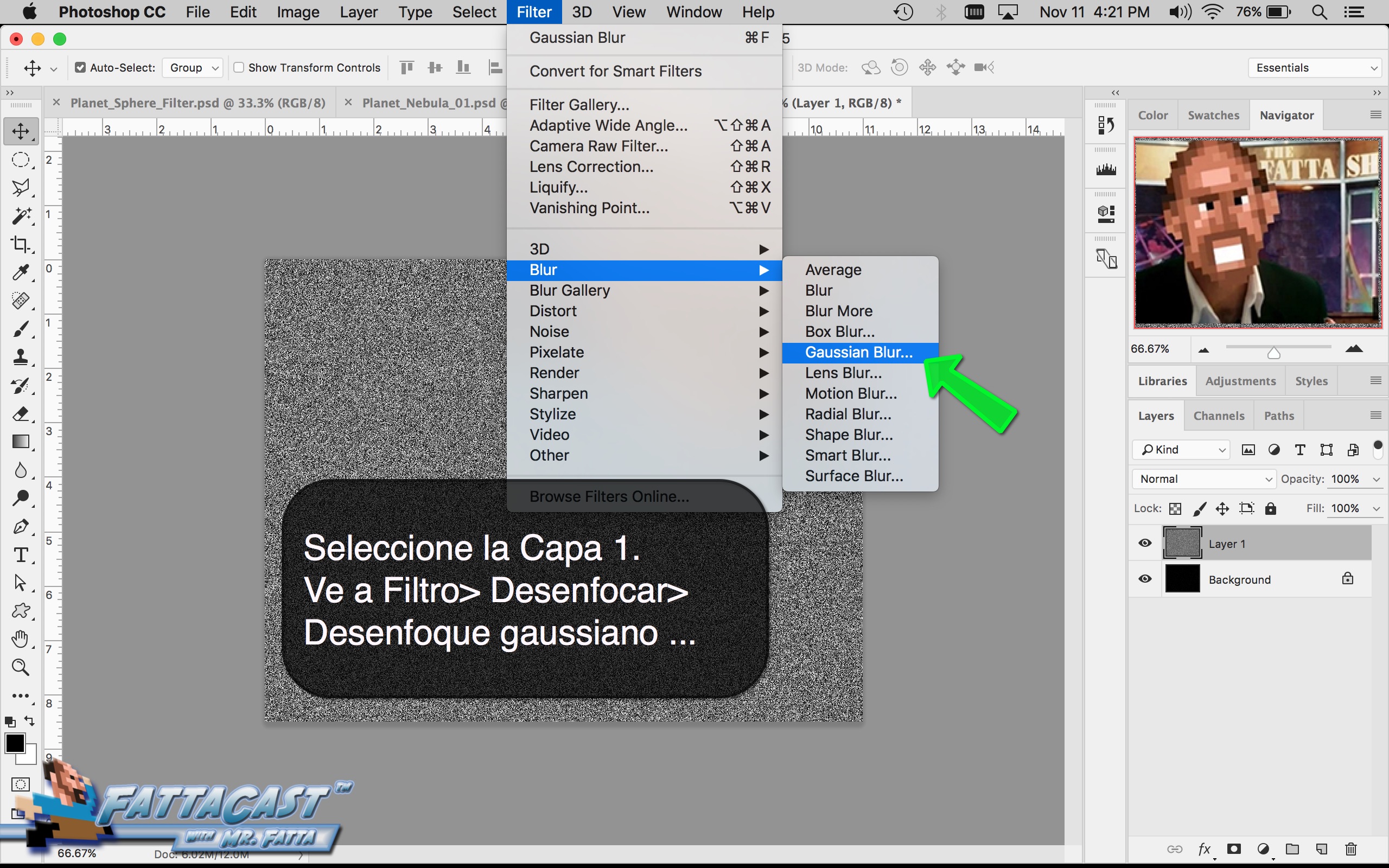
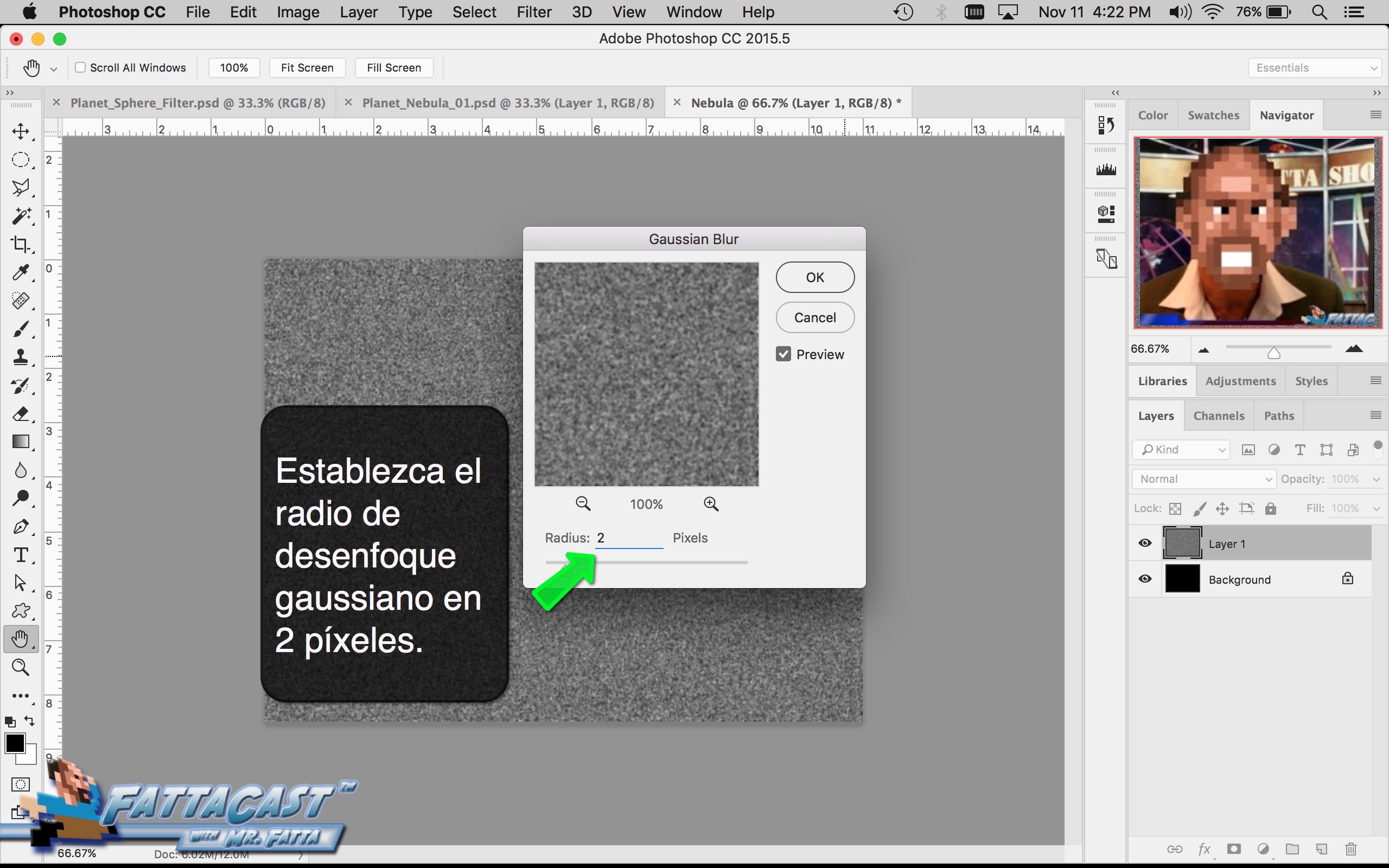
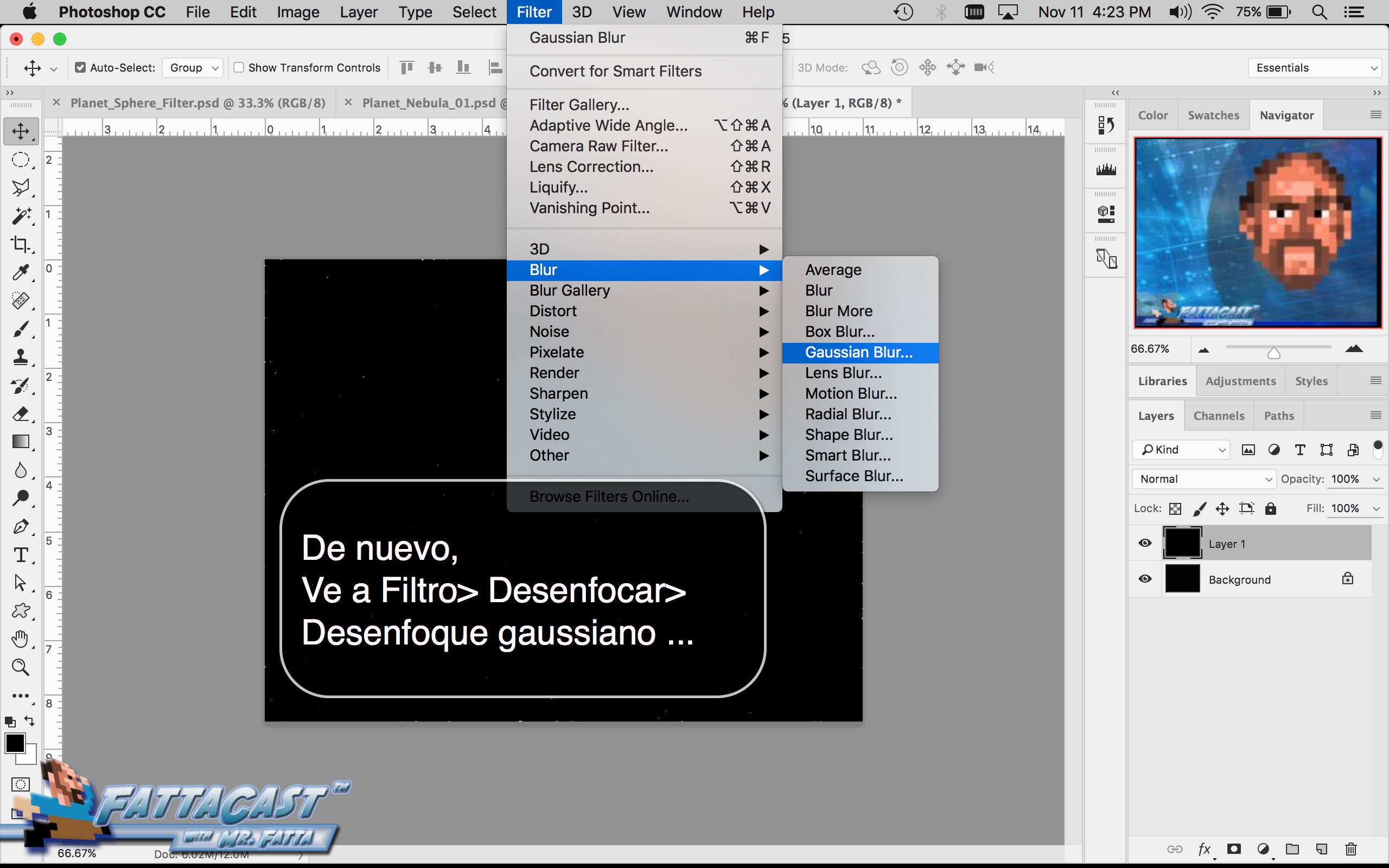
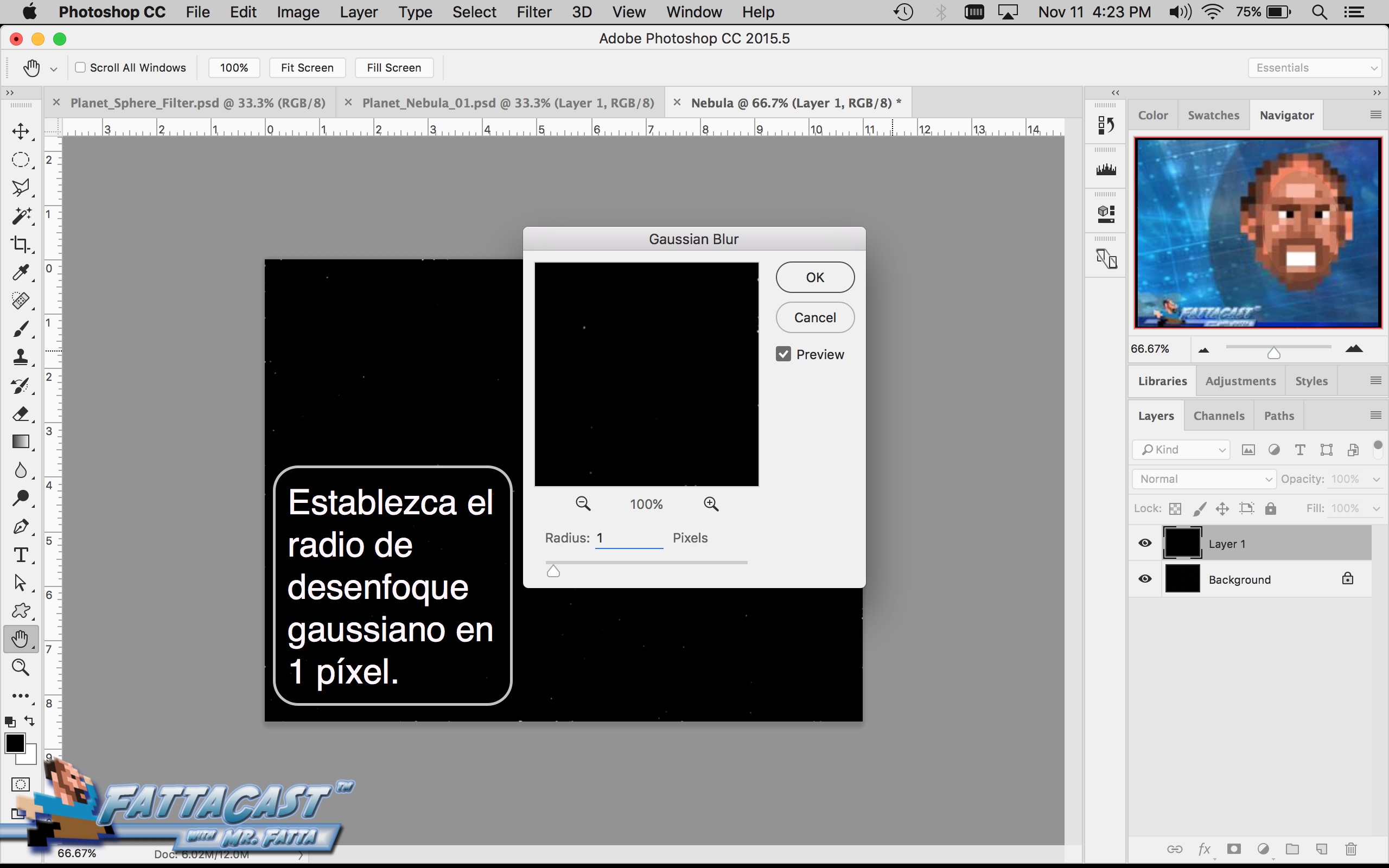
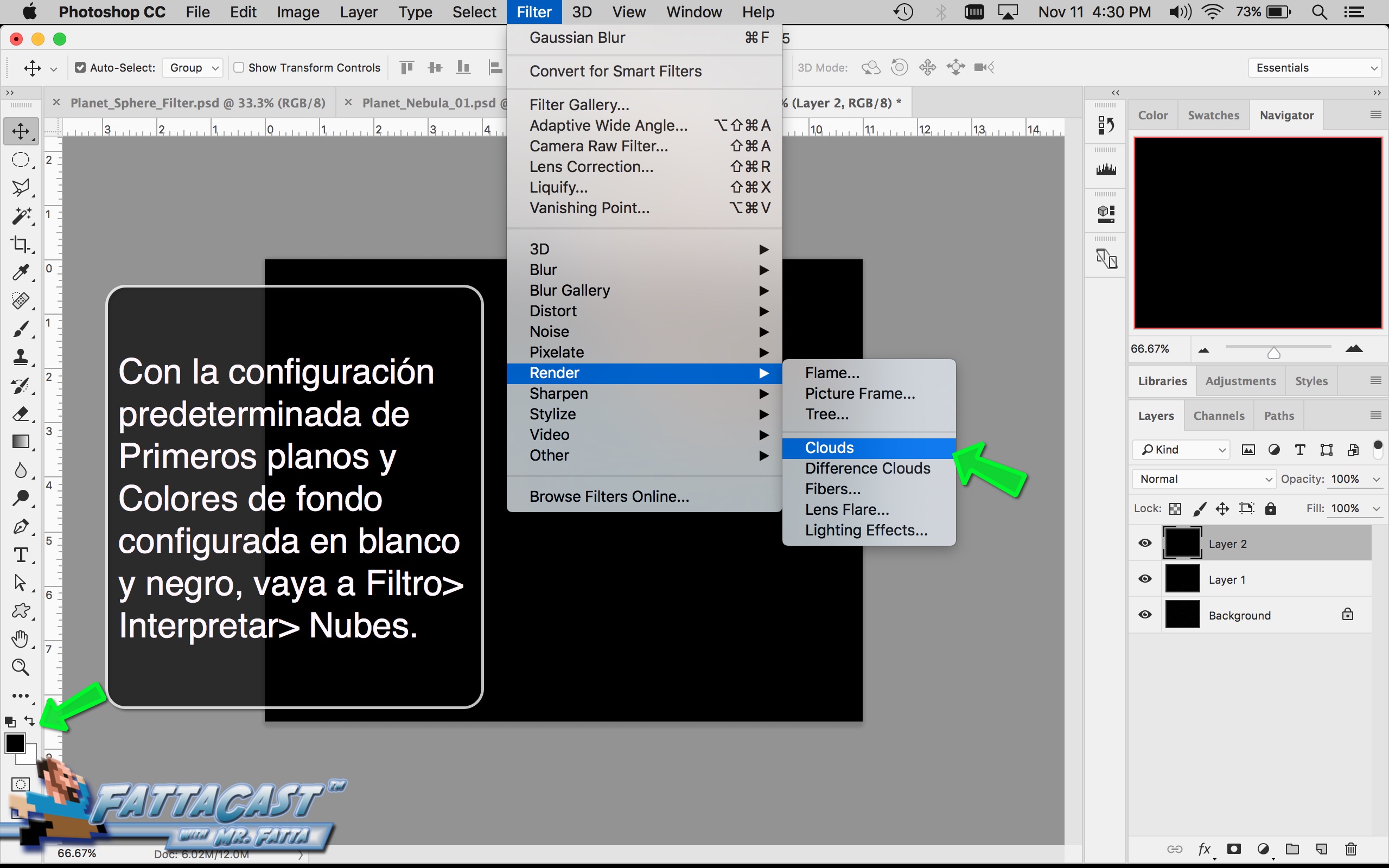
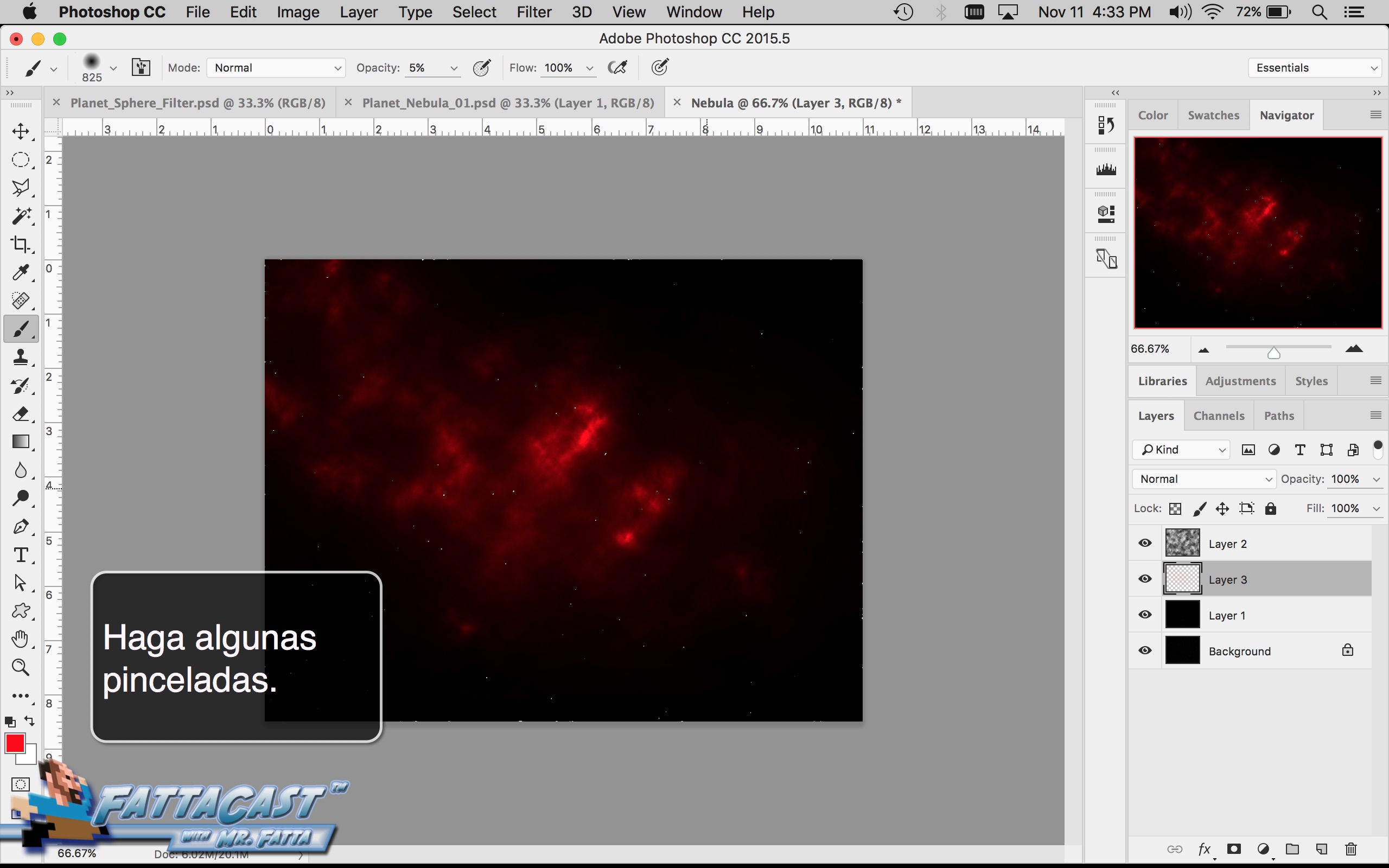
Space is infinite. To begin utilize the tutorial featured below learn how you can create a nebulous space cloud using the Gaussian Blur Filter and Render Clouds Filter in Adobe Photoshop.
Learning Targets
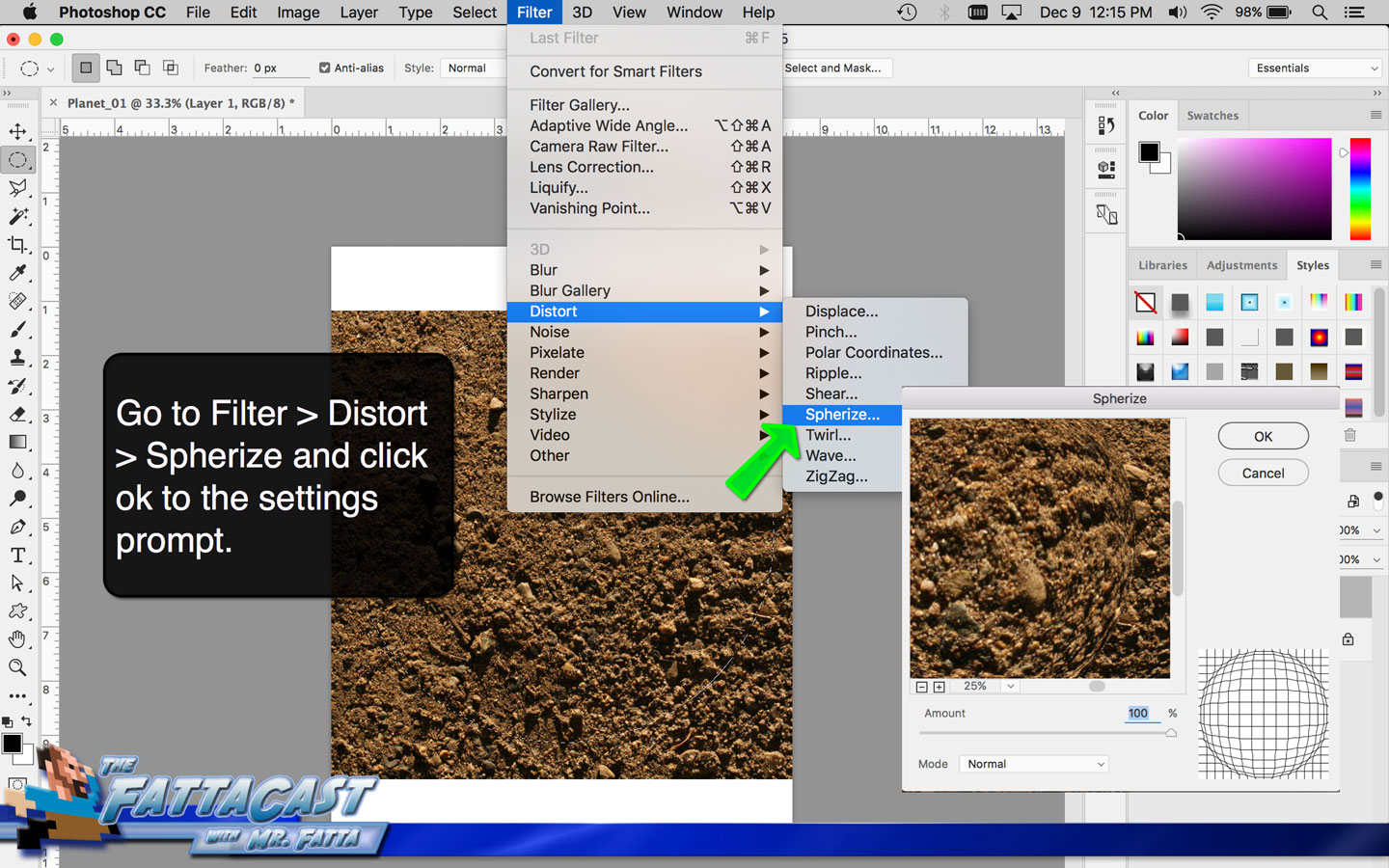
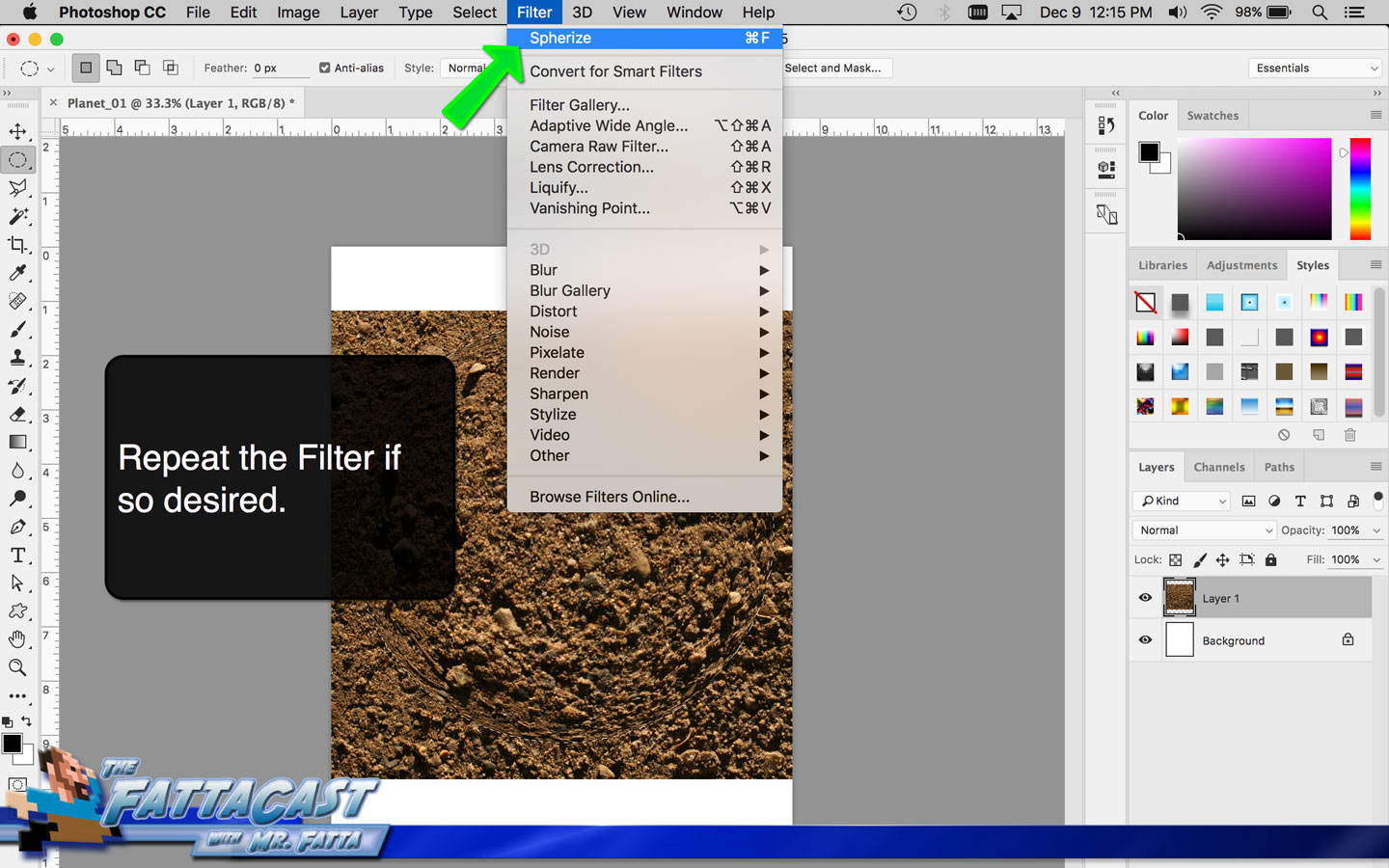
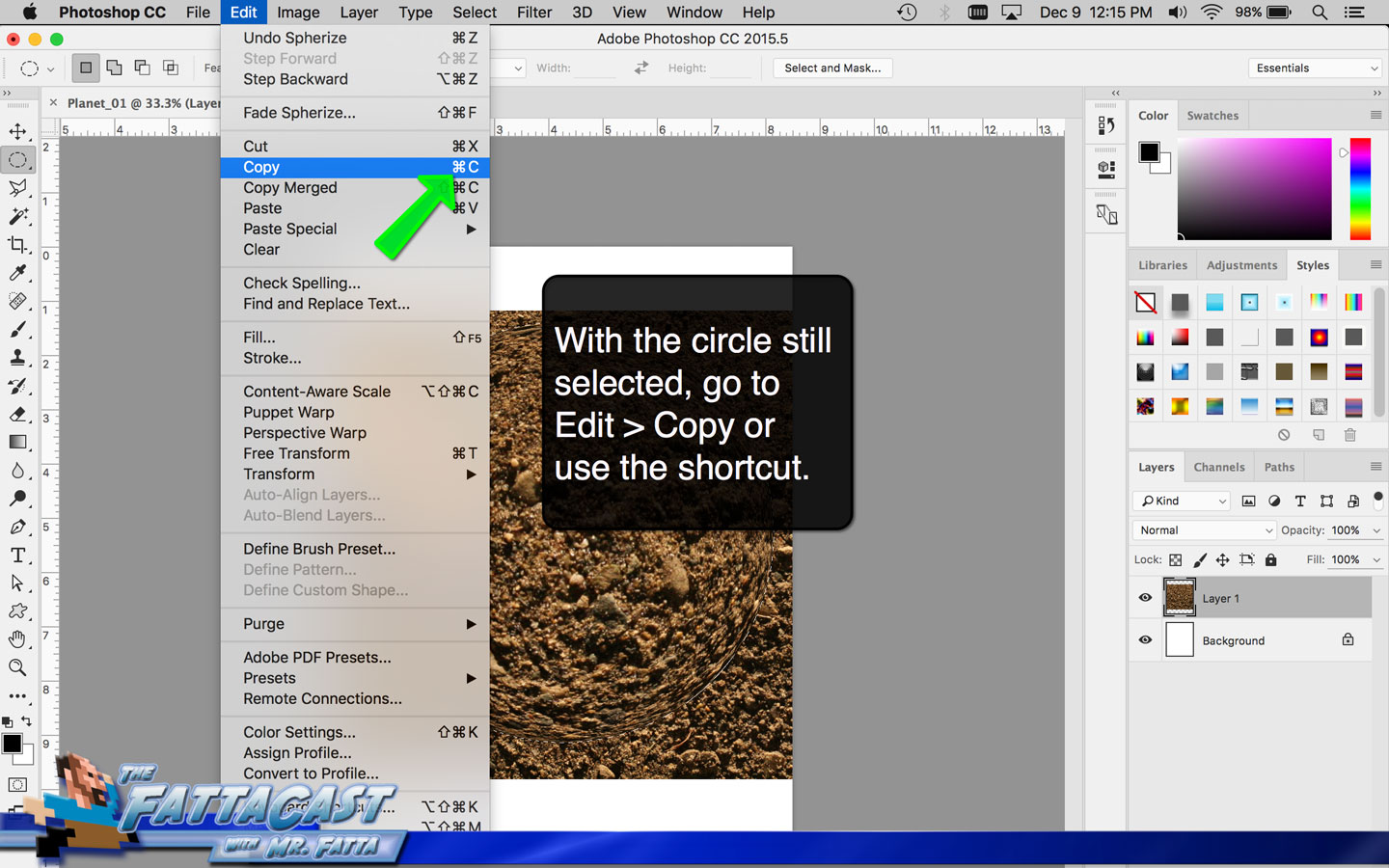
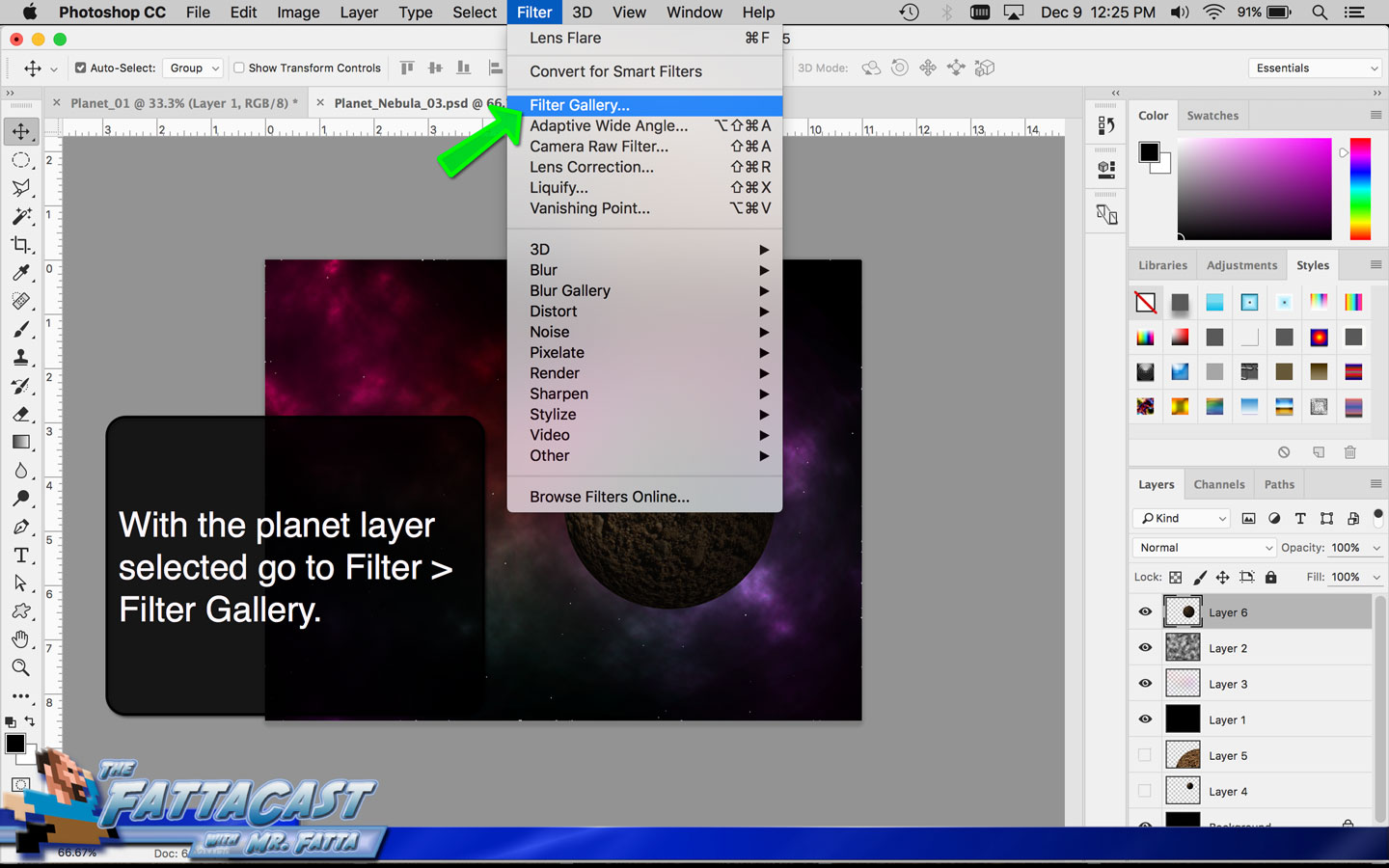
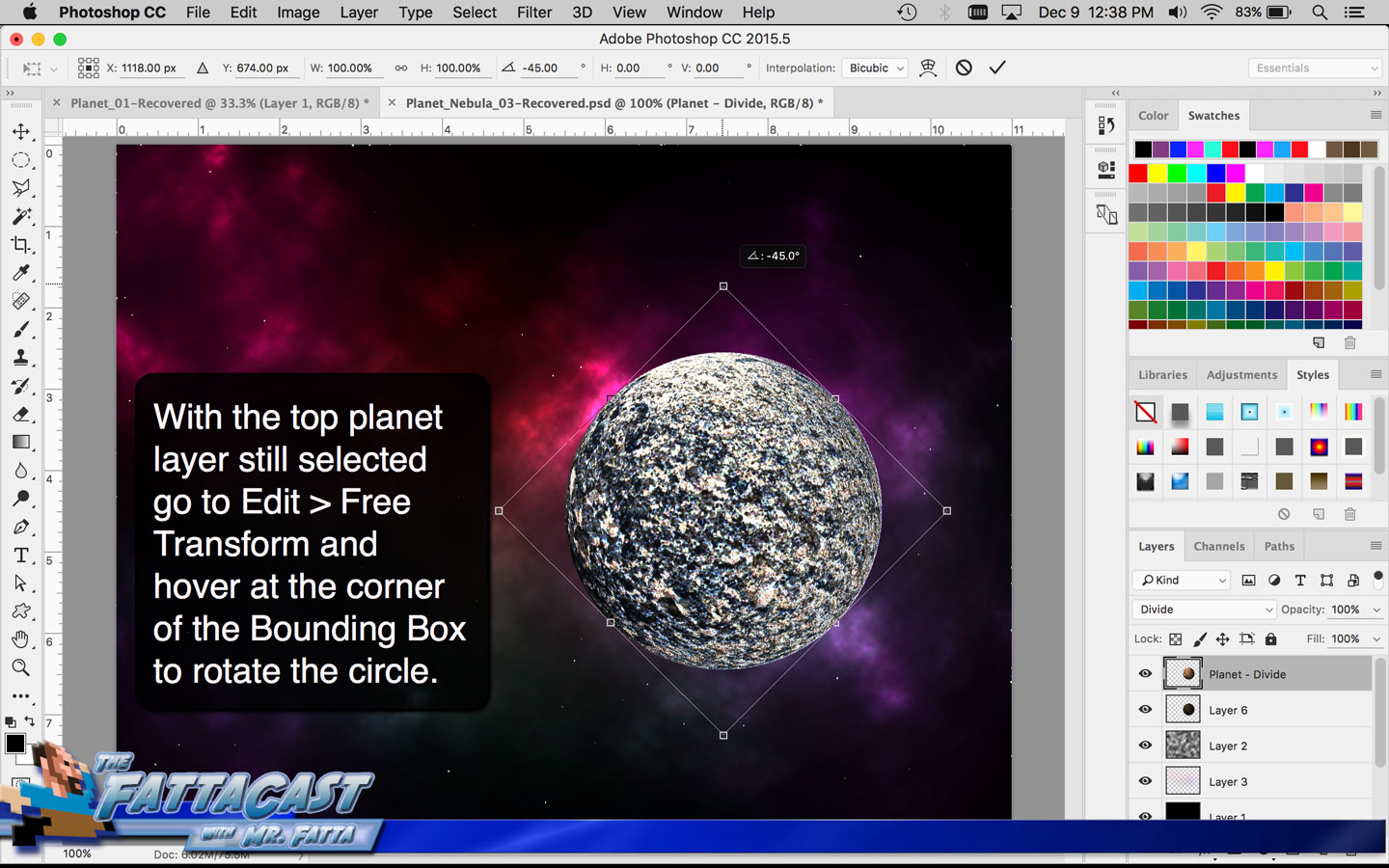
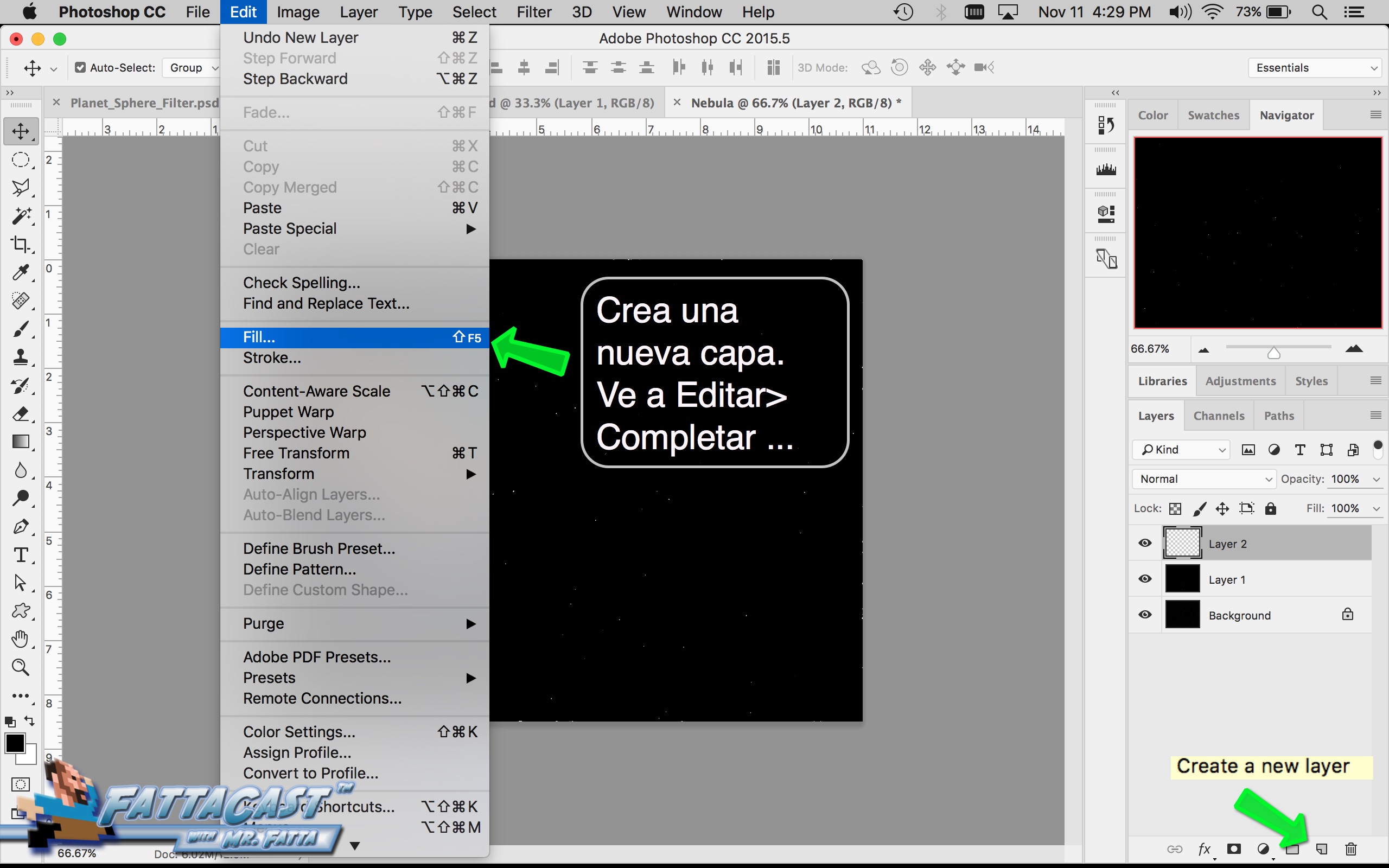
1. I can create the illusion of a spherical form using the Distort Spherize Effect on an image of a texture in AP.
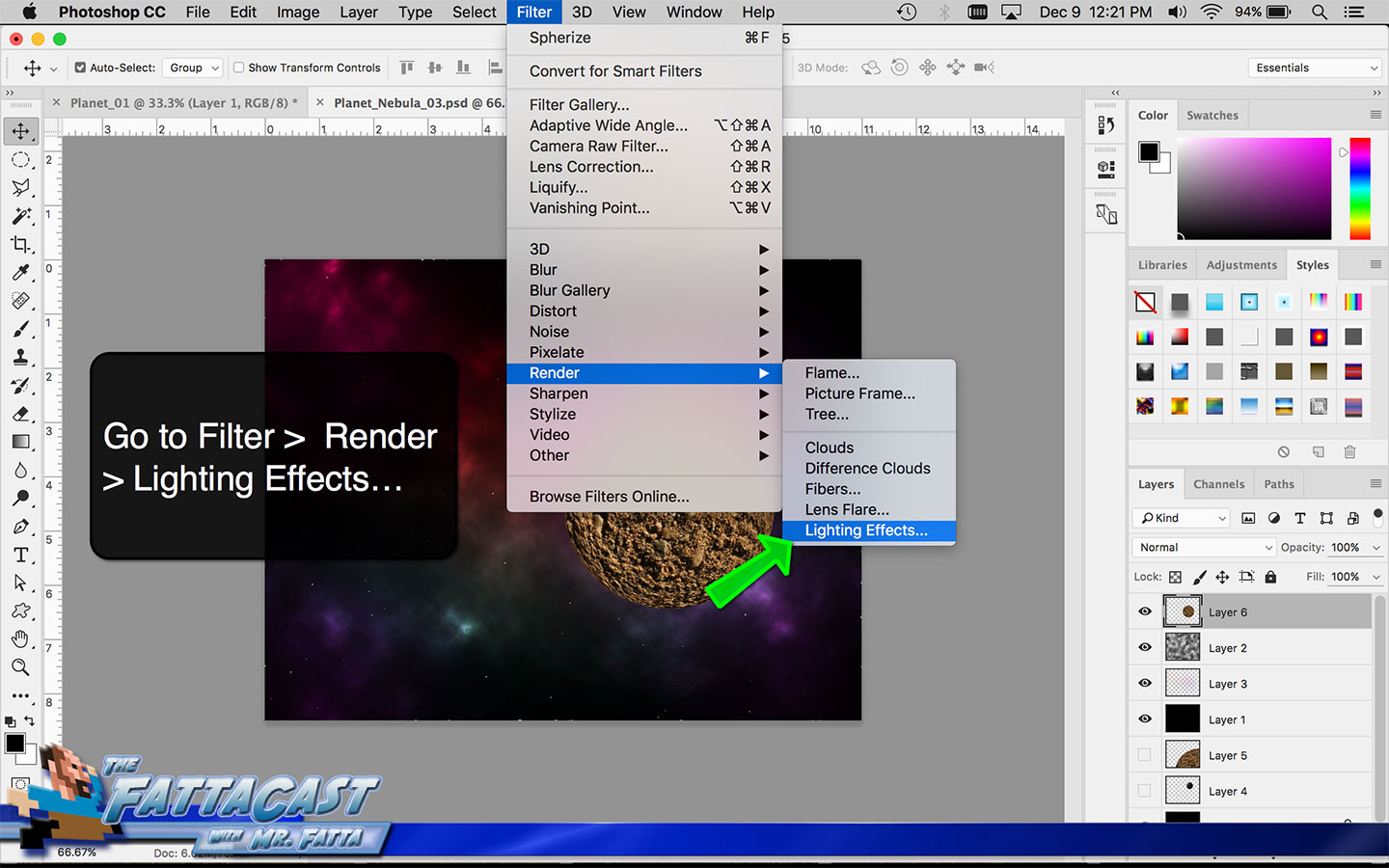
2. I can render the effect of light hiting a sphere and emphasize the 3D form of the planet by selecting Filter > Render > Lighting Effects from the menu bar in AP.
Creating a Planet
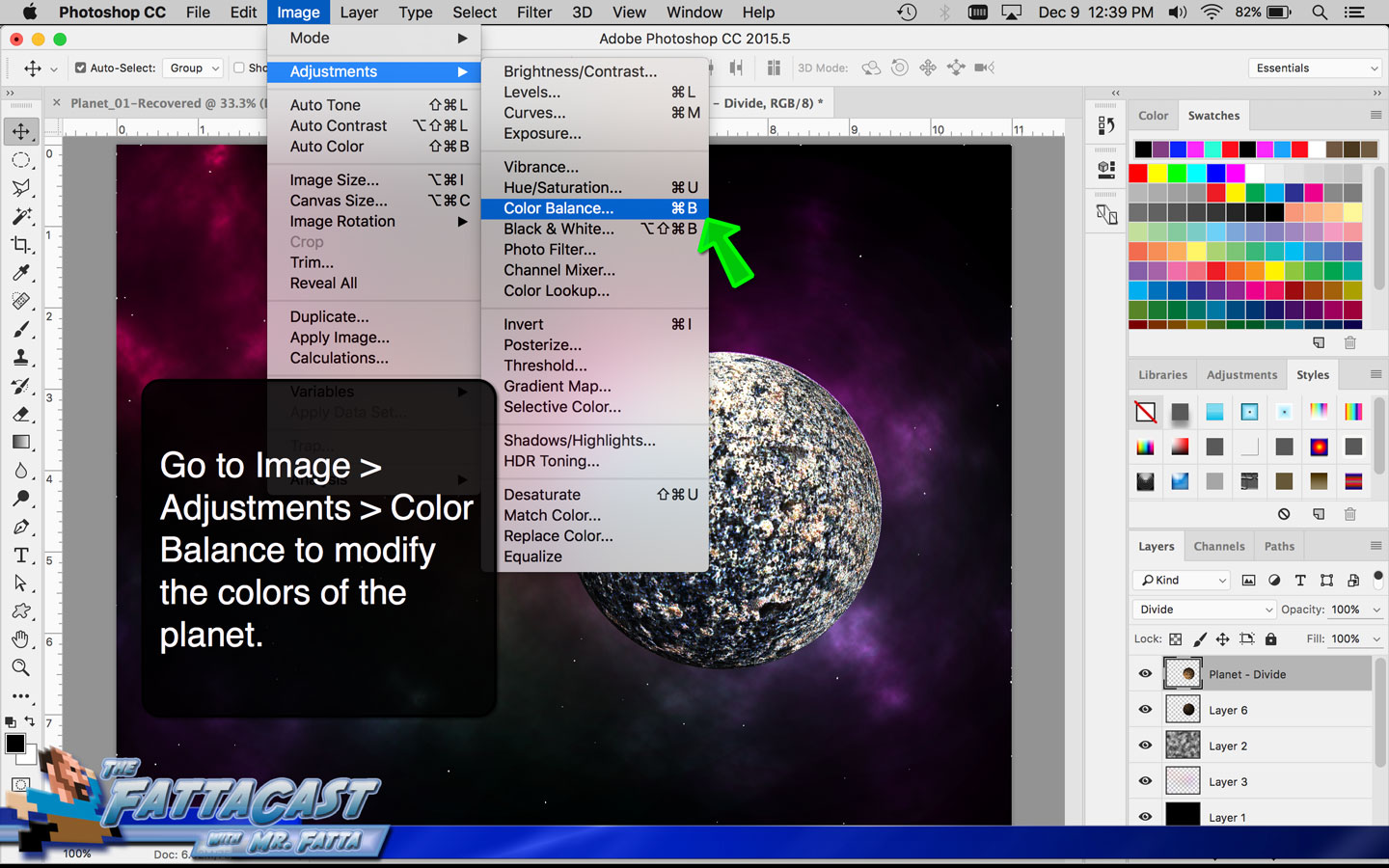
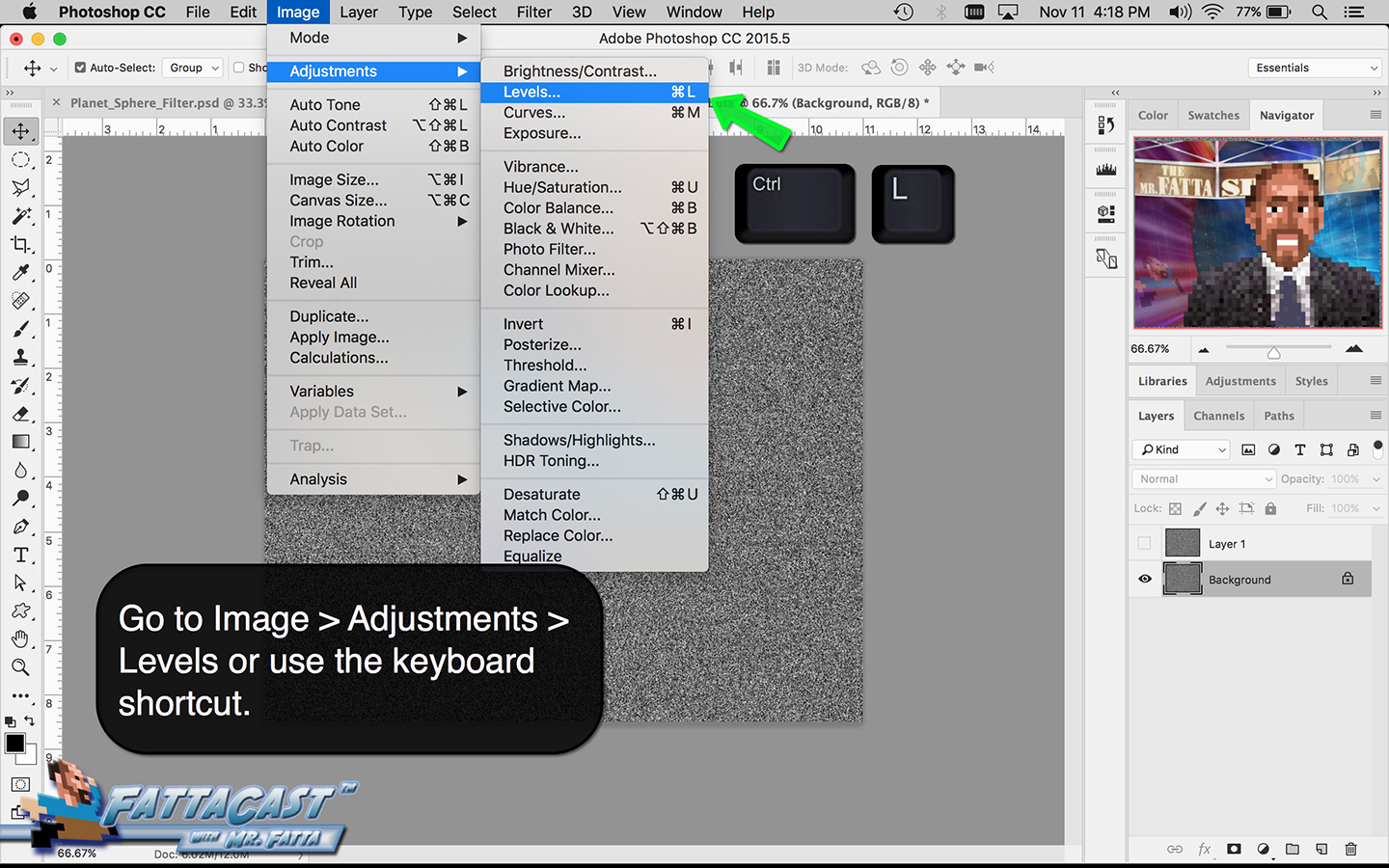
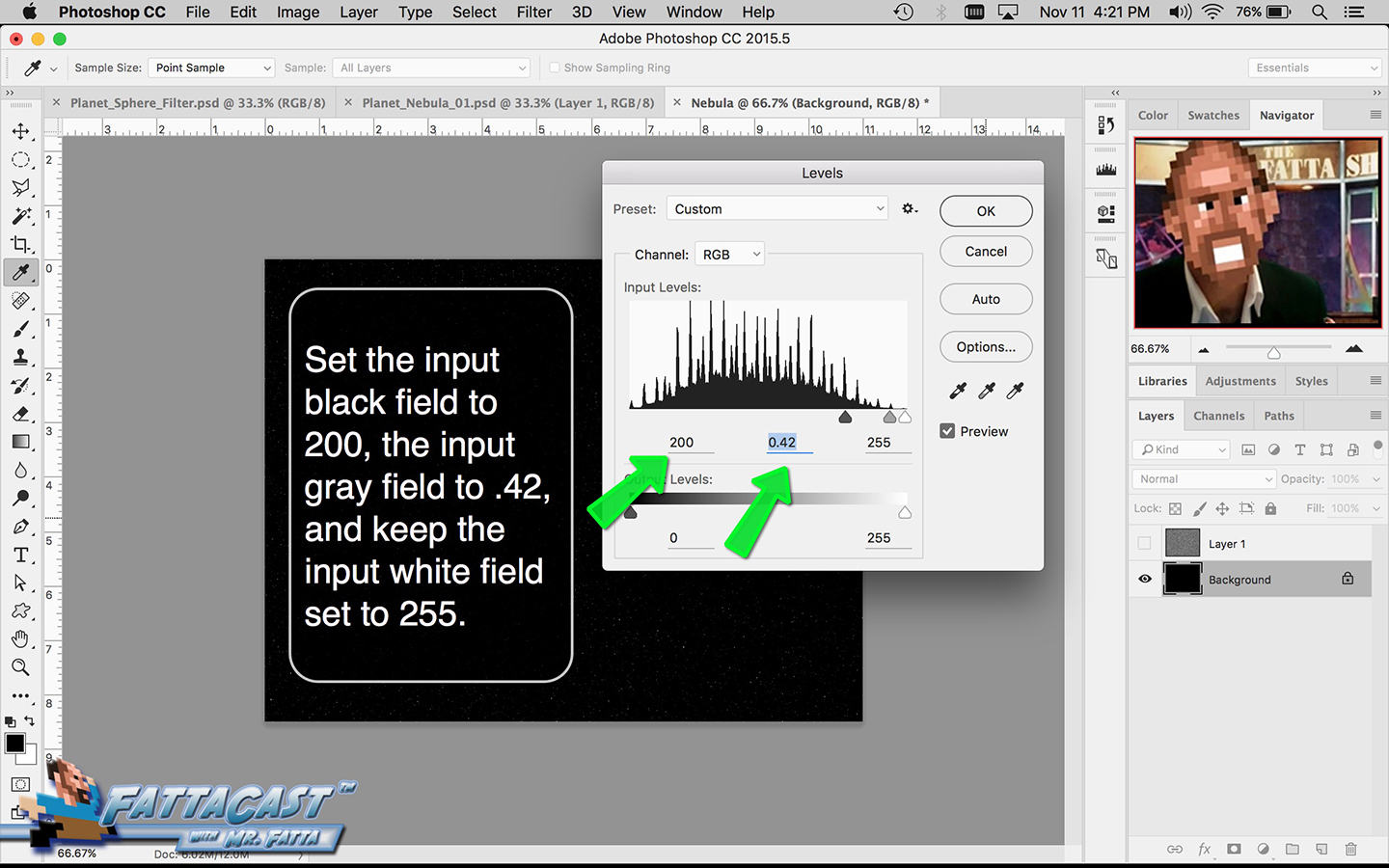
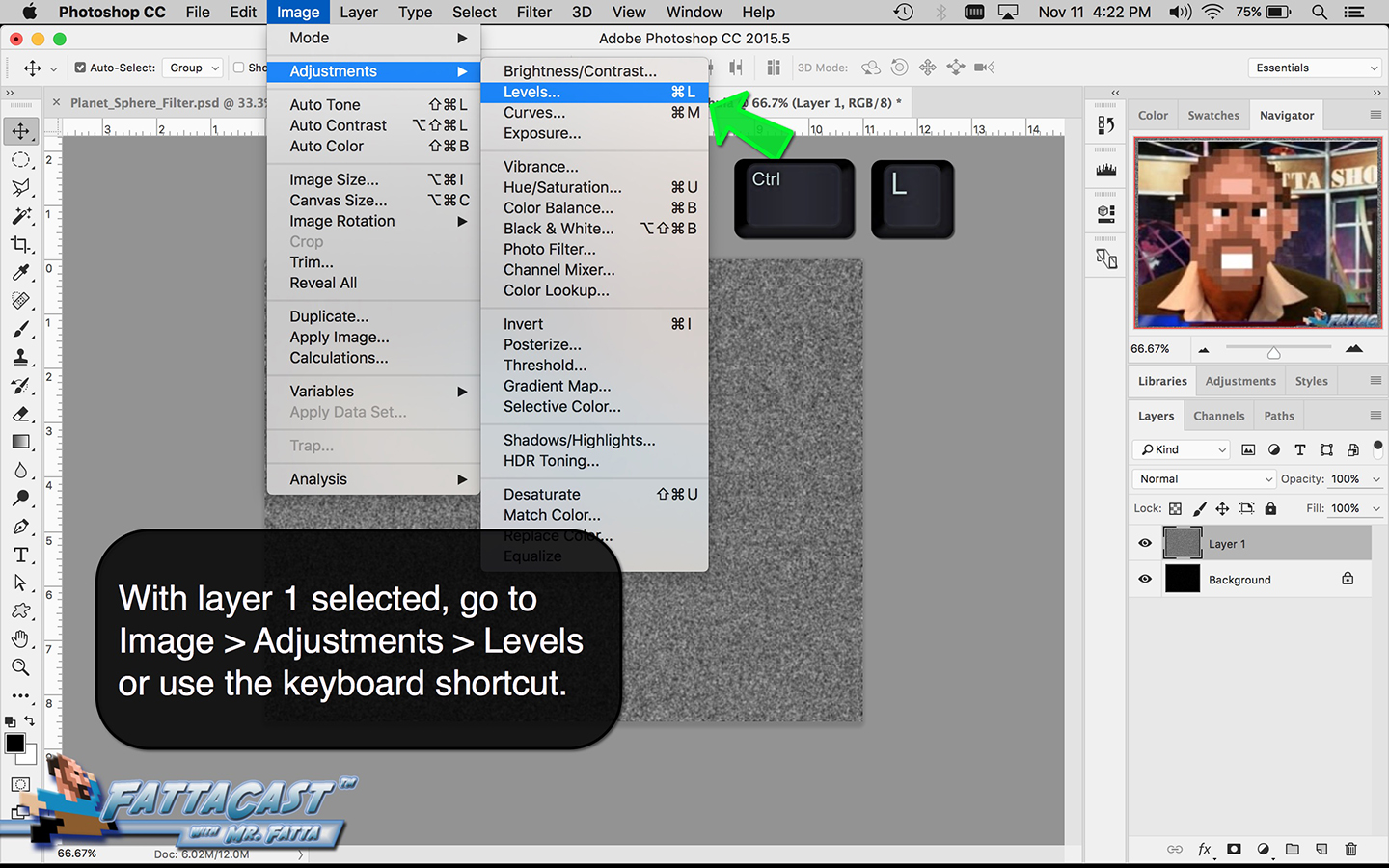
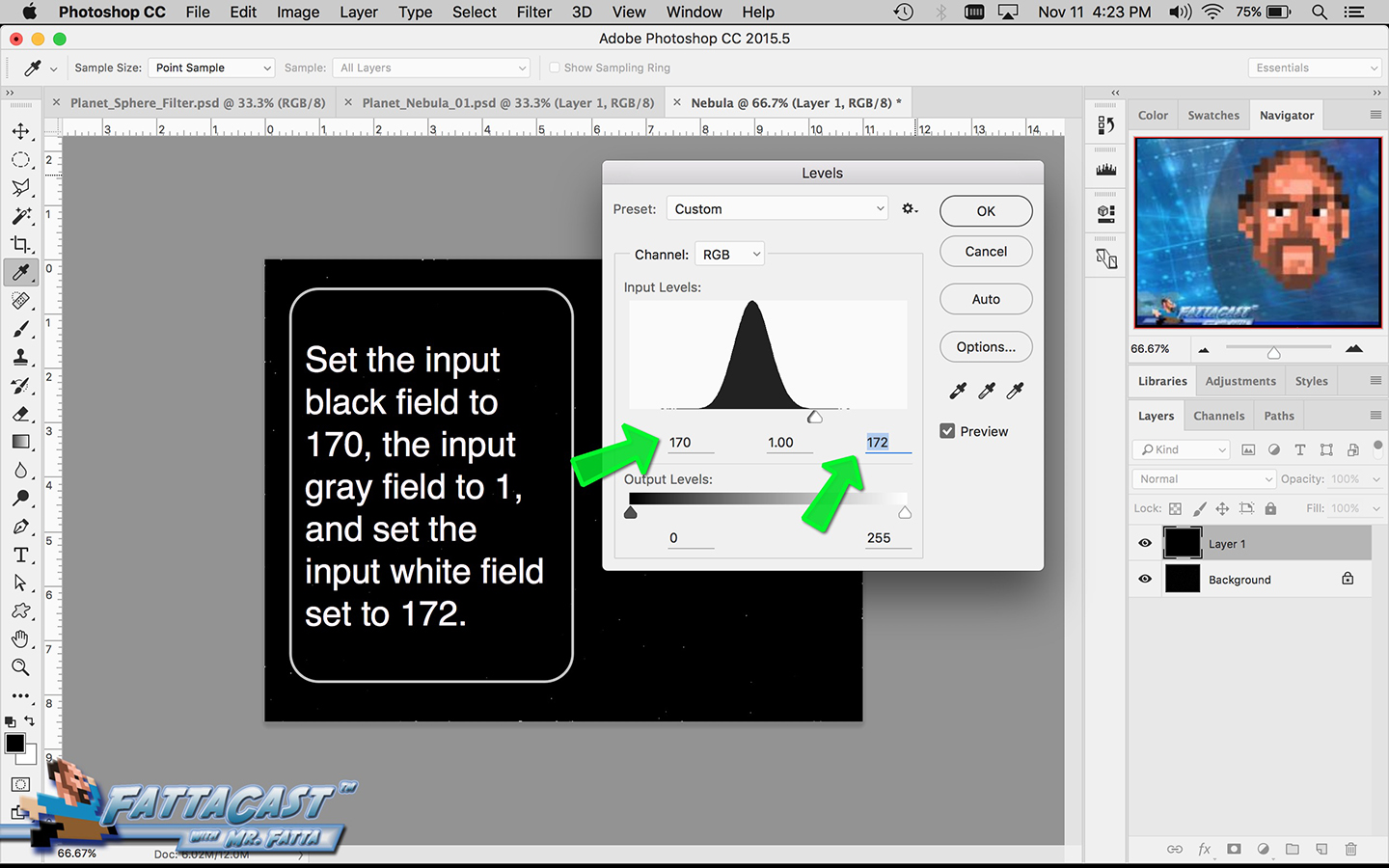
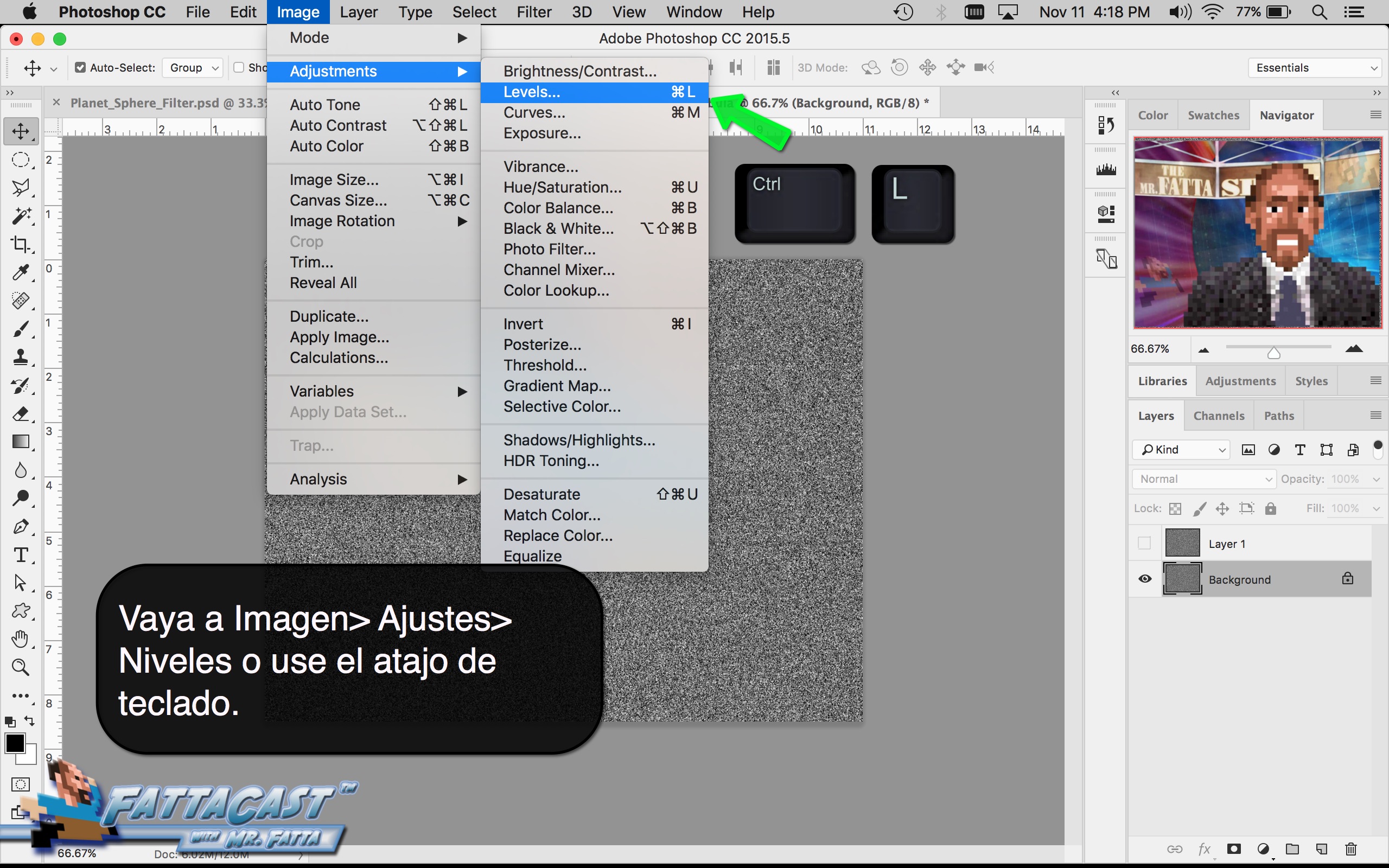
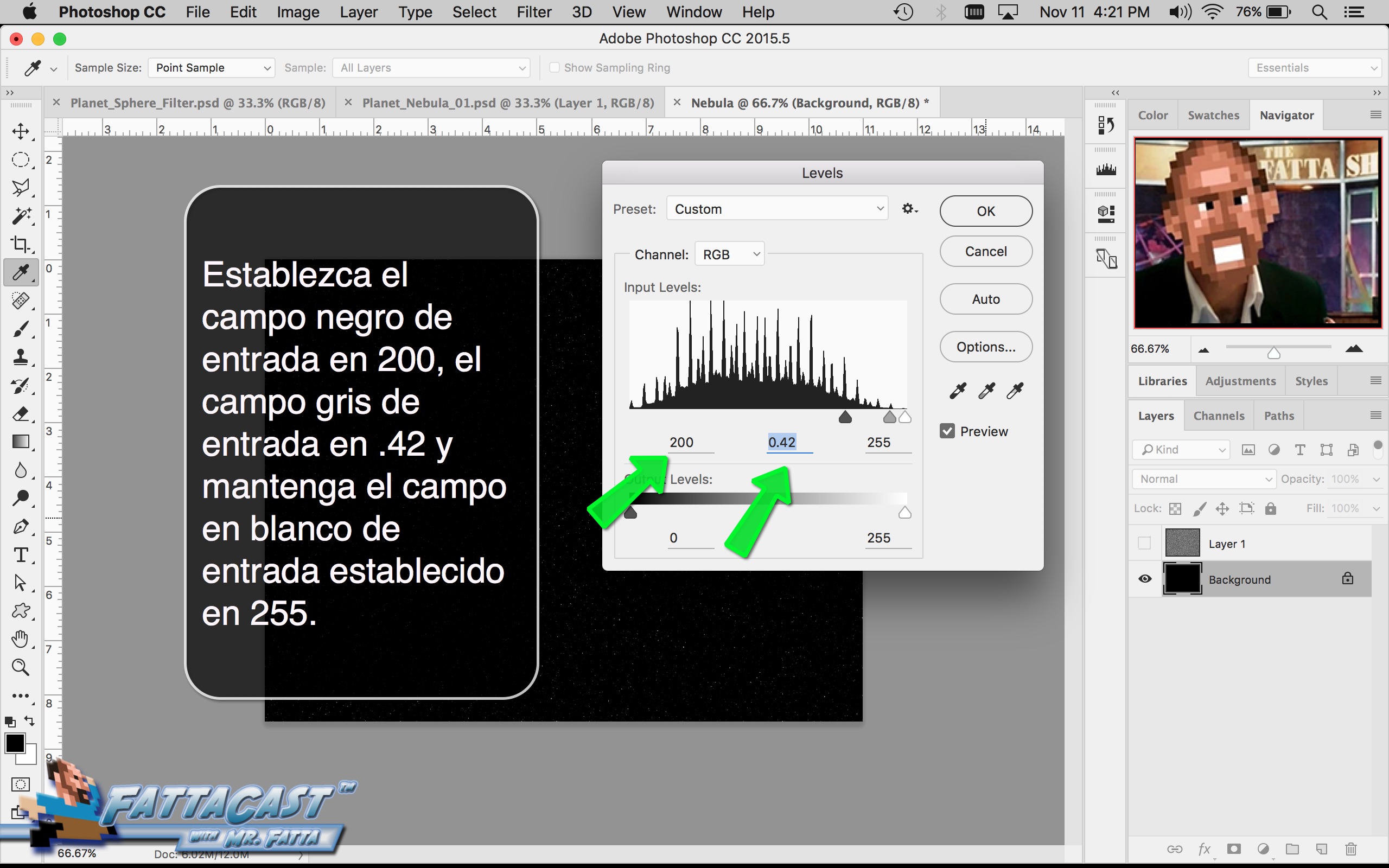
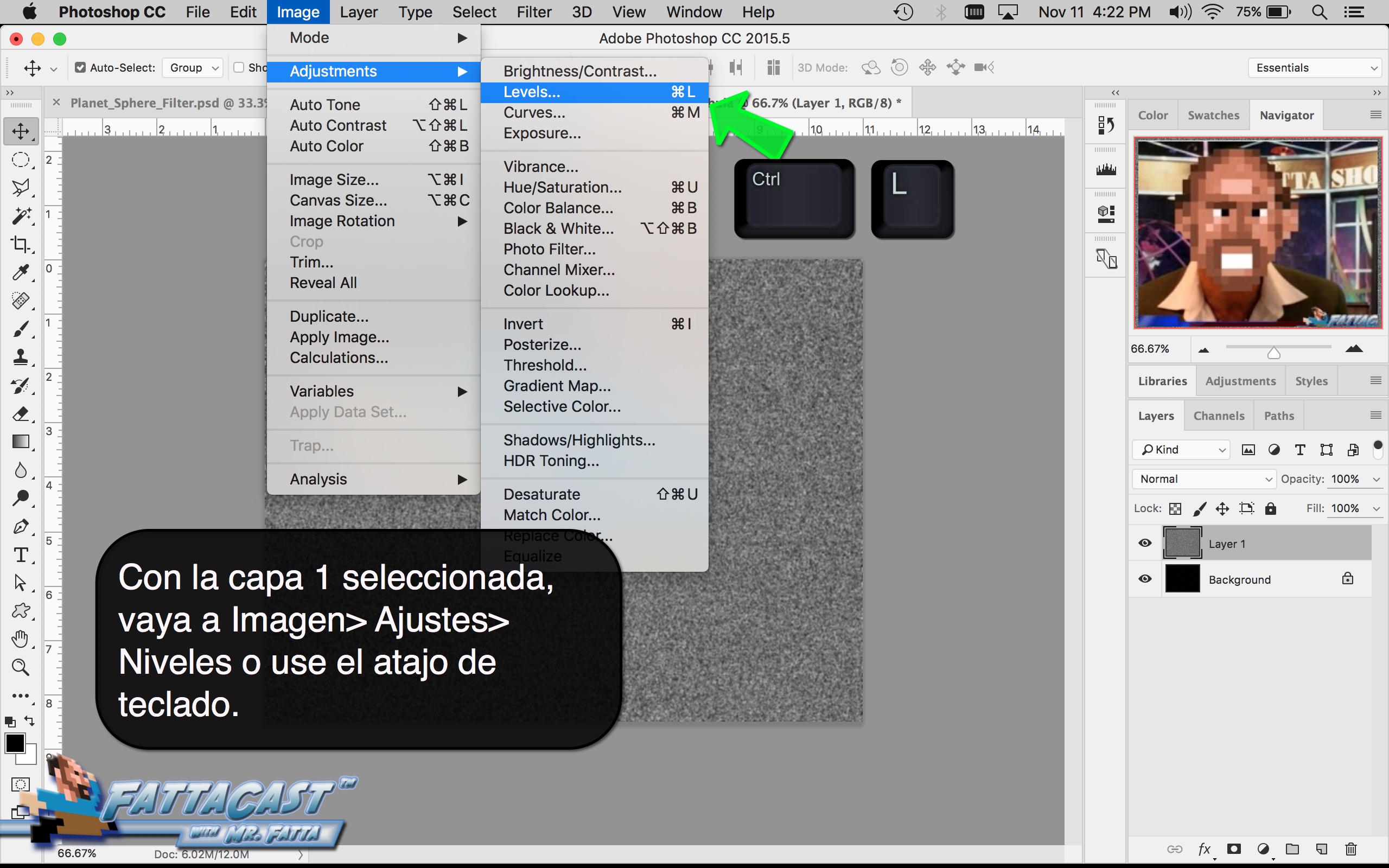
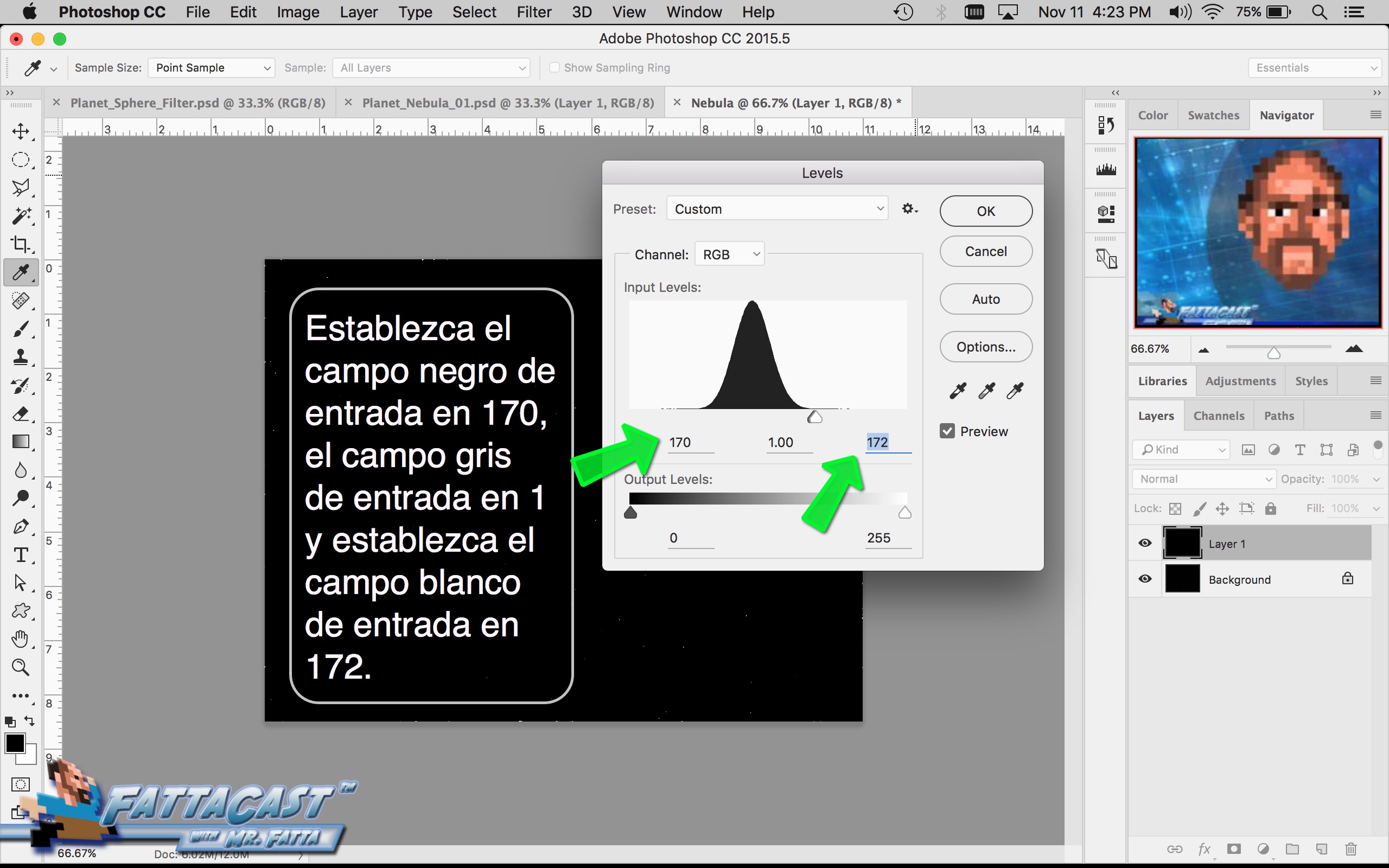
3. I can affect the output light levels in an image by modifying the Image Levels Adjustment.
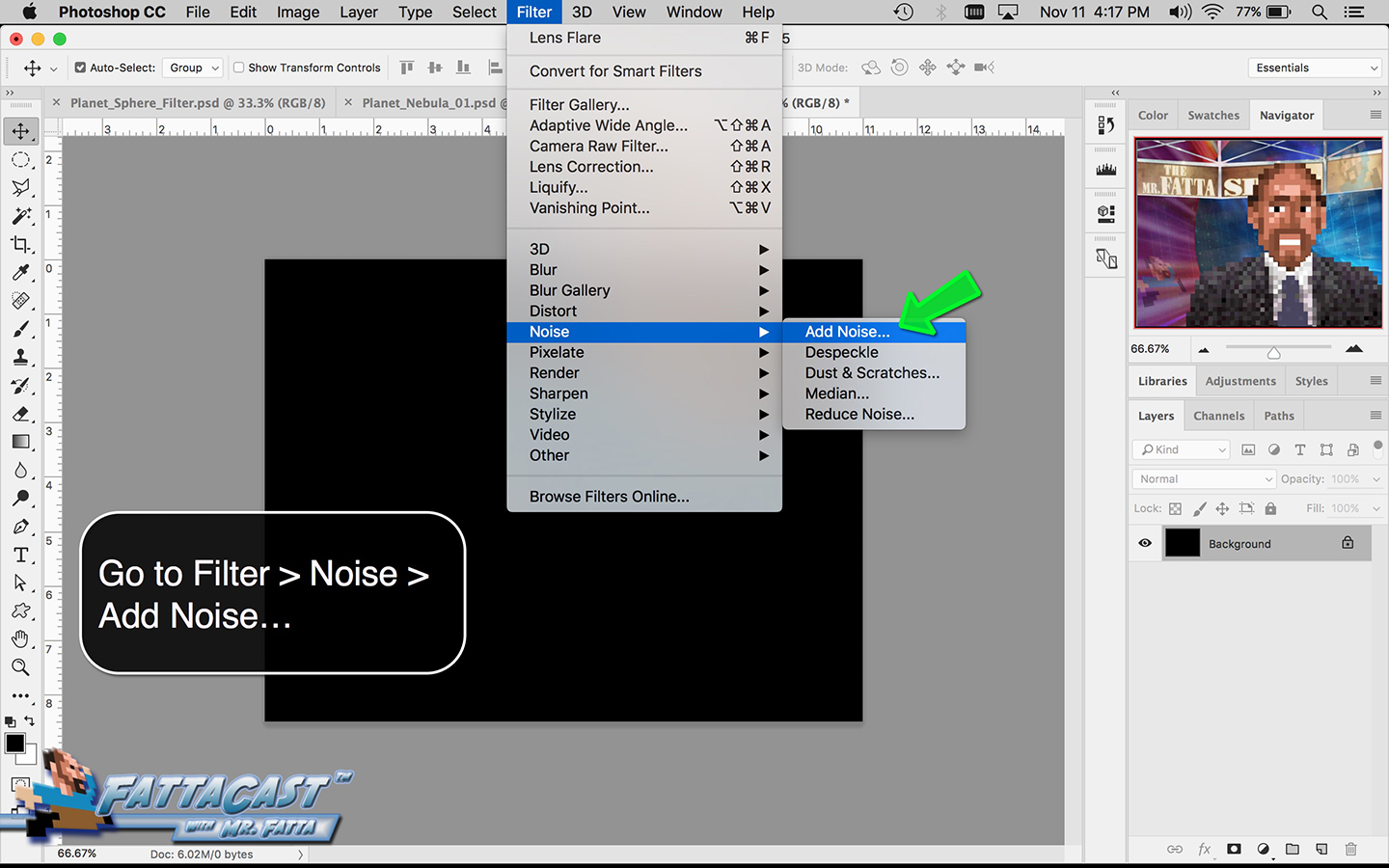
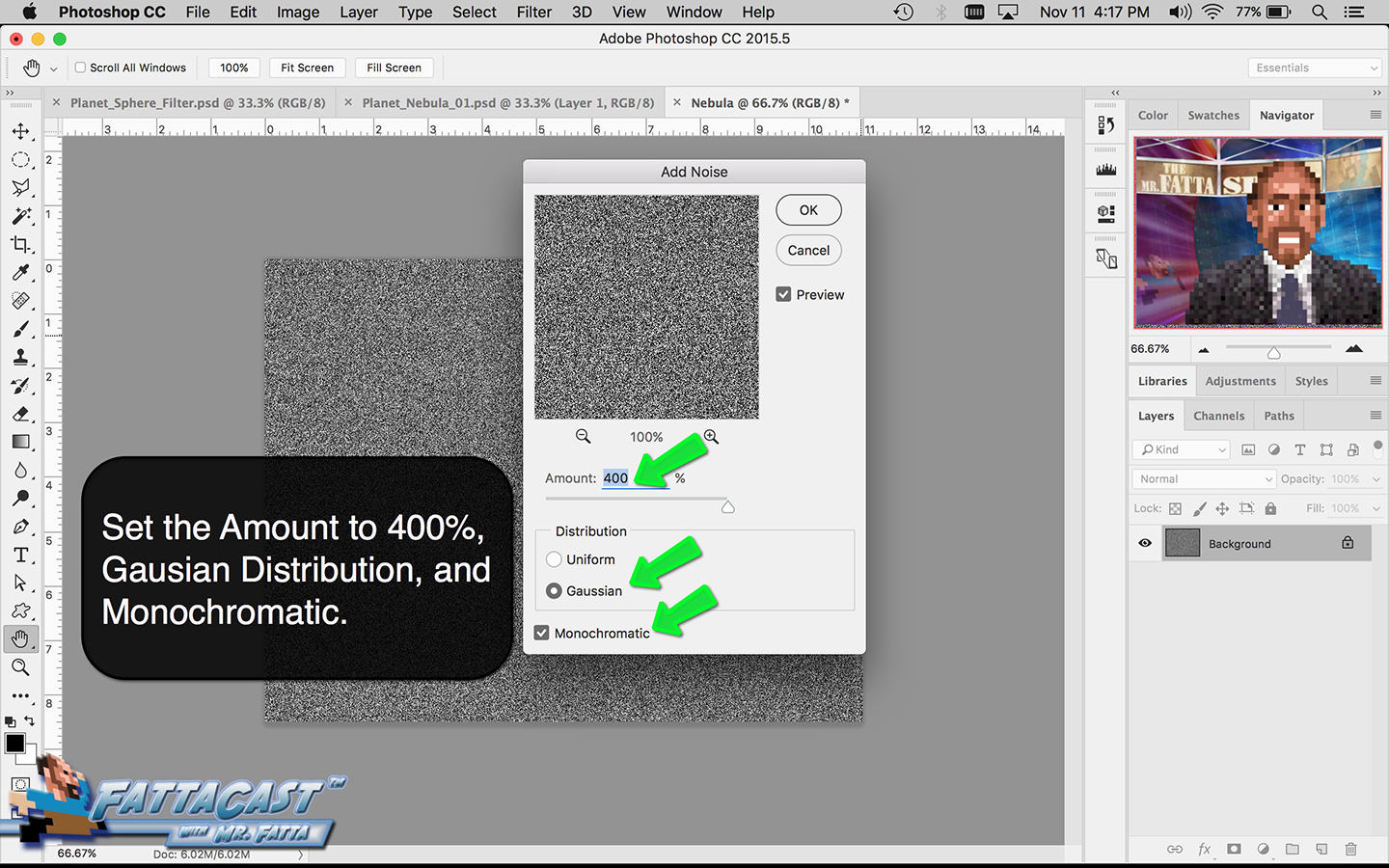
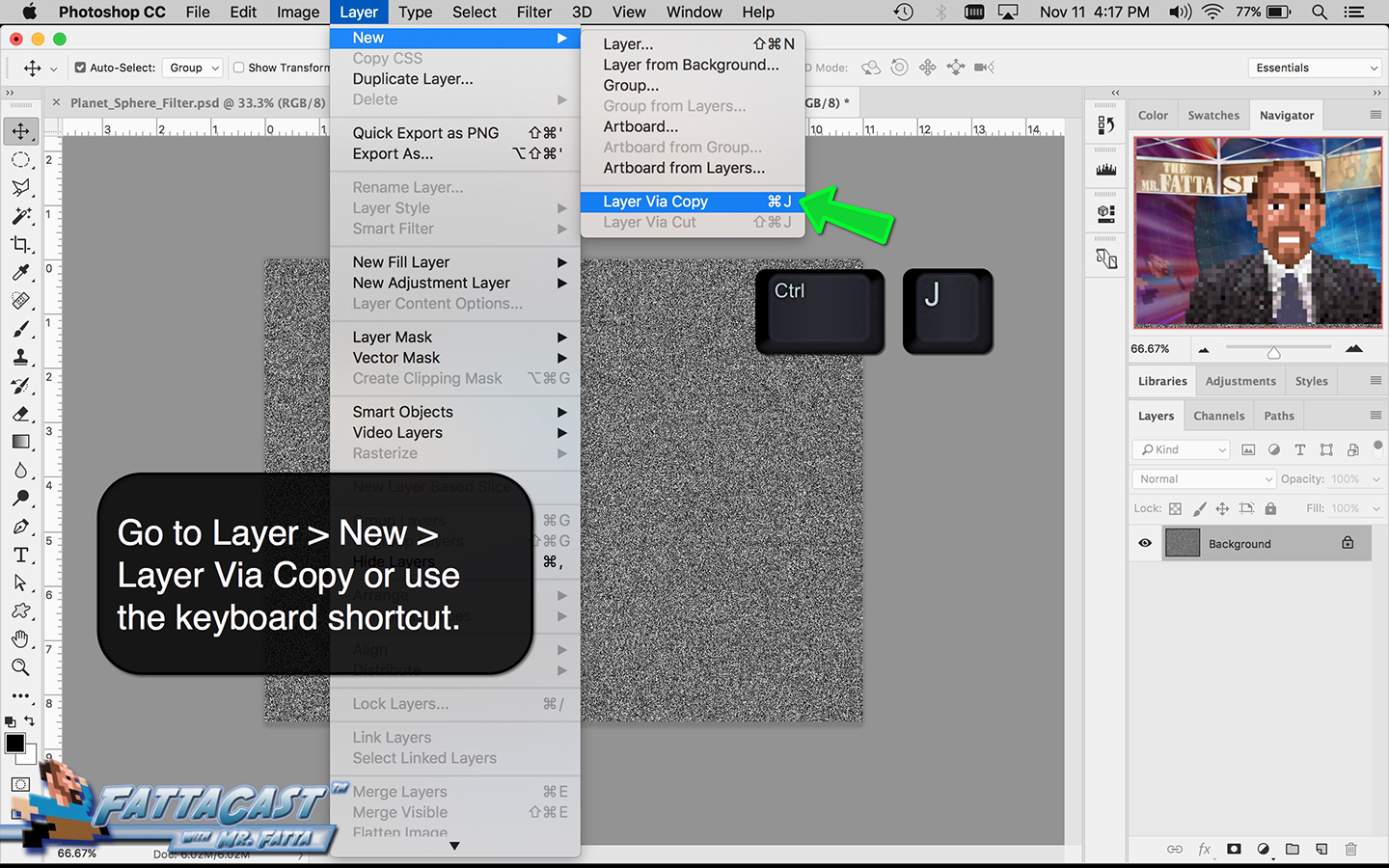
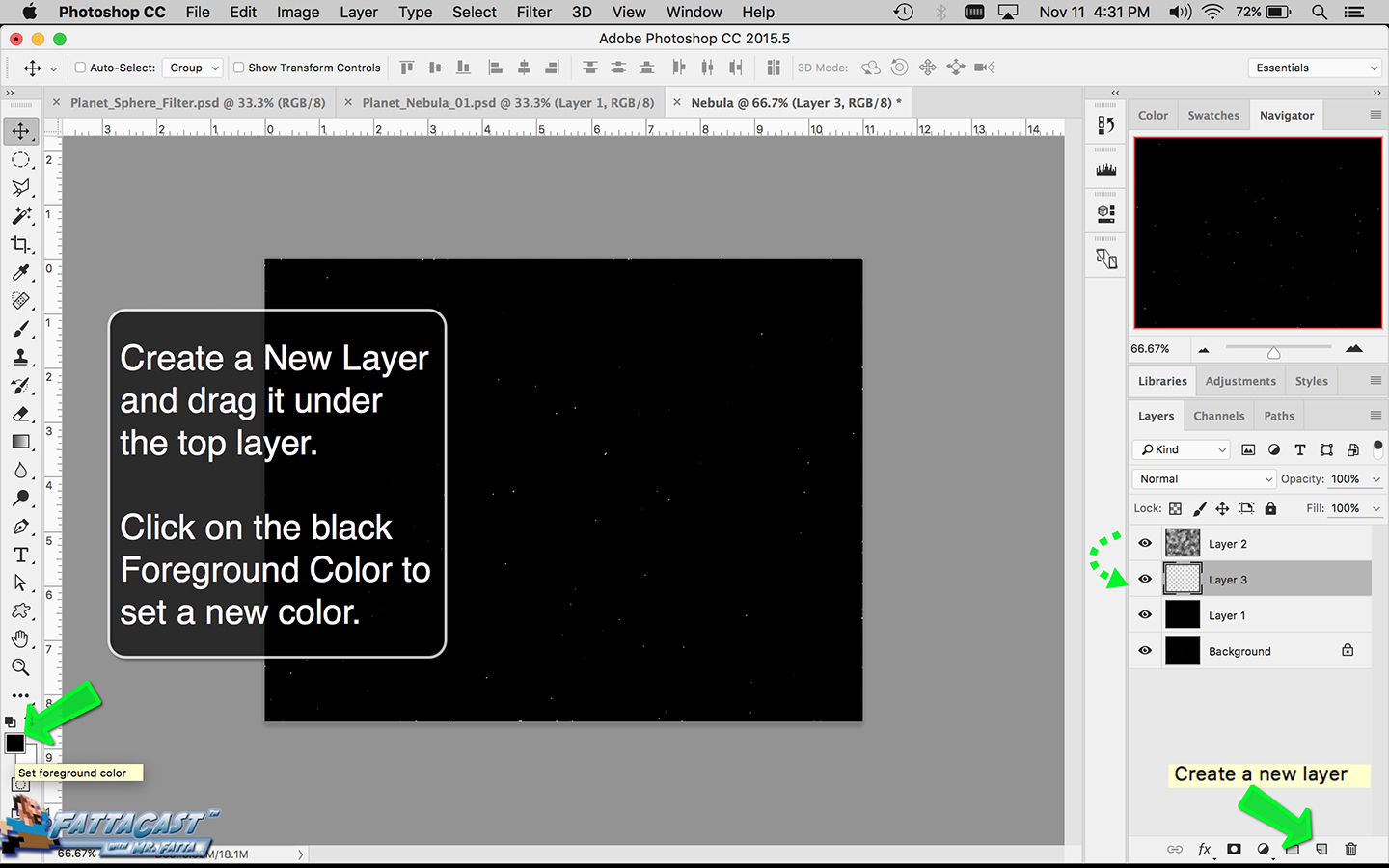
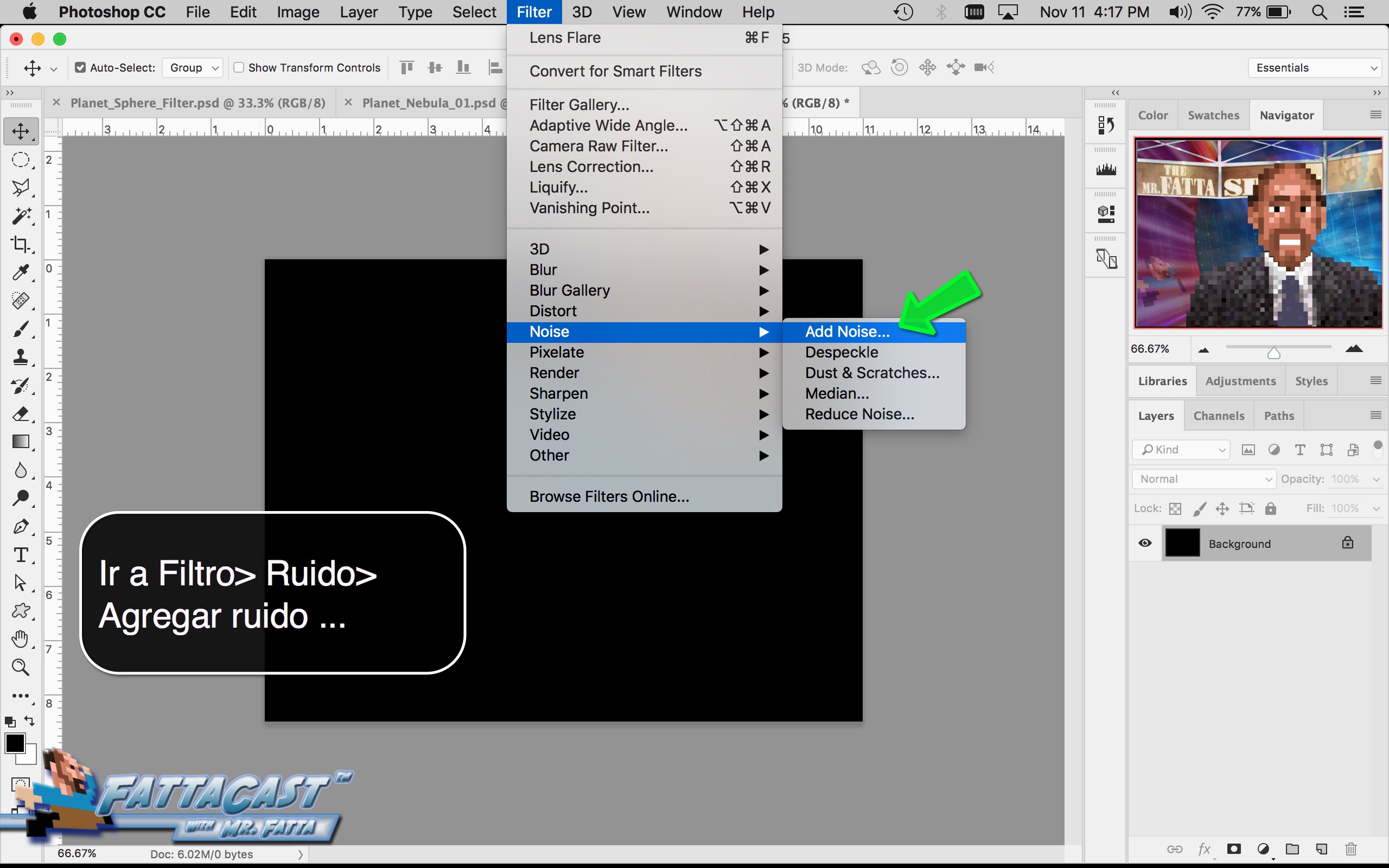
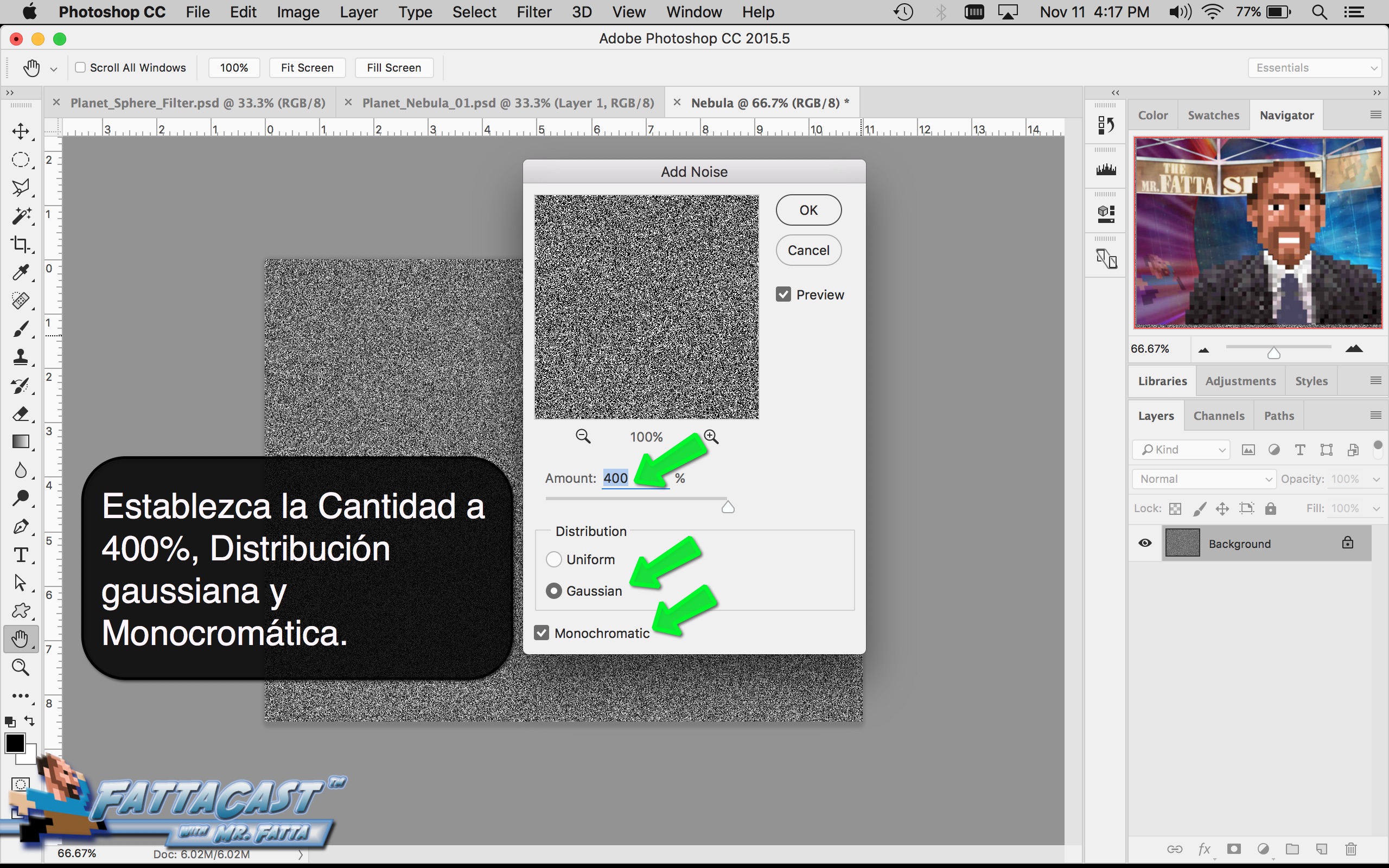
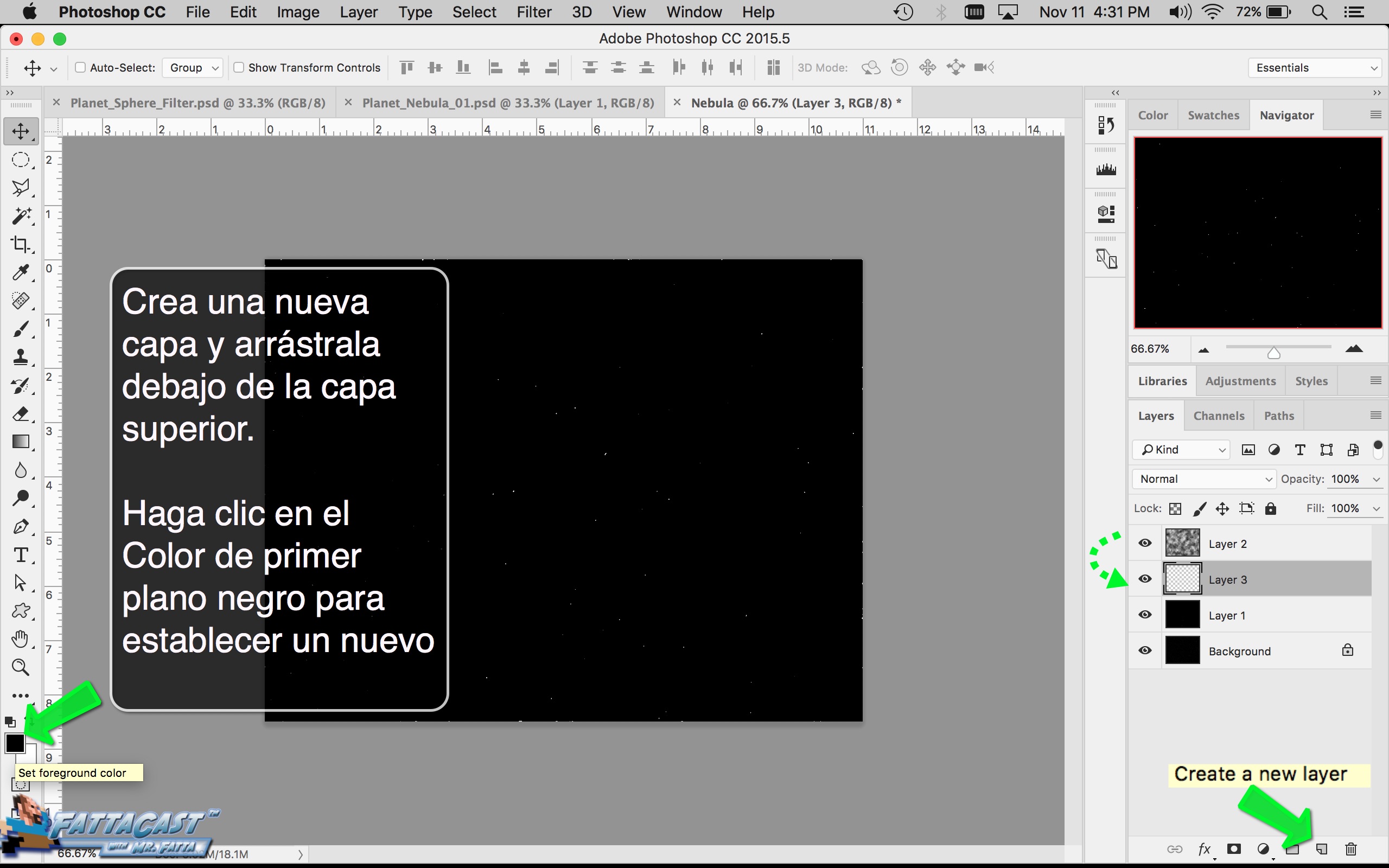
4. I can create a starry sky effect by applying a series of Noise Filters to a black background.
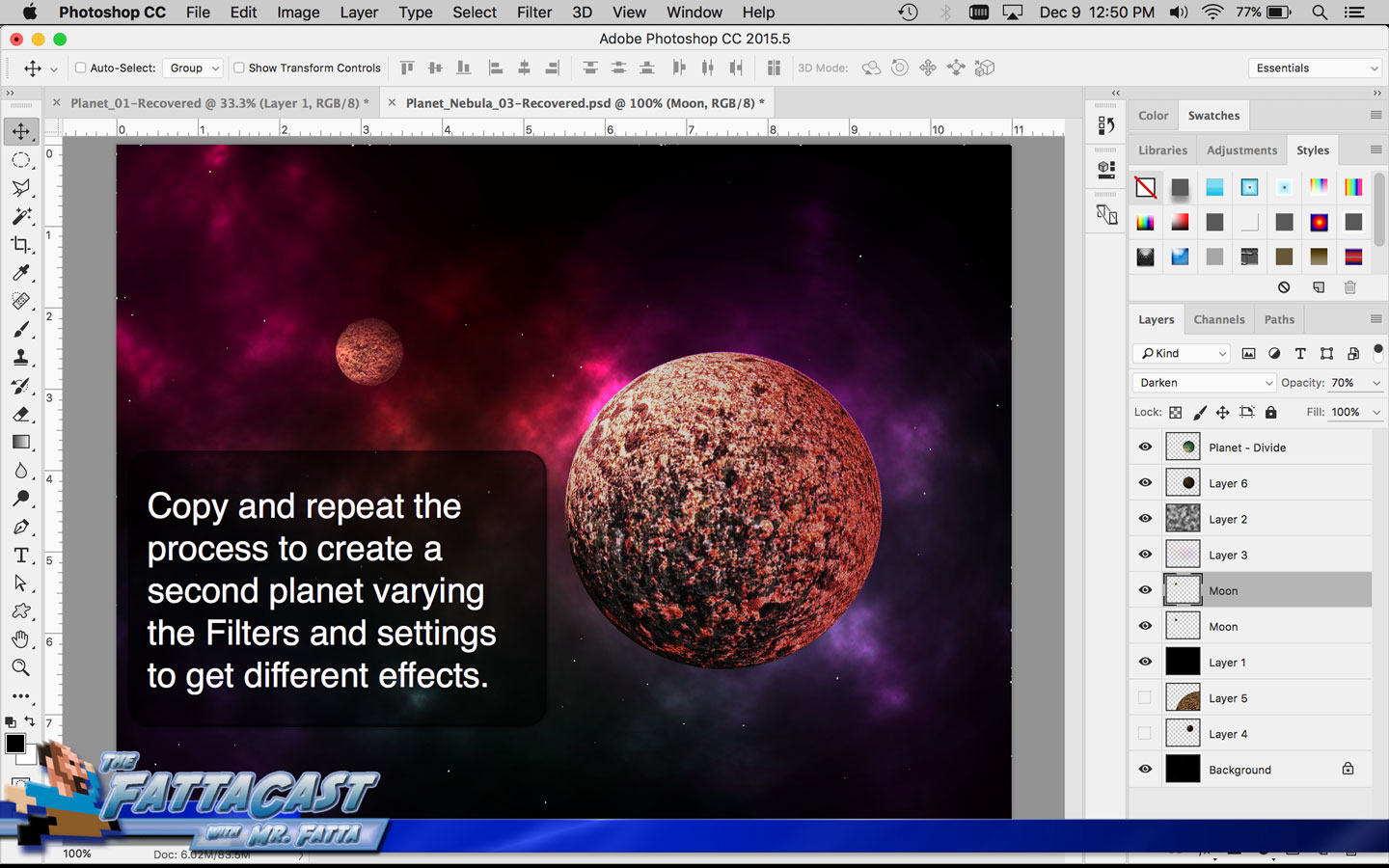
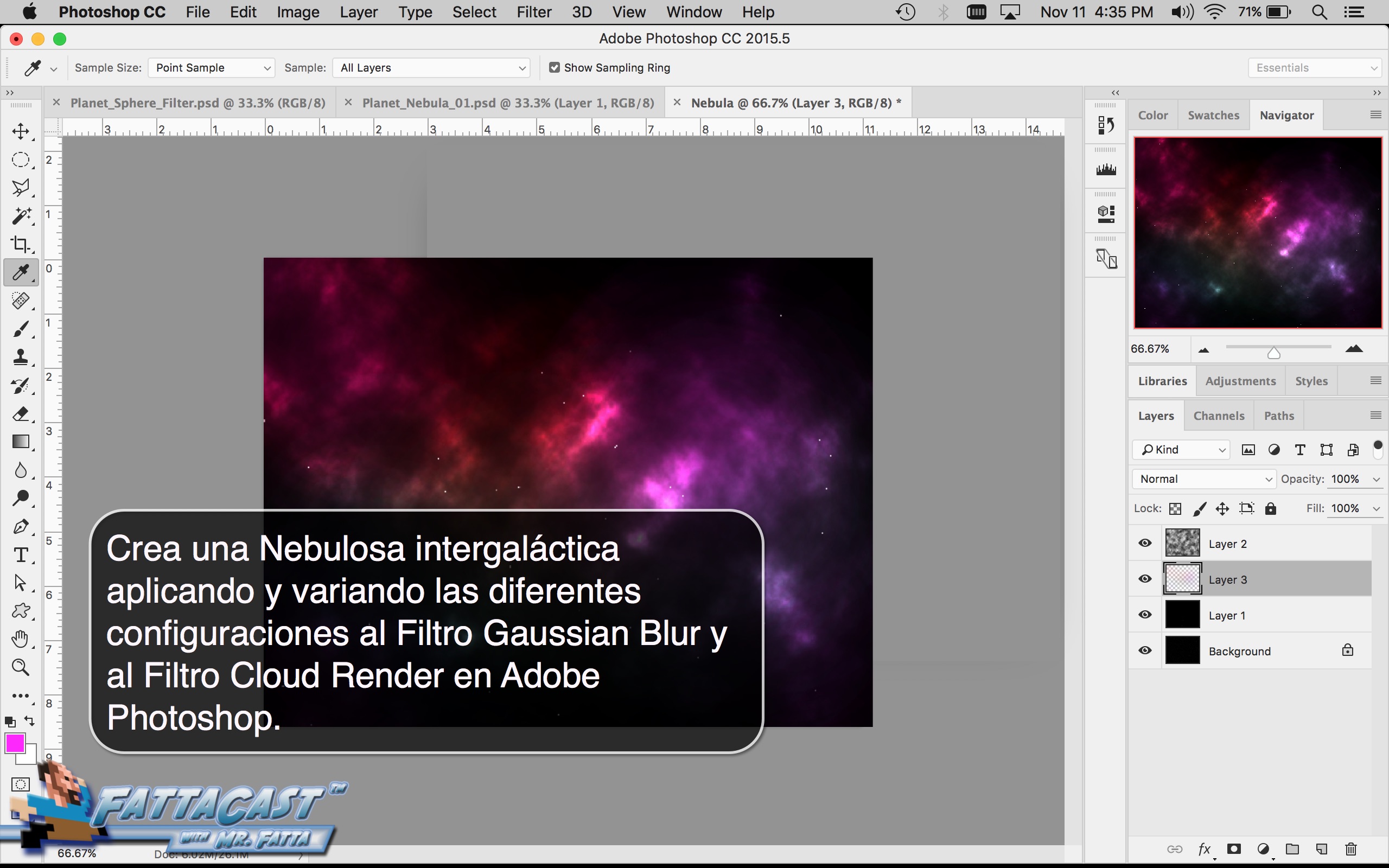
5. I can create an outer space nebulous effect using the a combination of various cloud rendering settings in Adobe Photoshop.
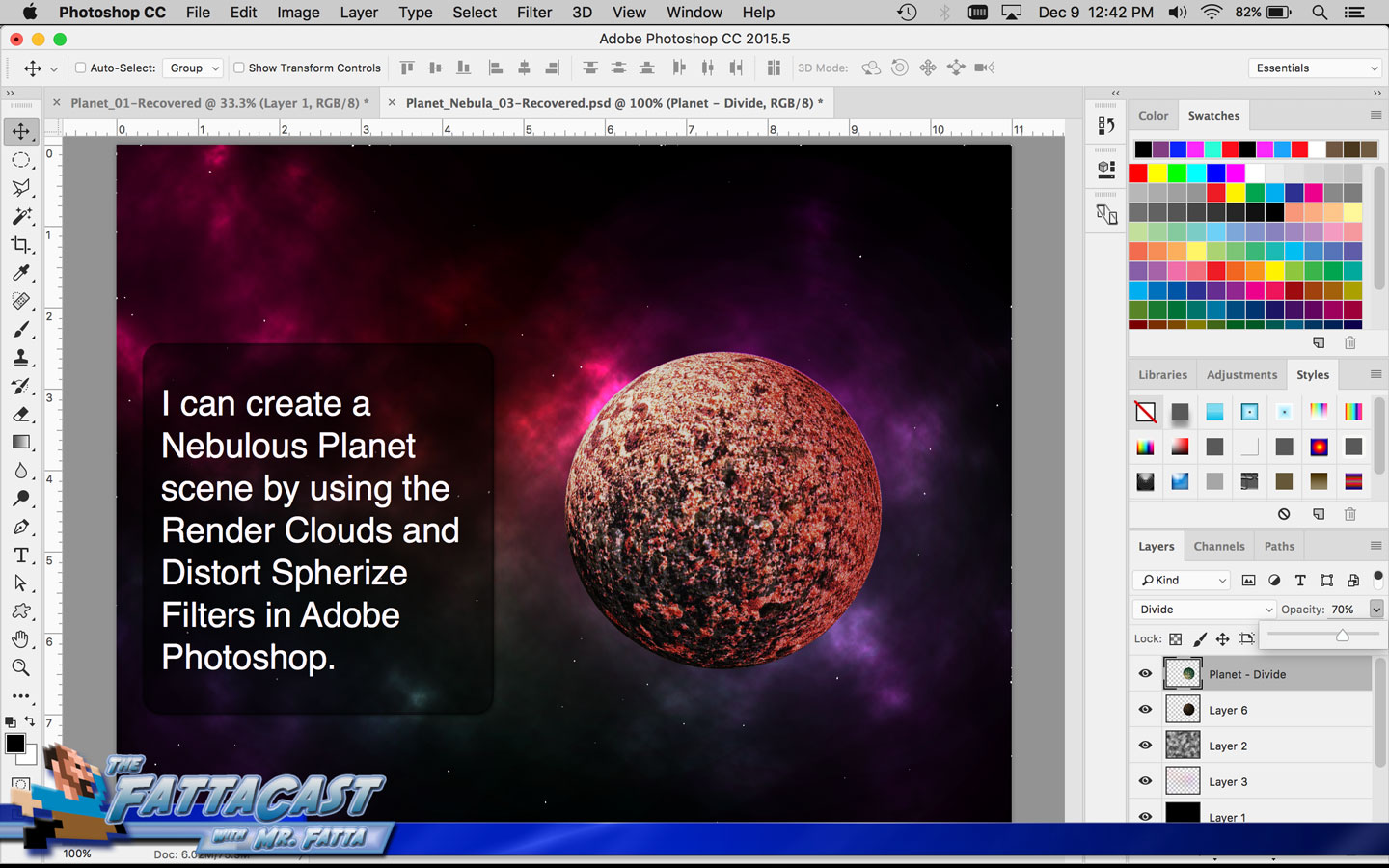
6. I can create an effect of an outer space nebulous using selecting Filter > Render > Clouds and using a combination of cloud rendering settings in Adobe Photoshop.
7. I can create a nebulous space cloud by using the Flamepainter site and setting the Noise adjustments high and painting in circular motions to create a grainy round cloud with a bright cluster at the center.
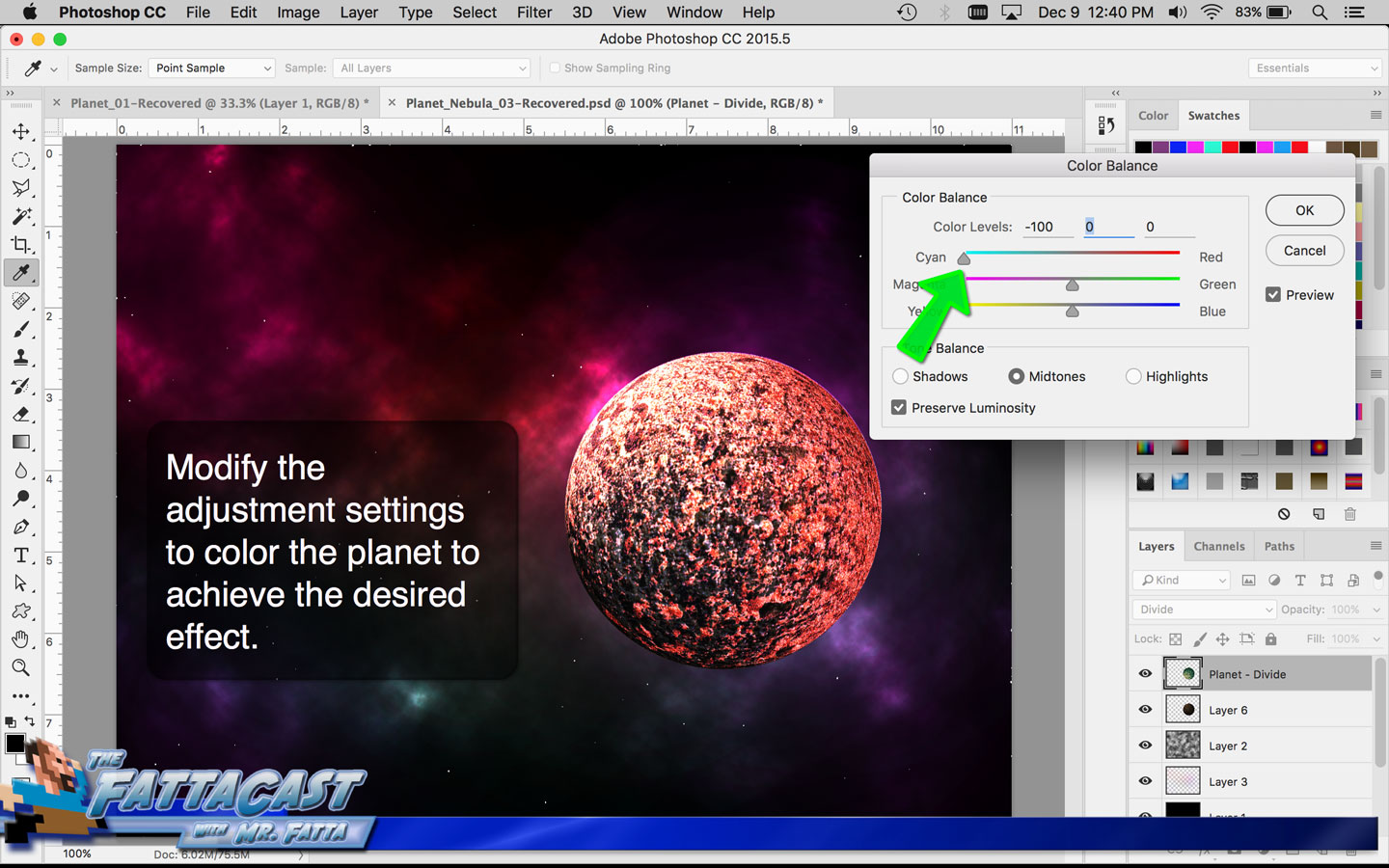
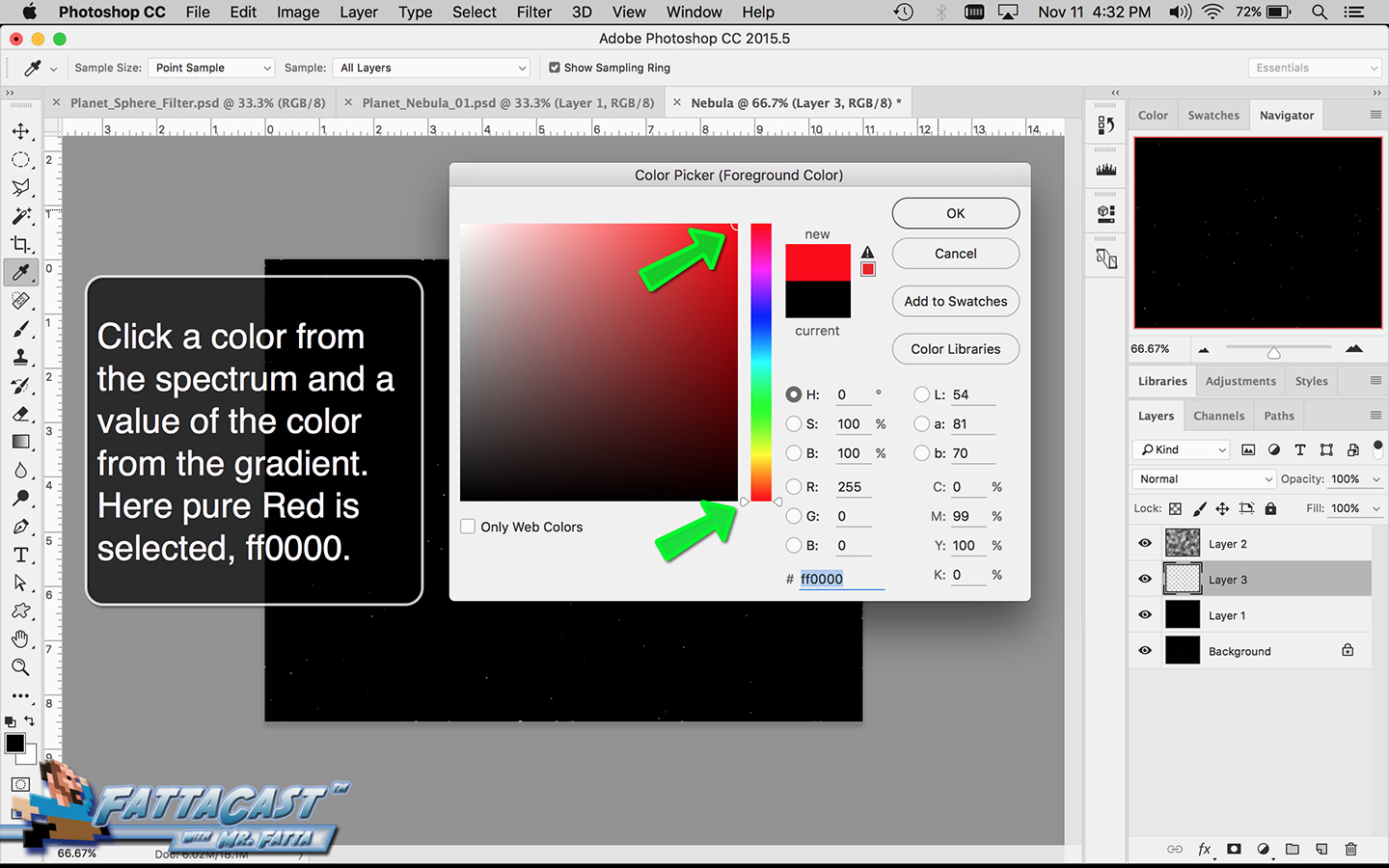
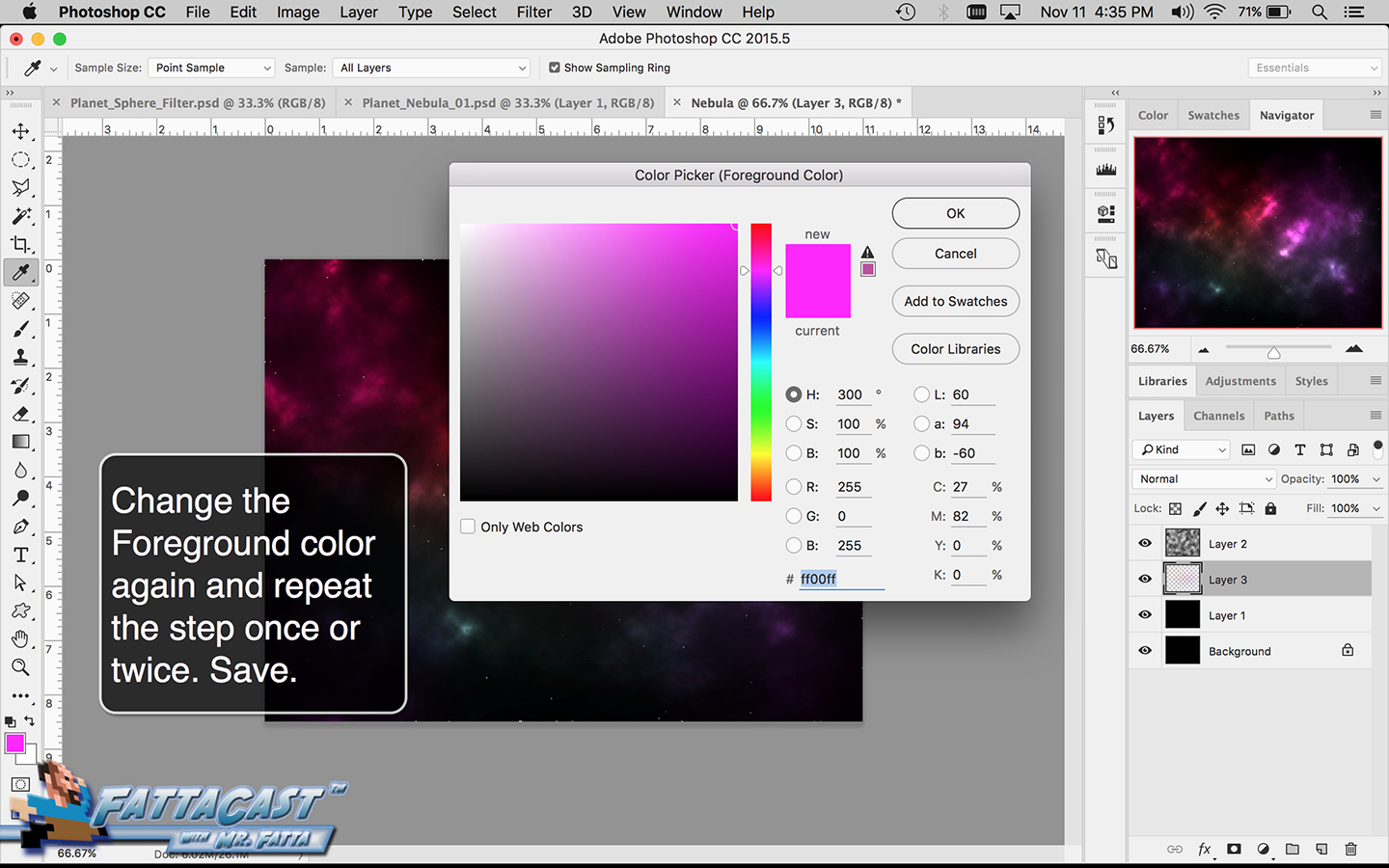
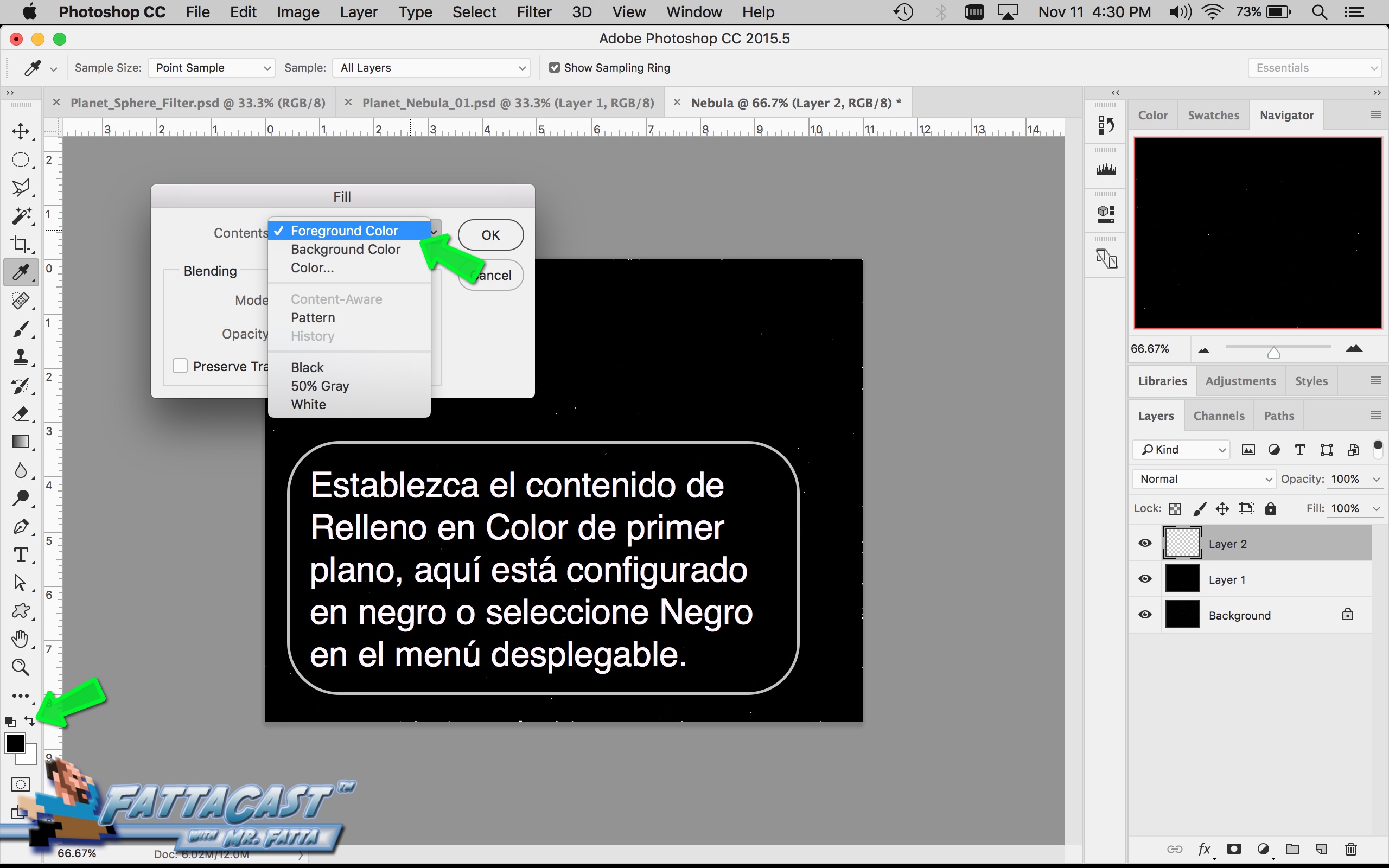
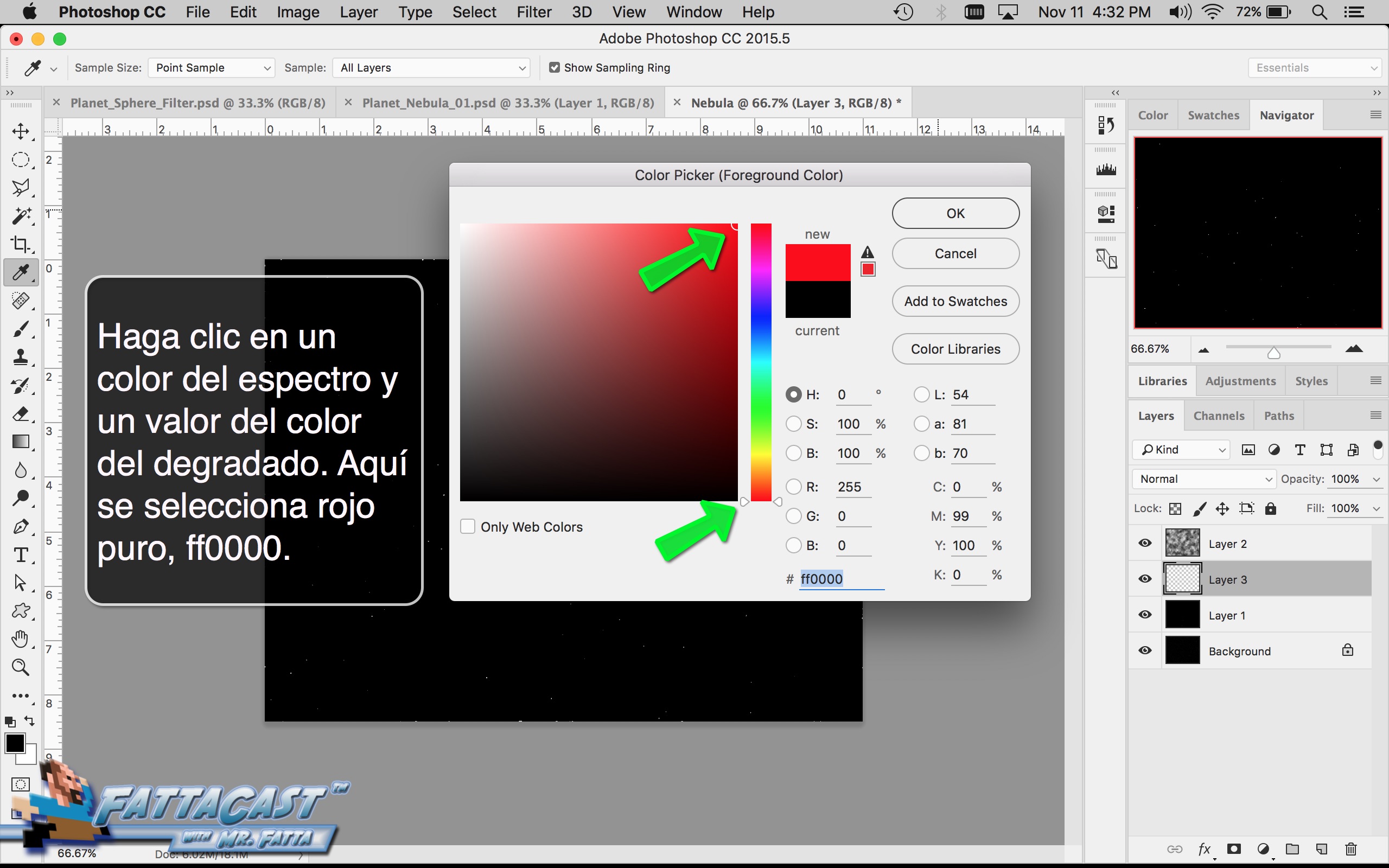
8. I can select and adjust the colors and values and apply them to the cloud effect by using the color picker adjustments in AP.
Creating a Nebula
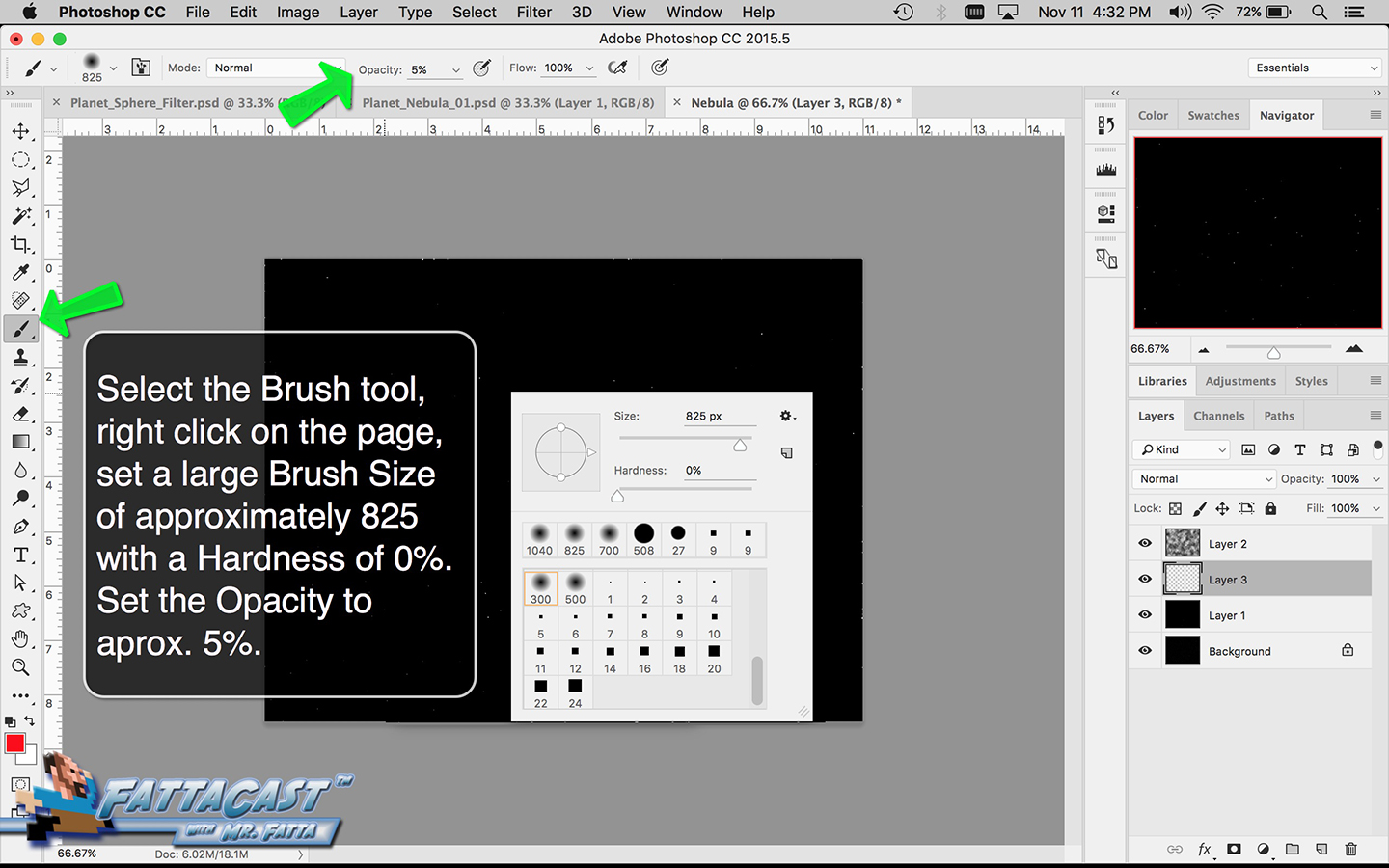
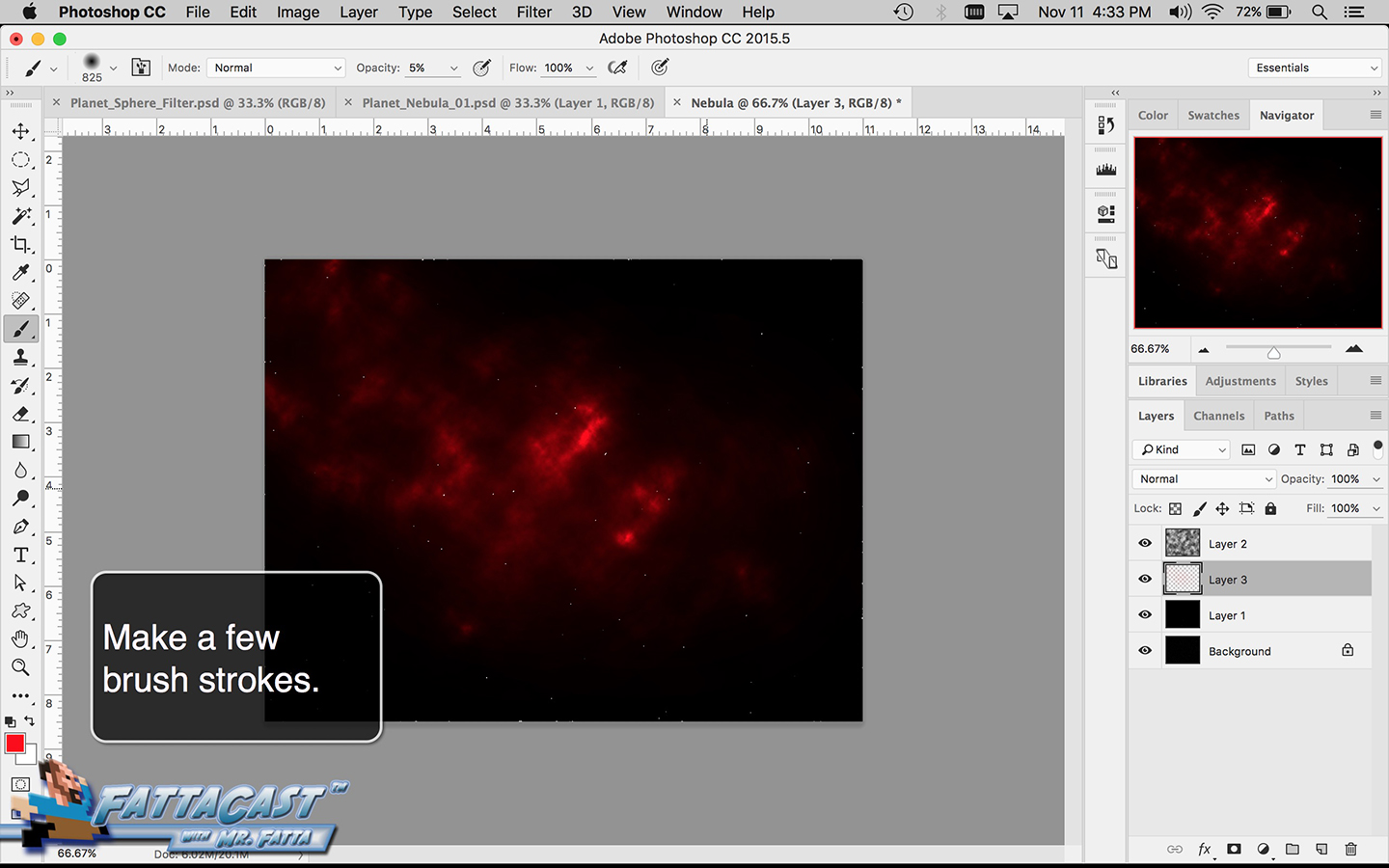
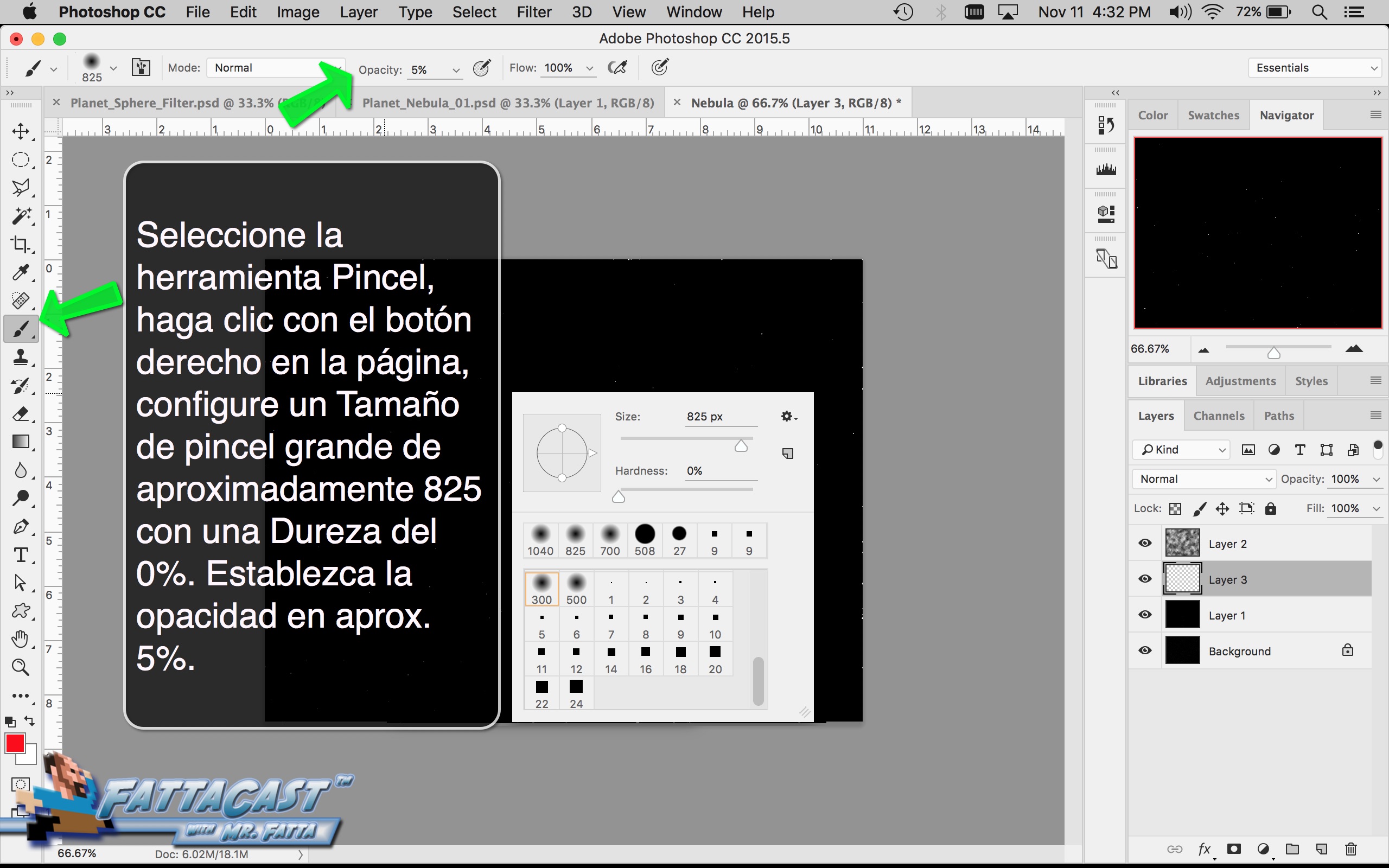
9. I can apply variously styled brush strokes by adjusting the Flow, Opacity, shape size, and Feather to the brush.
10. I can create a starry sky effect by applying a series of Noise Filters to a black background.
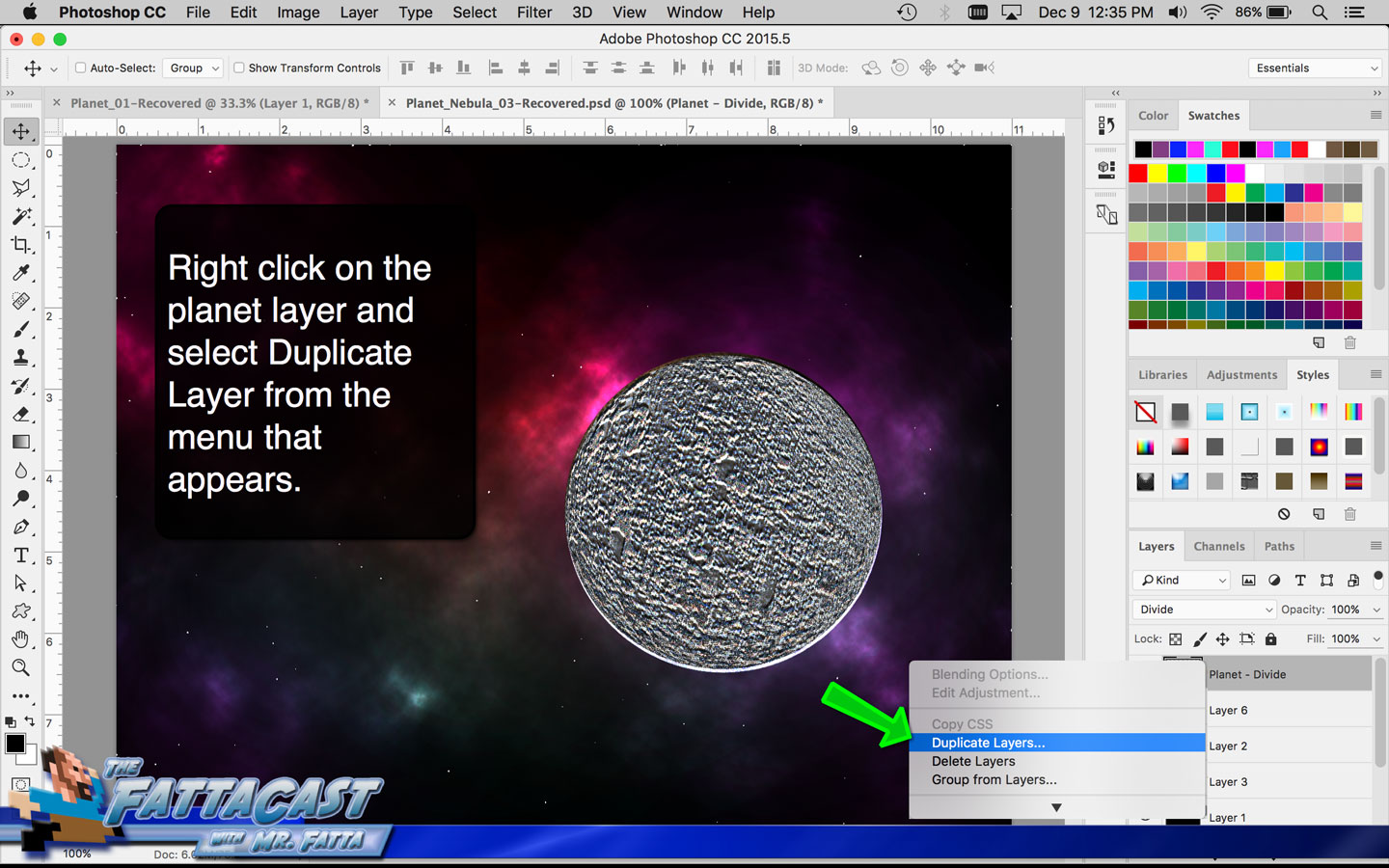
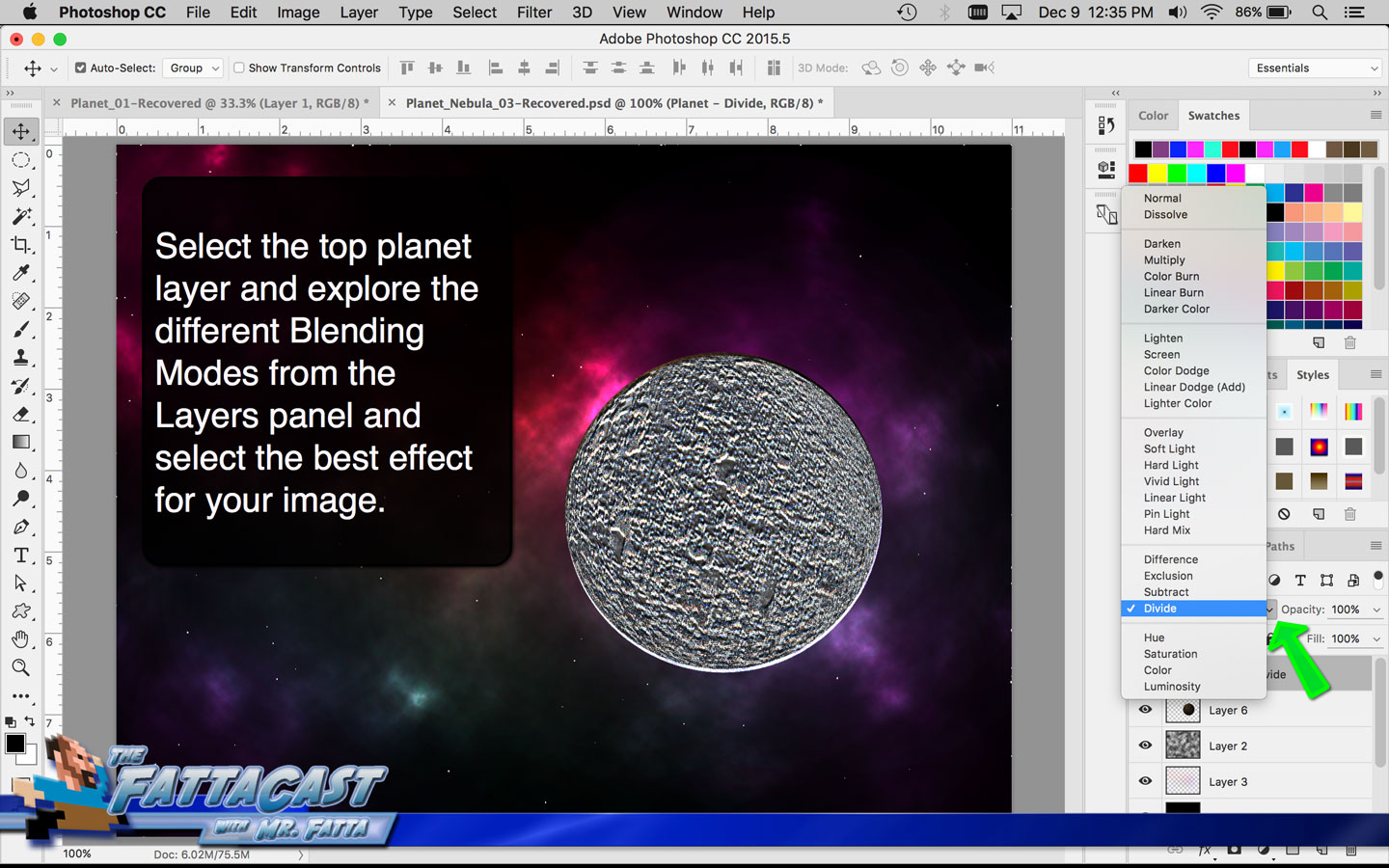
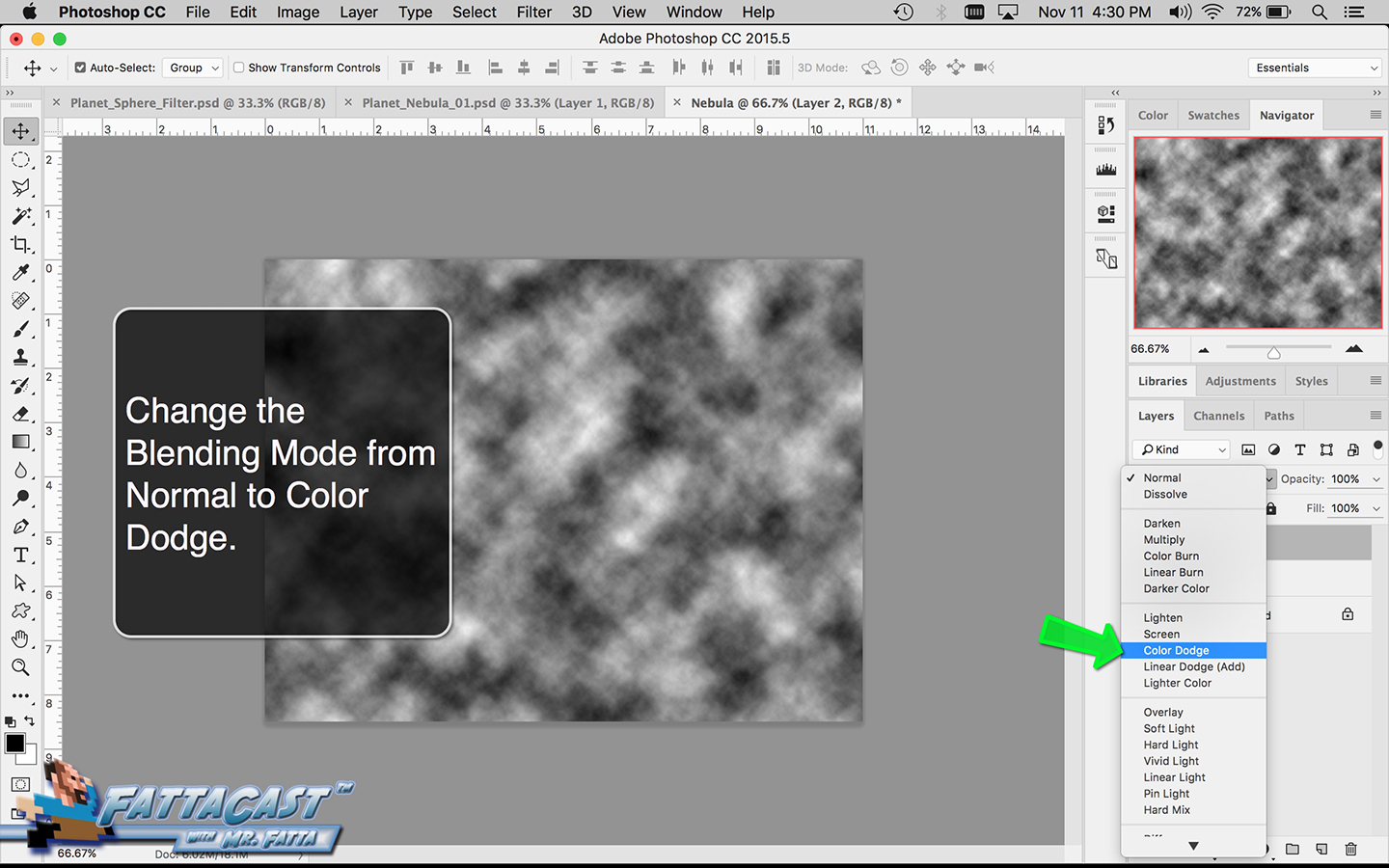
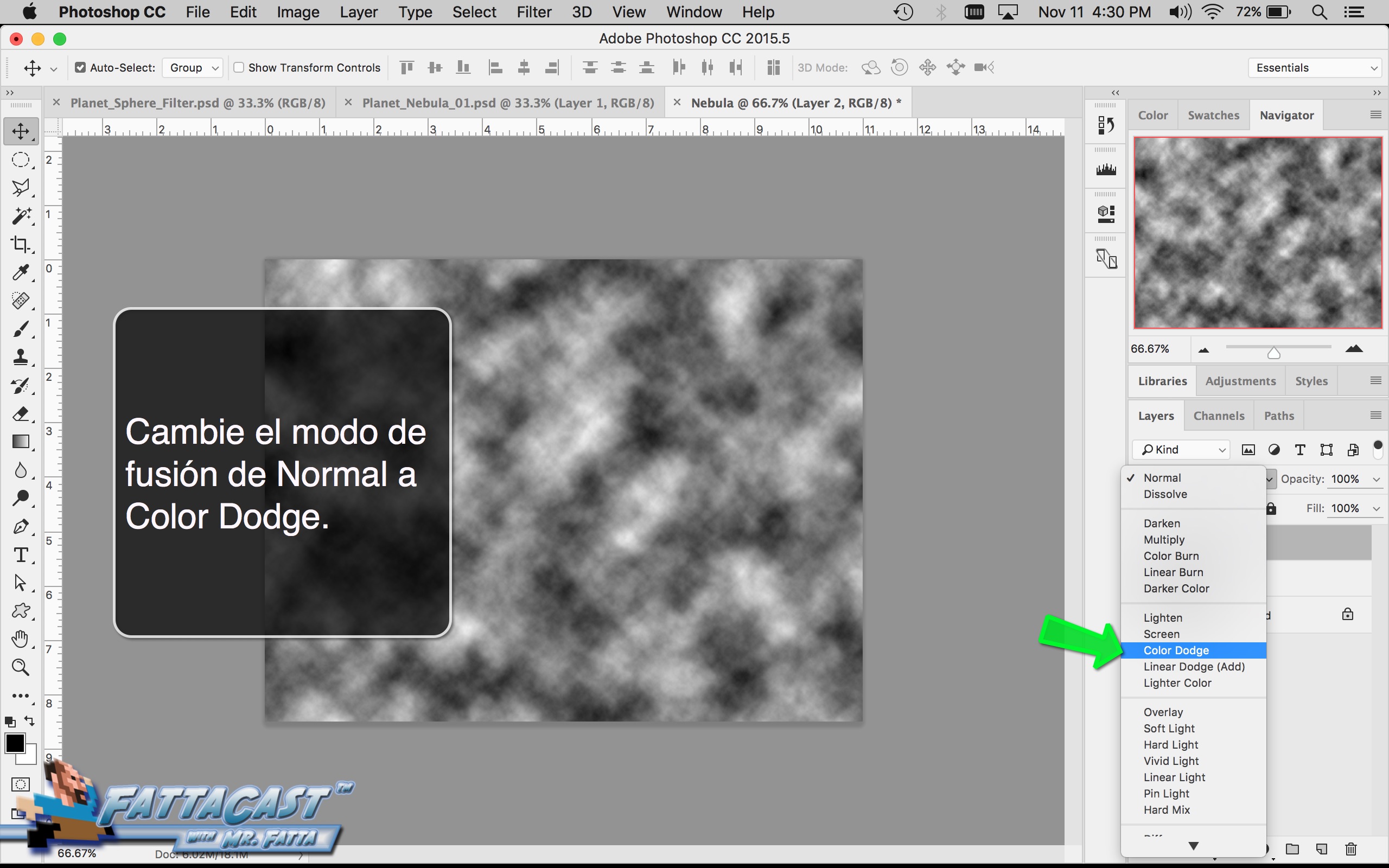
9. I can integrate or combine images by using the various Blending Modes in the Layers panel to get the layers to interact and mix.
10. I can assess, refine, and evaluate my works by comparing them to the components listed in the project rubric and adding attributes that are missing or need more refining.
- I can affect the output light levels in an image by modifying the Image Levels Adjustment.
- I can create a starry sky effect by applying a series of Noise Filters to a black background.
- I can create an outer space nebulous effect using the a combination of various cloud rendering settings in Adobe Photoshop.
- I can select and adjust the colors and values and apply them to the cloud effect by using the color picker adjustments in AP.
- I can apply variously styled brush strokes by adjusting the Flow, Opacity, shape size, and Feather to the brush.
- I can integrate or combine images and effects by using the various Blending Modes in the Layers panel to get the layers to interact.
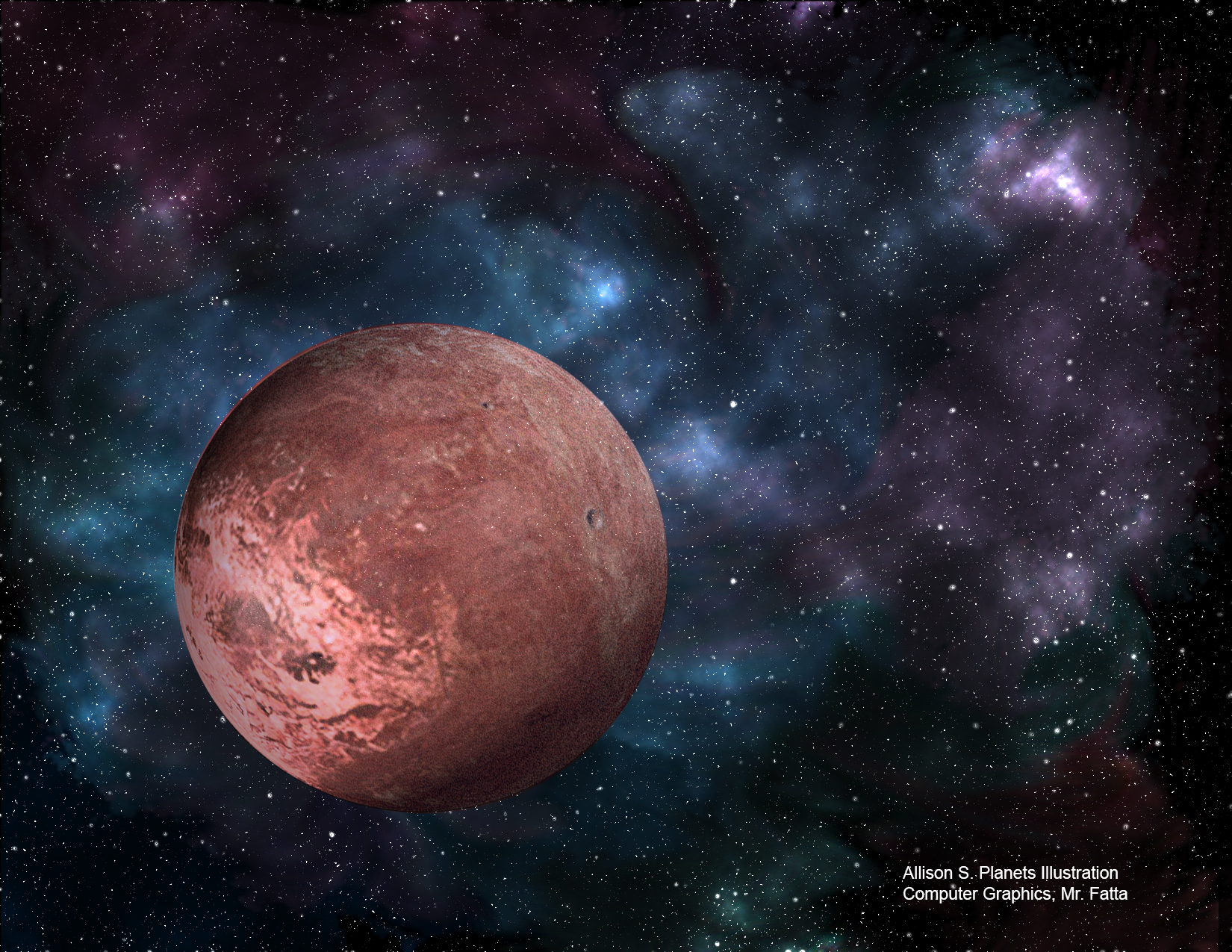
Mars
Often called the red planet due to it’s reddish color, Mars is the fourth planet from the sun. It is classified as a terrestrial planet and its landscape has many unique features. It has a canyon across the center that dwarfs our Grand Canyon here on Earth, and it has the highest mountain in our solar system called Olympus Mons.
Mars Image Link 1 Mars Image Link 2 Mars Image Link 3
Mars is 141,633,260 miles from the sun and is the fourth planet from the sun. Its orbit makes the year 697 days long while the rotation is about the same as Earth, 24 hours and 37 minutes. Temperatures range from -125ºF to 23ºF. Symbolized by the spear and shield, Mars is the Roman god of war.
.
Jupiter
Jupiter is one of the classical planets visible by the ancients and is named for the Roman god Jupiter. It is the fifth planet from the sun and is most noted for a centuries old mega-storm that swirls along its lower quarter. Jupiter is a gas giant comprised of mostly hydrogen and lacks a terrestrial surface. The outer atmosphere consists if latitudinal striations of turbulent colored bands resulting from the interacting boundaries of the numerous storms on the planet.
Jupiter Image Link 1 Jupiter Image Link 2 Jupiter Image Link 3
Construct the basic form of the planet utilizing the gradient tool. Paste a copy. Analyze the striations in the atmosphere, arrange a series of colors in the linear gradient window strip in the order they appear in the photo. Combine the atmosphere and the form by adjusting the Transparency setting, to create an atmospheric overlay.

Saturn
Named after the Roman god of agriculture Saturn has been known since prehistoric times. Saturn is the Roman equivalent to the ancient Greeks’ god Cronus. As the sixth planet from the Sun Saturn is a gas giant that has a pale yellow color from ammonia crystals in the atmosphere. It has a prominent series of rings consisting of nine main rings comprised of mostly ice.
Saturn Image Link 1 Saturn Image Link 2 Saturn Image Link 3
Venus
Video Milky Way and Andromeda
 Video Sol
Video Sol
Creating a Nebula
 Mr. Photo Tut Presents:
Mr. Photo Tut Presents:
Photoshop Tutorial: How To Make A Nebula
Video tutorial showing how to create a space nebula.
Sample Student Works
Student Saturn Art Link Student Kepler Art Link Student Mars Art Link
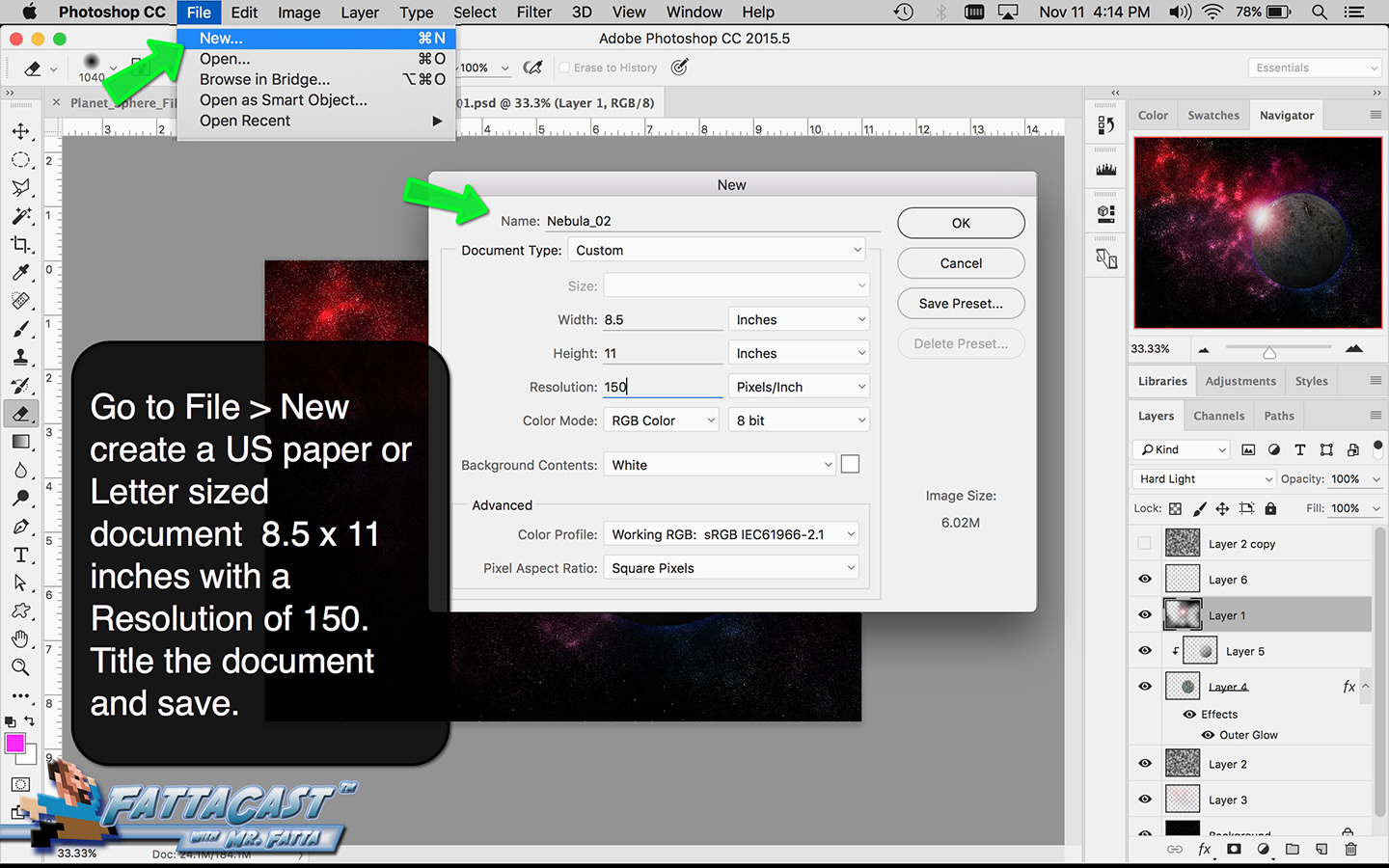
1. Create a third planet of your own in Photoshop
2. Compose a two or three paragraph description of Venus that includes a general description, statistical data, and mythological associations.
Project Rubric
Learning Target: I can assess and refine my work by comparing it to the items listed on the rubric and comparing it to other artist’s work as well as real images from space.
SpaceX – Falcon 9 – Liftoff & Landing
Elon Musk, founder of SapceX made aerospace history when the Falcon 9 took off to the edges of space, delivering the second stage rocket into orbit, and landing upright on the very same launch pad. Here is Mr. Fatta’s tribute to his favorite super-villain.
Writing Task
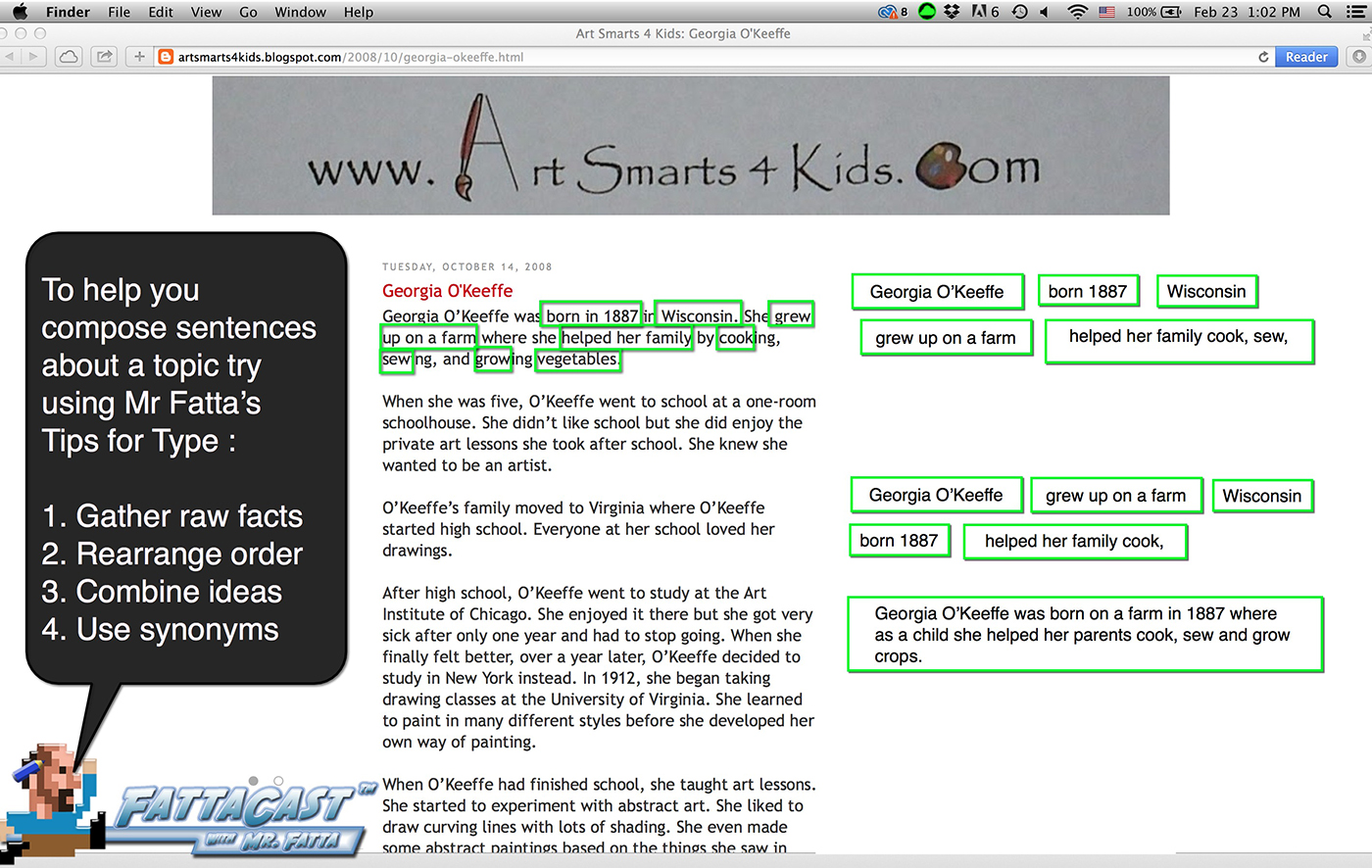
Use the links below to gather facts and stories about the planets in your illustrations. Create a slide in your Google Portfolio that addresses the following questions, work to compose complete sentences from the information you gather, exemplar work would feature the research in at least 2 complete paragraphs. Copy and Paste the “Questions to Answer” found below onto your new Google Document and respond to each question posed.
- What are the parts or distinguishing features of the planet?
- Is the planet a gas giant or a terrestrial planet?
- What position is it from the sun?
- How many moons does it have?
- How far is it from the sun, how long is a year, how long is a day, what is gravity like there?
- What is the climate or atmosphere like, what is the temperature range of the planet?
- What other distinguishing facts can you state about the planet?
- What is the Greek or Roman god that the planet is named from?
- Which of the planets did the ancient Greek and Romans know about?
- How did they know the planets where different than stars, why did they call them “planets”?
Useful Links
National Geographic – Solar System The best interactive site yet for finding great images and interesting features.
Planetary Mythology By Peter Grego. A brief overview of the mythologies associated with the five wanderers, planets the ancients knew.
The Solar System and the Gods By Jo Edkins. A brief overview of the mythologies associated with the planets with links detailing each Roman god/goddess as well their assignment to the days of the week and the origins of the names of the months.
Mythology of the Planets Universe Today. A comprehensive overview of the planet’s mythologies. These links cover the meaning of the symbols for Mercury, Venus, Mars, Saturn, and Jupiter.
Mythological Symbols Each planet has a mythological significance associated with it. The Greeks and Romans were most noted for the different gods they attributed to the planets. Click on the link above to find out more about the myths.
Solar System Symbols, NASA. Brief description of the planet’s symbol and its meaning.
BrainPop-Planets Login to BrainPop with the user name: eastramapo and password: learn. View the video of the solar system, and view the various videos of the planets you are thinking of working on.
Our Solar System A beautiful movie from NASA of our solar system and the layers around it within the Milky Way. Great size!
Slide Show of “Mythology of Mars” A slide show by Mr. Fatta about the mythology of Mars and some basic facts.
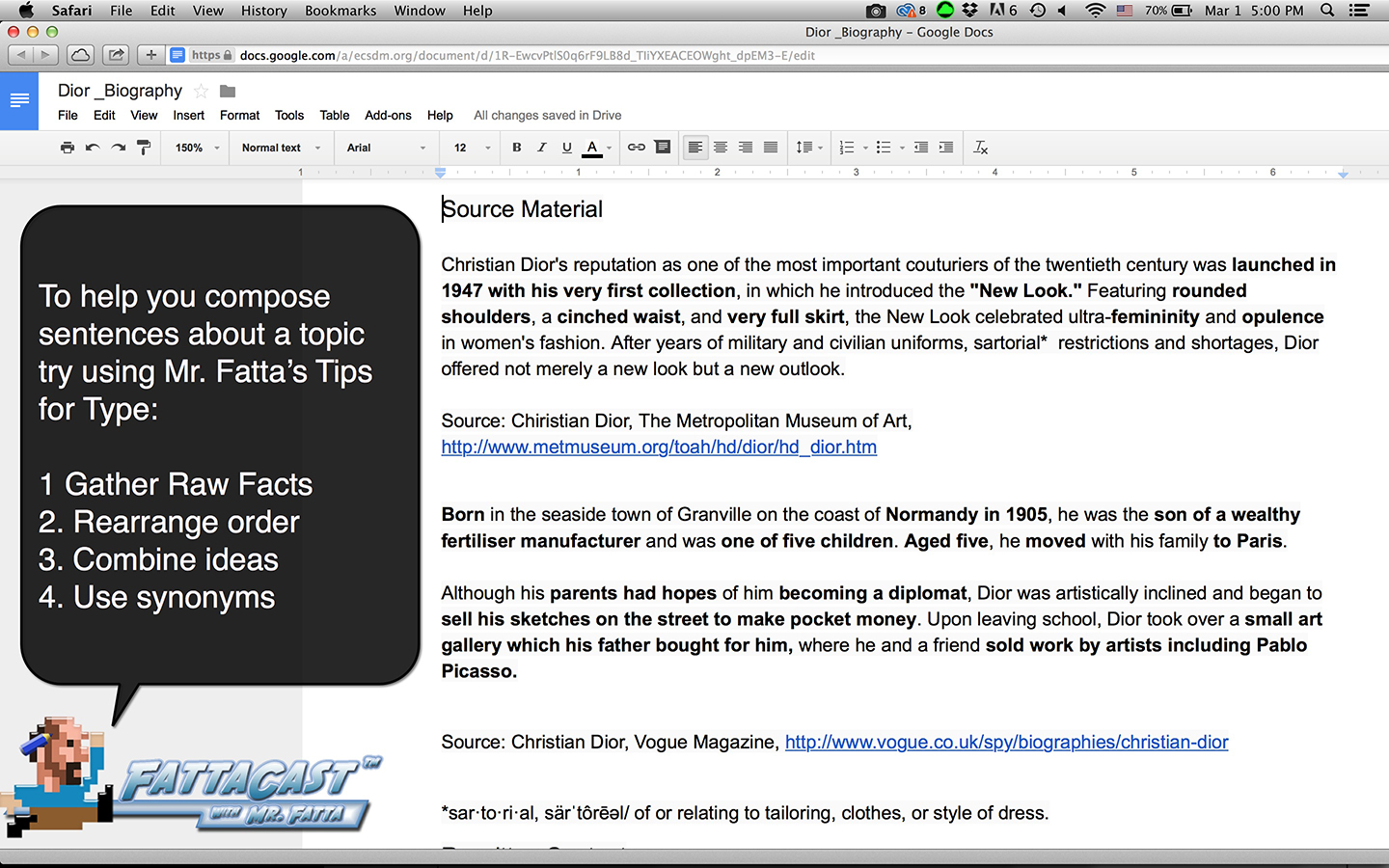
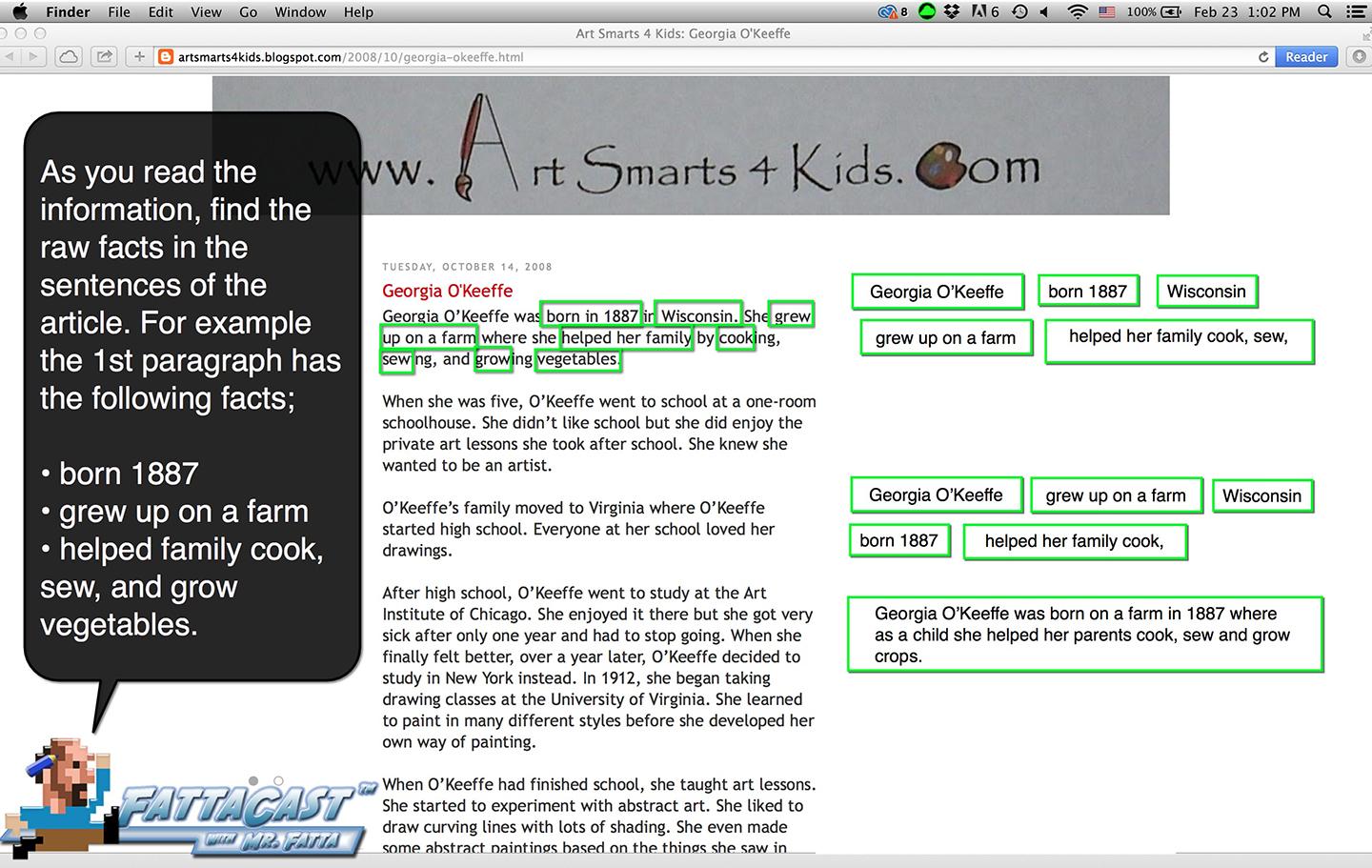
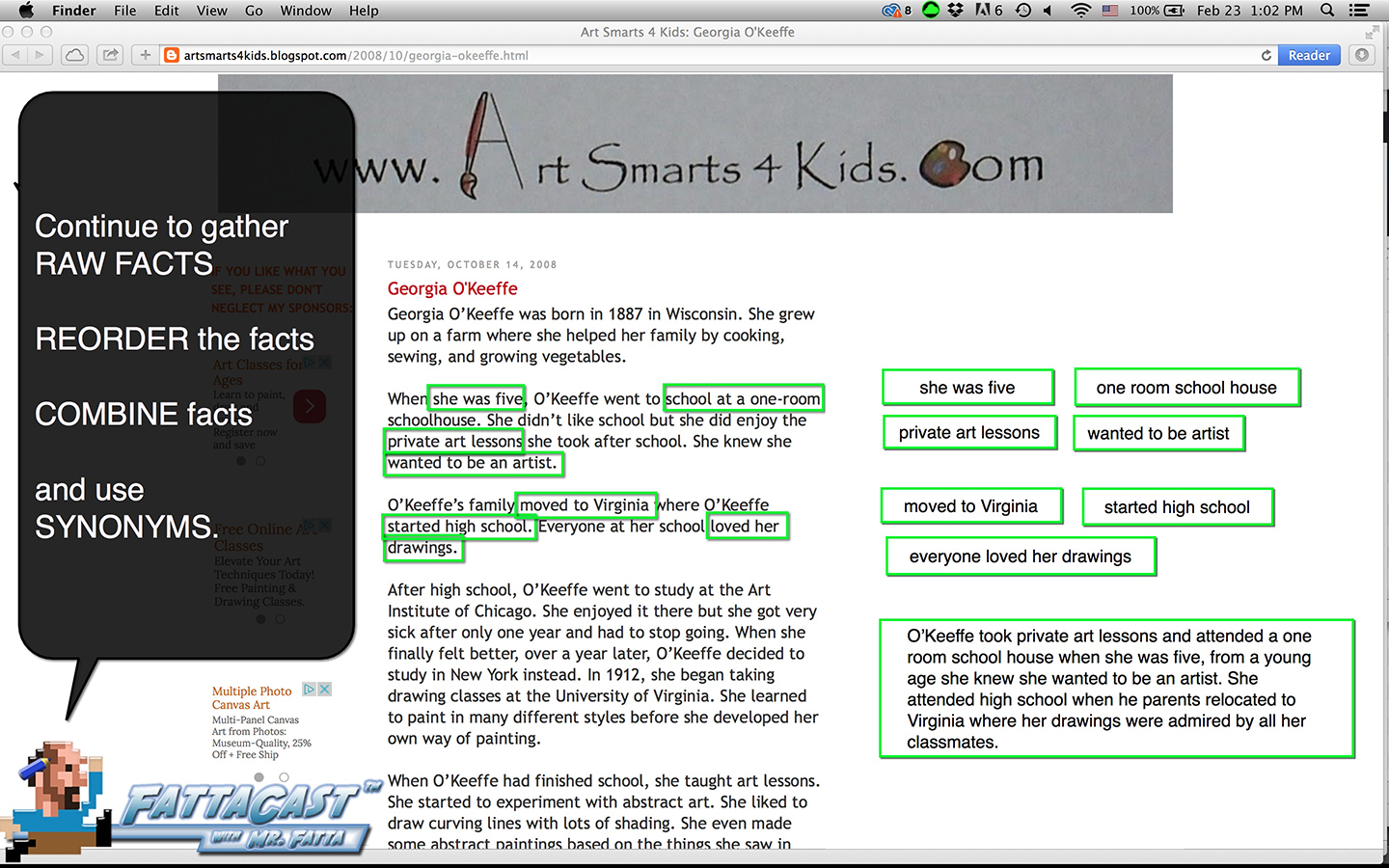
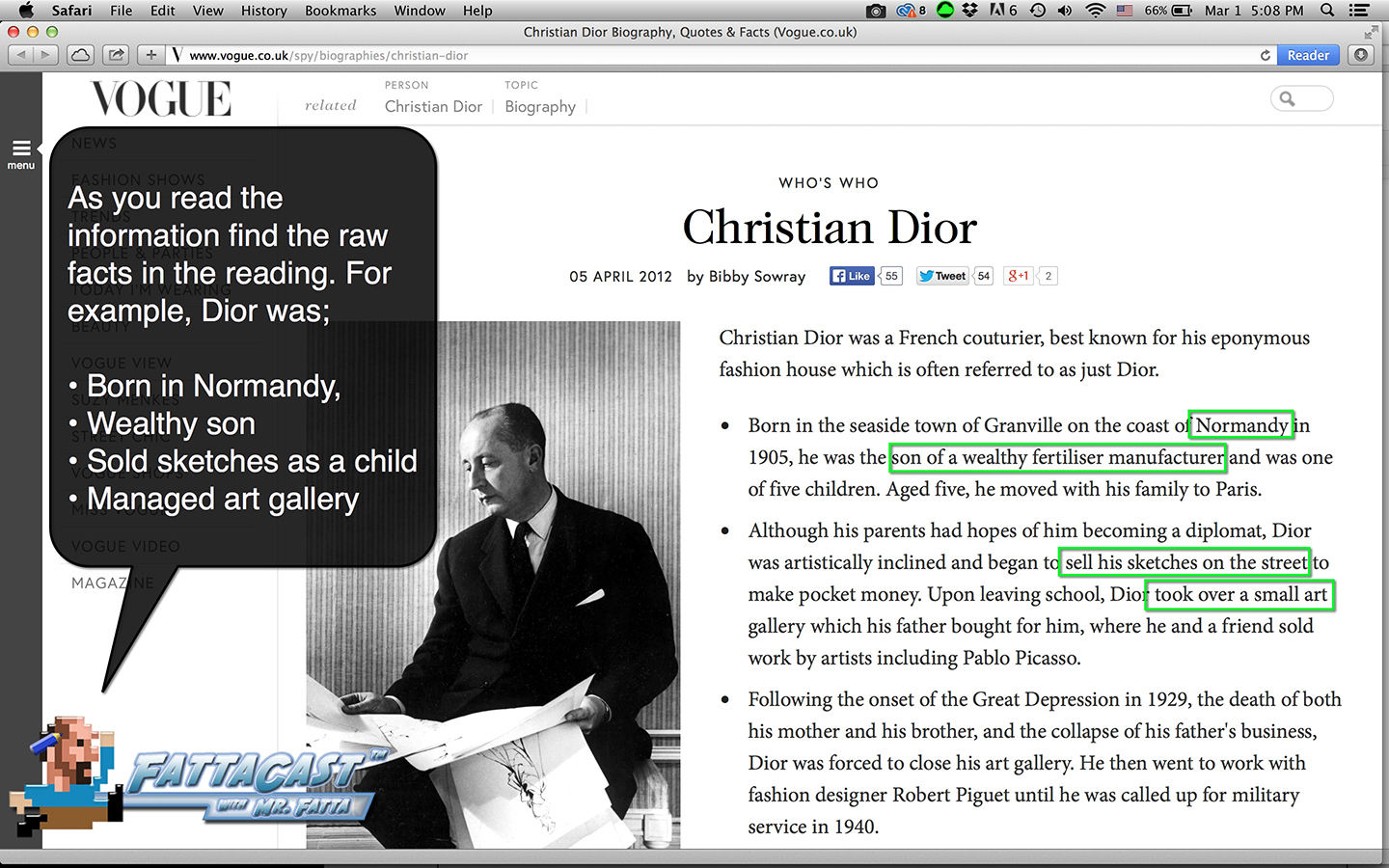
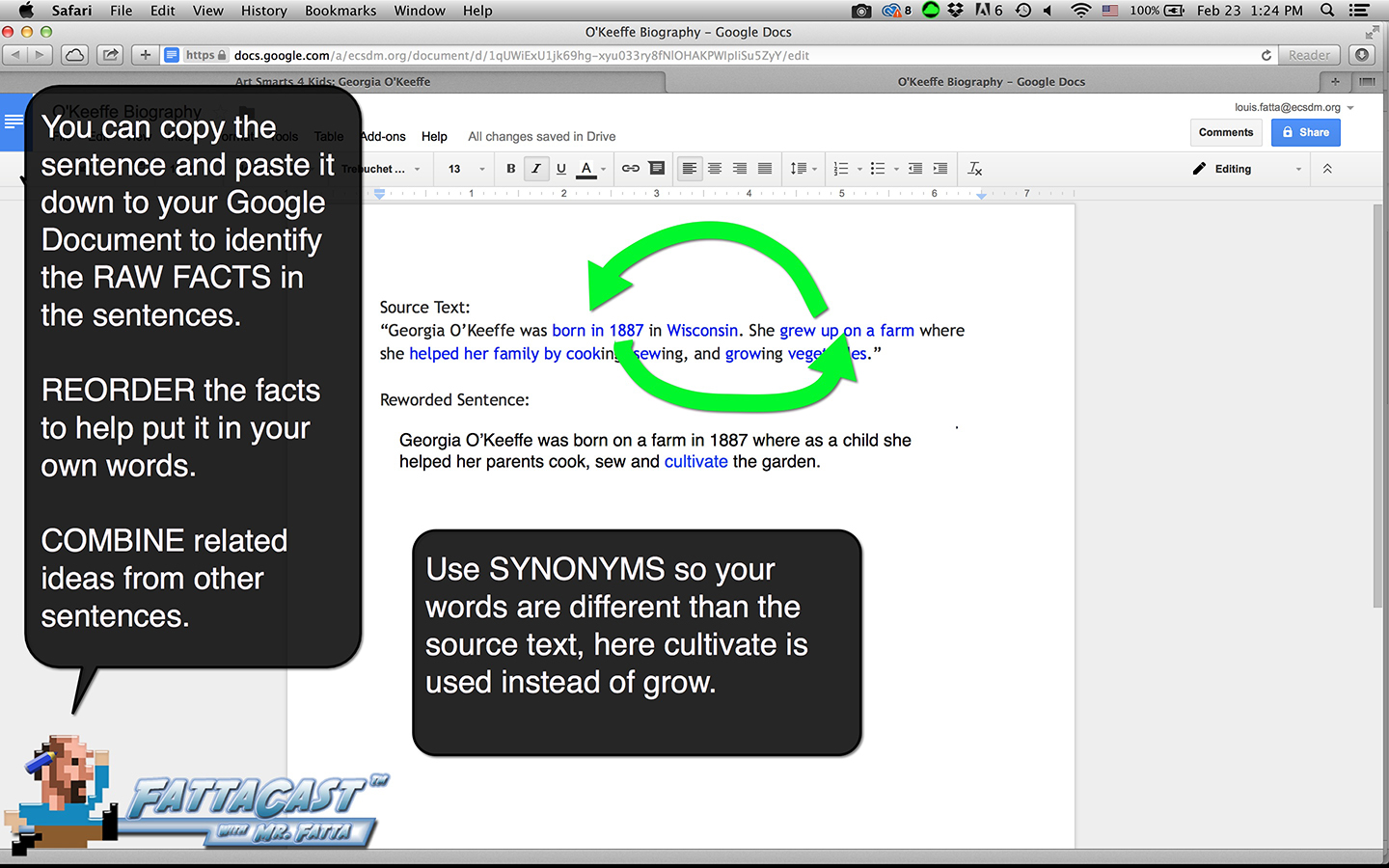
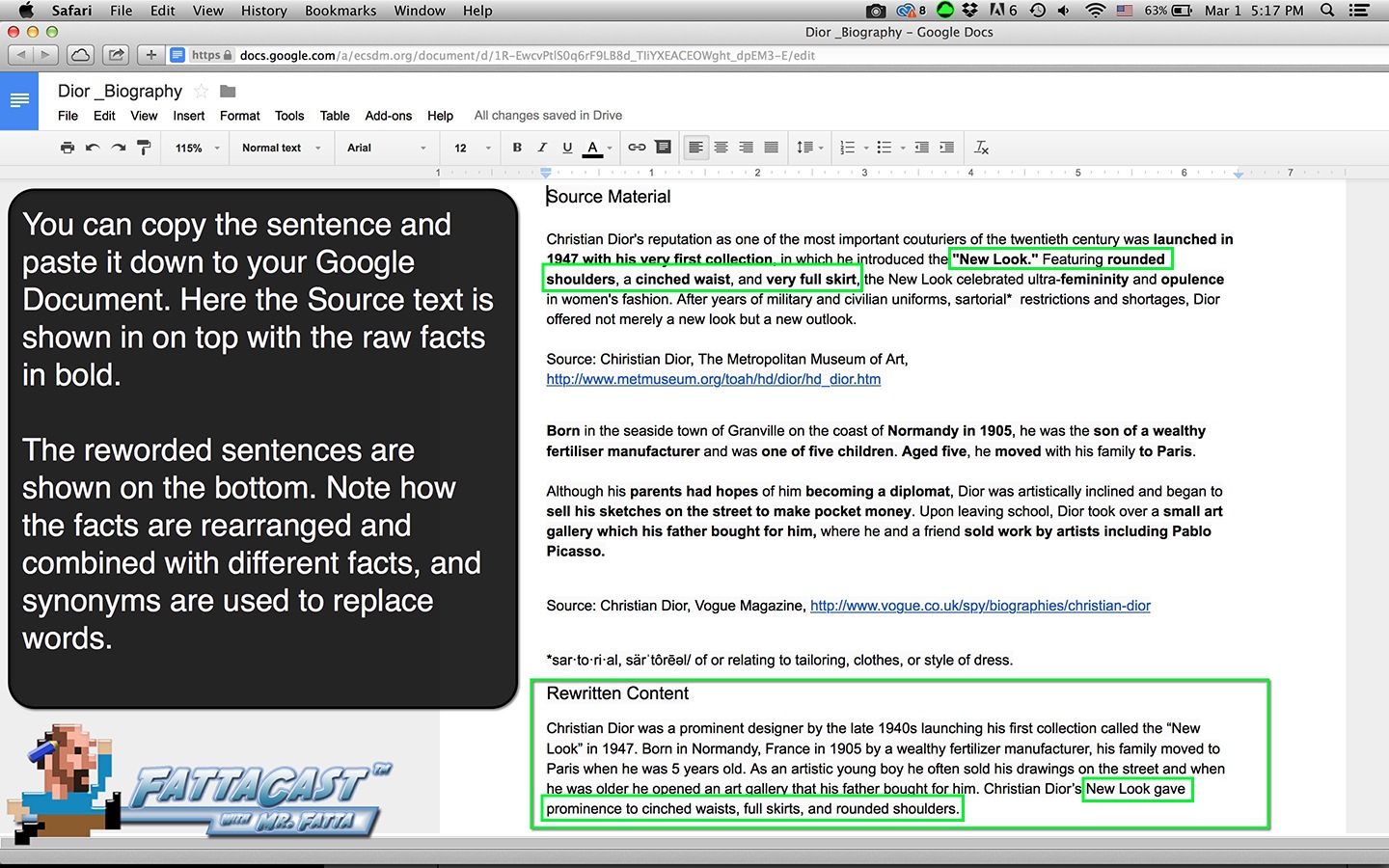
Writing from Source Material

http://www.cassiopeiaproject.com/Terms_Conditions.pdf